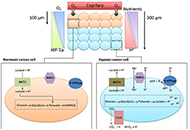
Dysregulation of cellular pH is frequent in solid tumours and provides potential opportunities for therapeutic intervention. The acidic microenvironment within a tumour can promote migration, invasion and metastasis of cancer cells through a variety of mechanisms. Pathways associated with the control of intracellular pH that are under consideration for intervention include carbonic anhydrase IX, the monocarboxylate transporters (MCT, MCT1 and MCT4), the vacuolar-type H+-ATPase proton pump, and the sodium-hydrogen exchanger 1. This review will describe progress in the development of inhibitors to these targets.
Read less.
All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) induces complete remission in a high proportion of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). Nevertheless it is be associated with adverse drug reactions that might be life-threatening including differentiation syndrome, myocarditis, myositis, Sweet’s syndrome and ulcers. We describe a case of APL who during induction therapy developed ATRA syndrome, cardiac arrhythmia and multiple episodes of intestinal necrosis that required surgery. In particular, we report here for the first intestinal necrosis attributable to ATRA treatment in the absence of histological evidence of promyelocytes infiltration or leukocytoclastic vasculitis.
Read less.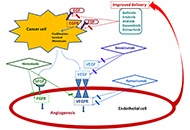
Several preclinical studies suggested a potential benefit from combined treatment with inhibitors of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and angiogenesis, both effective in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In pretreated patients with advanced EGFR wild type NSCLC, bevacizumab plus erlotinib improved progression-free survival as second-line therapy in the BeTa study and as maintenance therapy in the ATLAS trial, although the benefit was modest and did not translate into an advantage in overall survival. Disappointing results were reported with oral VEGF inhibitors plus erlotinib in pretreated patients with EGFR wild type NSCLC. On the contrary, erlotinib plus bevacizumab or ramucirumab showed a clinically relevant improvement of progression-free survival in naïve patients with EGFR mutations, leading to the approval of these two regimens as first-line treatment of NSCLC patients with EGFR mutant tumors. Several clinical studies are evaluating the feasibility and activity of osimertinib plus bevacizumab or ramucirumab. However, limits that could affect its use in clinical practice are the need of an intravenous infusion for angiogenesis inhibitors, the increased incidence of treatment associated adverse events, the exclusion of patients with tumors located in central position or at risk of hemorrhage. The identification of predictive biomarkers is an important goal of research to optimize the combined use of these agents.
Read less.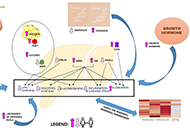
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) remains a major cause of chronic liver disease worldwide. Despite extensive studies, the heterogeneity of the risk factors as well as different disease mechanisms complicate the goals toward effective diagnosis and management. Recently, it has been shown that sex differences play a role in the prevalence and progression of NAFLD. In vitro, in vivo, and clinical studies revealed that the lower prevalence of NAFLD in premenopausal as compared to postmenopausal women and men is mainly due to the protective effects of estrogen and body fat distribution. It has been also described that males and females present differential pathogenic features in terms of biochemical profiles and histological characteristics. However, the exact molecular mechanisms for the gender differences that exist in the pathogenesis of NAFLD are still elusive. Lipogenesis, oxidative stress, and inflammation play a key role in the progression of NAFLD. For NAFLD, only a few studies characterized these mechanisms at the molecular level. Therefore, we aim to review the reported differential molecular mechanisms that trigger such different pathogenesis in both sexes. Differences in lipid metabolism, glucose homeostasis, oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis were discussed based on the evidence reported in recent publications. In conclusion, with this review, we hope to provide a new perspective for the development of future practice guidelines as well as a new avenue for the management of the disease.
Read less.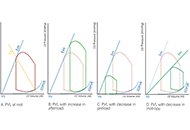
Left ventricular ejection fraction is the critical parameter used for heart failure classification, decision making and assessing prognosis. It is defined as a volumetric ratio and is essentially a composite of arterial and ventricular elastances, but not intrinsic contractility. The clinician should be aware of its numerous limitations when measuring and reporting it. And make a step toward more insightful understanding of hemodynamics.
Read less.
Rational government of patient fluxes from primary care to hepatology clinic is a priority of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) research. Estimating pre-test probability of disease, risk of fibrosis progression, and exclusion of competing causes of liver disease must be addressed. Here we propose a novel taxonomic classification of NAFLD based on hepatic, pathogenic and systemic features of disease in the individual patient. The variable course of disease in any given patient remains a clinical enigma. Therefore, future studies will have to better characterize the role of genetic polymorphisms, family and personal history, diet, alcohol, physical activity and drugs as modifiers of the course of disease and clues to the early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. A better understanding of these, together with a taxonomic diagnosis, may prompt a more accurate personalization of care. For example, understanding the putative role of psycho-depression in NAFLD promises to revolutionize disease management in a proportion of cases. Similarly, sex differences in outcome and response to treatment are insufficiently characterized. More studies are awaited regarding those forms of NAFLD which occur secondary to endocrine derangements. The intersections between NAFLD and the lung must better be defined. These include the bi-directional associations of NAFLD and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and sleep apnoea syndrome, as well as the totally unexplored chapter of NAFLD and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Finally, the therapeutic roles of intermittent fasting and anticoagulation must be assessed. In conclusion, over the last 20 years, NAFLD has taught us a lot regarding the pathogenic importance of insulin resistance, the limitations of correcting this in the treatment of NAFLD, the root causes of diabetes and the metabolic syndrome, sex differences in disease and the role of nuclear receptors. However, the overwhelming COVID-19 pandemic is now expected to reset the priorities of public health.
Read less.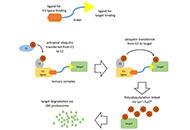
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is a common form of leukemia and is dependent on growth-promoting signaling via the B-cell receptor. The Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) is an important mediator of B-cell receptor signaling and the irreversible BTK inhibitor ibrutinib can trigger dramatic clinical responses in treated patients. However, emergence of resistance and toxicity are major limitations which lead to treatment discontinuation. There remains, therefore, a clear need for new therapeutic options. In this review, we discuss recent progress in the development of BTK-targeted proteolysis targeting chimeras (PROTACs) describing how such agents may provide advantages over ibrutinib and highlighting features of PROTACs that are important for the development of effective BTK degrading agents. Overall, PROTACs appear to be an exciting new approach to target BTK. However, development is at a very early stage and considerable progress is required to refine these agents and optimize their drug-like properties before progression to clinical testing.
Read less.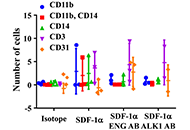
Aim:
To test if the impairment of mononuclear cell (MNC) migration in patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) is due to the reduction of the endoglin (ENG) receptor on the cell surface and oxidative stress.
Methods:
MNCs of HHT patients and normal controls were subjected to migration assay. Fractions of MNCs were pre-incubated with antibodies specific to HHT causative genes ENG [hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia type 1 (HHT1)] or activin receptor-like kinase 1 [ALK1, hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia type 2 (HHT2)], AMD3100 or Diprotin-A to block ENG, ALK1 C-X-C chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) or CD26 (increased in HHT1 MNCs) before migration assay. The MNCs were allowed to migrate toward stromal cell-derived factor-1α (SDF-1α) for 18 h. The expression of CXCR4, CD26, superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) and glutathione peroxidase 1 (GPX1) in MNCs and nitric oxide levels in the plasma were analyzed.
Results:
Compared to the controls, fewer HHT1 MNCs and similar number of HHT2 MNCs migrated toward SDF-1α. Diprotin-A pre-treatment improved HHT1 MNC-migration, but had no effect on normal and HHT2 MNCs. Pre-incubation with an anti-ENG antibody reduced the migration of normal MNCs. Diprotin-A did not improve the migration of ENG antibody pre-treated MNCs. Anti-ALK1 antibody had no effect on MNC-migration. AMD3100 treatment reduced normal and HHT MNC-migration. ENG mRNA level was reduced in HHT1 and HHT2 MNCs. ALK1 mRNA was reduced in HHT2 MNCs only. CD26 expression was higher in HHT1 MNCs. Pre-treatment of MNCs with anti-ENG or anti-ALK1 antibody had no effect on CD26 and CXCR4 expression. The expression of antioxidant enzymes, SOD1, was reduced in HHT1 MNCs, which was accompanied with an increase of ROS in HHT MNCs and nitric oxide in HHT1 plasma.
Conclusions:
Reduction of ENG receptor on MNC surface reduced monocyte migration toward SDF-1α independent of CD26 expression. Increased oxidative stress could alter HHT MNC migration behavior.
Aim:
Epigenetic variation of DNA methylation of the mu-opioid receptor gene (OPRM1) has been identified in the blood and saliva of individuals with opioid use disorder (OUD) and infants with neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome (NOWS). It is unknown whether epigenetic variation in OPRM1 exists within placental tissue in women with OUD and whether it is associated with NOWS outcomes. In this pilot study, the authors aimed to 1) examine the association between placental OPRM1 DNA methylation levels and NOWS outcomes, and 2) compare OPRM1 methylation levels in opioid-exposed versus non-exposed control placentas.
Methods:
Placental tissue was collected from eligible opioid (n = 64) and control (n = 29) women after delivery. Placental DNA was isolated and methylation levels at six cytosine-phosphate-guanine (CpG) sites within the OPRM1 promoter were quantified. Methylation levels were evaluated for associations with infant NOWS outcome measures: need for pharmacologic treatment, length of hospital stay (LOS), morphine treatment days, and treatment with two medications. Regression models were created and adjusted for clinical co-variates. Methylation levels between opioid and controls placentas were also compared.
Results:
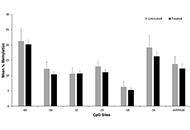
The primary opioid exposures were methadone and buprenorphine. Forty-nine (76.6%) of the opioid-exposed infants required pharmacologic treatment, 10 (15.6%) two medications, and average LOS for all opioid-exposed infants was 16.5 (standard deviation 9.7) days. There were no significant associations between OPRM1 DNA methylation levels in the six CpG sites and any NOWS outcome measures. No significant differences were found in methylation levels between the opioid and control samples.
Conclusions:
No significant associations were found between OPRM1 placental DNA methylation levels and NOWS severity in this pilot cohort. In addition, no significant differences were seen in OPRM1 methylation in opioid versus control placentas. Future association studies examining methylation levels on a genome-wide level are warranted.
Aim:
Recent randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have tested the efficacy of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA) to specifically treat non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). We performed a meta-analysis of RCTs to investigate the efficacy of GLP-1 RAs for treatment of NAFLD or non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
Methods:
We systematically searched PubMed and ClinicalTrials.Gov databases utilizing specific terms to identify placebo-controlled or head-to-head RCTs (last research on March 1, 2020) involving NAFLD patients with the aim of evaluating the efficacy of GLP-1 RAs to treat NAFLD/NASH. Primary outcomes were changes in serum liver enzymes, liver fat content, or histologic resolution of NASH. Weighted mean differences (WMD) were used to test the differences between the treatment arms.
Results:
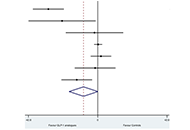
Overall, we found 7 placebo-controlled or head-to-head RCTs involving 472 middle-aged individuals (66% men; 77% with established diabetes) followed for a median of 16 weeks that have used liraglutide or exenatide to treat NAFLD on imaging (n = 6) or biopsy (n = 1). Compared to placebo or reference therapy, treatment with GLP-1 RAs decreased serum alanine aminotransferase [n = 7 studies; WMD: –8.77 IU/L, 95% confidence intervals (CI) –17.69 to 0.14 IU/L; I2 = 87.3%], gamma-glutamyltransferase levels (n = 4 studies; WMD: –10.17 IU/L, 95% CI –14.27 IU/L to –6.07 IU/L; I2 = 0%) and imaging-defined liver fat content (n = 4 studies; WMD: –6.23%, 95% CI –8.95% to –3.51%; I2 = 85.9%). In one RCT involving 55 patients with biopsy-proven NASH, a 48-week treatment with liraglutide also led to a greater histological resolution of NASH than placebo.
Conclusions:
GLP-1 RAs (mostly liraglutide) seem to be a promising treatment option for NAFLD or NASH.
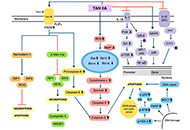
Tanshinone is a herbal medicinal compound described in Chinese medicine, extracted from the roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza (Danshen). This family of compounds, including Tanshinone IIA and Tanshinone I, have shown remarkable potential as anti-cancer molecules, especially against breast, cervical, colorectal, gastric, lung, and prostate cancer cell lines, as well as leukaemia, melanoma, and hepatocellular carcinoma among others. Recent data has indicated that Tanshinones can modulate multiple molecular pathways such as PI3K/Akt, MAPK and JAK/STAT3, and exert their pharmacological effects against different malignancies. In addition, preclinical and clinical data, together with the safety profile of Tanshinones, encourage further applications of these compounds in cancer therapeutics. In this review article, the effect of Tanshinones on different cancers, challenges in their pharmacological development, and opportunities to harness their clinical potential have been documented.
Read less.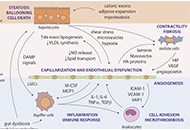
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a substantial and growing problem worldwide and has become the second most common indication for liver transplantation as it may progress to cirrhosis and develop complications from portal hypertension primarily caused by advanced fibrosis and erratic tissue remodeling. However, elevated portal venous pressure has also been detected in experimental models of fatty liver and in human NAFLD when fibrosis is far less advanced and cirrhosis is absent. Early increases in intrahepatic vascular resistance may contribute to the progression of liver disease. Specific pathophenotypes linked to the development of portal hypertension in NAFLD include hepatocellular lipid accumulation and ballooning injury, capillarization of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells, enhanced contractility of hepatic stellate cells, activation of Kupffer cells and pro-inflammatory pathways, adhesion and entrapment of recruited leukocytes, microthrombosis, angiogenesis and perisinusoidal fibrosis. These pathological events are amplified in NAFLD by concomitant visceral obesity, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes and dysbiosis, promoting aberrant interactions with adipose tissue, skeletal muscle and gut microbiota. Measurement of the hepatic venous pressure gradient by retrograde insertion of a balloon-tipped central vein catheter is the current reference method for predicting outcomes of cirrhosis associated with clinically significant portal hypertension and guiding interventions. This invasive technique is rarely considered in the absence of cirrhosis where currently available clinical, imaging and laboratory correlates of portal hypertension may not reflect early changes in liver hemodynamics. Availability of less invasive but sufficiently sensitive methods for the assessment of portal venous pressure in NAFLD remains therefore an unmet need. Recent efforts to develop new biomarkers and endoscopy-based approaches such as endoscopic ultrasound-guided measurement of portal pressure gradient may help achieve this goal. In addition, cellular and molecular targets are being identified to guide emerging therapies in the prevention and management of portal hypertension.
Read less.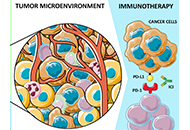
Immunotherapy has shifted the therapeutic landscape in thoracic cancers. However, assessment of biomarkers for patient selection and disease monitoring remain challenging, especially considering the lack of tissue sample availability for clinical and research purposes. In this scenario, liquid biopsy (LB), defined as the study and characterization of biomarkers in body fluids, represents a useful alternative strategy. In other malignancies such as colorectal cancer, breast cancer or melanoma, the potential of LB has been more extensively explored for monitoring minimal residual disease or response to treatment, and to investigate mechanisms of resistance to targeted agents. Even if various experiences have already been published about the applications of LB in immunotherapy in thoracic cancers, the standardization of methodology and assessment of its clinical utility is still pending. In this review, the authors will focus on the applications of LB in immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer, small cell lung cancer, and malignant pleural mesothelioma, describing available data and future perspectives.
Read less.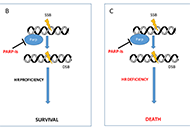
Poly-ADP-ribose polymerase inhibitors (PARP-I) represent one of the most attractive and promising class of biological agents studied both in relapsed ovarian cancer (OC) and in the advanced setting. The availability of this new class of drugs has changed the clinical management of OC ensuring an unprecedented advance in such an aggressive cancer. Three oral PARP-I are currently available: olaparib, niraparib and rucaparib. Another two are in active clinical exploration: veliparib and talazoparib. Here the authors report clinical data with PARP-I with a particular emphasis on the phase II and III trials that support PARP-I approval by regulatory agencies in OC patients.
Read less.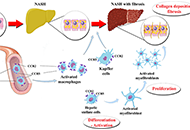
Pooled prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) globally is about 25%. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) with advanced fibrosis has been linked with substantial morbidity and mortality, without having to-date any licensed treatment. C-C chemokine receptor (CCR) antagonists have been investigated as candidates for the treatment of NASH. Inhibition of CCR2 is expected to mitigate hepatic inflammation, through reducing the activation of Kupffer cells, as well as the infiltration of monocytes and macrophages into the liver. Inhibition of CCR5 is expected to mitigate hepatic fibrogenesis, through impairing the activation of hepatic stellate cells, as well as to mitigate hepatic inflammation, through impairing the activation of Kupffer cells and macrophages. Cenicriviroc (CVC) is the first in class, dual inhibitor of CCR2 and CCR5. After exhibiting favorable results in animal models, CVC was shown to be beneficial in NASH patients with more severe fibrosis at a phase 2b trial (CENTAUR) and is currently at a phase 3 clinical trial (AURORA). Apart from CVC, other CCR5 mono-antagonists, such as maraviroc, are under evaluation in clinical trials with human immunodeficiency virus patients with NAFLD. The aim of this review was to summarize existing evidence on CVC and other CCR antagonists in NASH patients, primarily focusing on their clinical efficacy and safety.
Read less.
The currently ongoing coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) pandemic has affected globally human health and economy. Research in progress has shown facts associated with this disease and raised questions relevant for disease control and prevention. In this perspective, the collaboration between science and art in visual communication using the artwork “Enseñanza” (“Teaching”) contributes to the representation of the lessons learned from COVID-19 and the way forward. To advance preparedness for current and future pandemics, the authors propose to address international collaborations, support to science, access to food supplies and health services, sustainable development and a “One Health” approach searching a balanced interaction of humanity with nature and a more holistic approach to disease prevention and control.
Read less.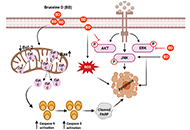
Cancer remains the second leading cause of mortality globally. In combating cancer, conventional chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy are administered as first-line therapy. However, these are usually accompanied with adverse side effects that decrease the quality of patient’s lives. As such, natural bioactive compounds have gained an attraction in the scientific and medical community as evidence of their anticancer properties and attenuation of side effects mounted. In particular, quassinoids have been found to exhibit a plethora of inhibitory activities such as anti-proliferative effects on tumor development and metastasis. Recently, bruceine D, a quassinoid isolated from the shrub Brucea javanica (L.) Merr. (Simaroubaceae), has come under immense investigation on its antineoplastic properties in various human cancers including pancreas, breast, lung, blood, bone, and liver. In this review, we have highlighted the antineoplastic effects of bruceine D and its mode of actions in different tumor models.
Read less.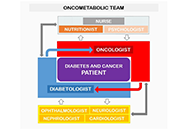
Diabetes and cancer are widespread worldwide and the number of subjects presenting both diseases increased over the years. The management of cancer patients having diabetes represents a challenge not only because of the complexity and heterogeneity of these pathologies but also for the lack of standardised clinical guidelines. The diagnosis of cancer is traumatizing and monopolizes the attention of both patients and caregivers. Thus, pre-existent or new-onset diabetes can be overshadowed thus increasing the risk for short- and long-term adverse events. Moreover, drugs used for each disease can interfere with the clinical course of the concomitant disease, making challenging the management of these patients. Over the years, this issue has become more relevant because of the increased patients’ life expectancy due to the improved efficacy of diabetes and cancer therapies.
The purpose of this review is to highlight what is known and what should be taken into consideration to optimise the clinical management of patients with diabetes and cancer. Due to the complexity of these diseases, a multidisciplinary, shared approach, including all the protagonists involved, is necessary to improve patients’ quality of life and lifespan.
Read less.
The prevalence of nonalcoholic or more recently re-defined metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) is rapidly growing worldwide. It is characterized by hepatic fat accumulation exceeding 5% of liver weight not attributable to alcohol consumption. MAFLD refers to an umbrella of conditions ranging from simple steatosis to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis which may finally progress to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. MAFLD is closely related to components of the metabolic syndrome and to environmental factors. In addition to the latter, genetic predisposition plays a key role in MAFLD pathogenesis and strictly contributes to its progressive forms. The candidate genes which have been related to MAFLD hereditability are mainly involved in lipids remodeling, lipid droplets assembly, lipoprotein packaging and secretion, de novo lipogenesis, and mitochondrial redox status. In the recent years, it has emerged the opportunity to translate the genetics into clinics by aggregating the genetic variants mostly associated with MAFLD in polygenic risk scores. These scores might be used in combination with metabolic factors to identify those patients at higher risk to develop more severe liver disease and to schedule an individual therapeutic approach.
Read less.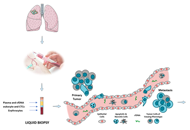
Lung cancer represents the world’s most common cause of cancer death. In recent years, we moved from a generic therapeutic strategy to a personalized approach, based on the molecular characterization of the tumor. In this view, liquid biopsy is becoming an important tool for assessing the progress or onset of lung disease. Liquid biopsy is a non-invasive procedure able to isolate circulating tumor cells, tumor educated platelets, exosomes and free circulating tumor DNA from body fluids. The characterization of these liquid biomarkers can help to choose the therapeutic strategy for each different case. In this review, the authors will analyze the main aspects of lung cancer and the applications currently in use focusing on the benefits associated with this approach for predicting the prognosis and monitoring the clinical conditions of lung cancer disease.
Read less.
Dysregulation of cellular pH is frequent in solid tumours and provides potential opportunities for therapeutic intervention. The acidic microenvironment within a tumour can promote migration, invasion and metastasis of cancer cells through a variety of mechanisms. Pathways associated with the control of intracellular pH that are under consideration for intervention include carbonic anhydrase IX, the monocarboxylate transporters (MCT, MCT1 and MCT4), the vacuolar-type H+-ATPase proton pump, and the sodium-hydrogen exchanger 1. This review will describe progress in the development of inhibitors to these targets.
Dysregulation of cellular pH is frequent in solid tumours and provides potential opportunities for therapeutic intervention. The acidic microenvironment within a tumour can promote migration, invasion and metastasis of cancer cells through a variety of mechanisms. Pathways associated with the control of intracellular pH that are under consideration for intervention include carbonic anhydrase IX, the monocarboxylate transporters (MCT, MCT1 and MCT4), the vacuolar-type H+-ATPase proton pump, and the sodium-hydrogen exchanger 1. This review will describe progress in the development of inhibitors to these targets.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2020.00005

All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) induces complete remission in a high proportion of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). Nevertheless it is be associated with adverse drug reactions that might be life-threatening including differentiation syndrome, myocarditis, myositis, Sweet’s syndrome and ulcers. We describe a case of APL who during induction therapy developed ATRA syndrome, cardiac arrhythmia and multiple episodes of intestinal necrosis that required surgery. In particular, we report here for the first intestinal necrosis attributable to ATRA treatment in the absence of histological evidence of promyelocytes infiltration or leukocytoclastic vasculitis.
All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) induces complete remission in a high proportion of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). Nevertheless it is be associated with adverse drug reactions that might be life-threatening including differentiation syndrome, myocarditis, myositis, Sweet’s syndrome and ulcers. We describe a case of APL who during induction therapy developed ATRA syndrome, cardiac arrhythmia and multiple episodes of intestinal necrosis that required surgery. In particular, we report here for the first intestinal necrosis attributable to ATRA treatment in the absence of histological evidence of promyelocytes infiltration or leukocytoclastic vasculitis.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2020.00007

Several preclinical studies suggested a potential benefit from combined treatment with inhibitors of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and angiogenesis, both effective in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In pretreated patients with advanced EGFR wild type NSCLC, bevacizumab plus erlotinib improved progression-free survival as second-line therapy in the BeTa study and as maintenance therapy in the ATLAS trial, although the benefit was modest and did not translate into an advantage in overall survival. Disappointing results were reported with oral VEGF inhibitors plus erlotinib in pretreated patients with EGFR wild type NSCLC. On the contrary, erlotinib plus bevacizumab or ramucirumab showed a clinically relevant improvement of progression-free survival in naïve patients with EGFR mutations, leading to the approval of these two regimens as first-line treatment of NSCLC patients with EGFR mutant tumors. Several clinical studies are evaluating the feasibility and activity of osimertinib plus bevacizumab or ramucirumab. However, limits that could affect its use in clinical practice are the need of an intravenous infusion for angiogenesis inhibitors, the increased incidence of treatment associated adverse events, the exclusion of patients with tumors located in central position or at risk of hemorrhage. The identification of predictive biomarkers is an important goal of research to optimize the combined use of these agents.
Several preclinical studies suggested a potential benefit from combined treatment with inhibitors of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and angiogenesis, both effective in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In pretreated patients with advanced EGFR wild type NSCLC, bevacizumab plus erlotinib improved progression-free survival as second-line therapy in the BeTa study and as maintenance therapy in the ATLAS trial, although the benefit was modest and did not translate into an advantage in overall survival. Disappointing results were reported with oral VEGF inhibitors plus erlotinib in pretreated patients with EGFR wild type NSCLC. On the contrary, erlotinib plus bevacizumab or ramucirumab showed a clinically relevant improvement of progression-free survival in naïve patients with EGFR mutations, leading to the approval of these two regimens as first-line treatment of NSCLC patients with EGFR mutant tumors. Several clinical studies are evaluating the feasibility and activity of osimertinib plus bevacizumab or ramucirumab. However, limits that could affect its use in clinical practice are the need of an intravenous infusion for angiogenesis inhibitors, the increased incidence of treatment associated adverse events, the exclusion of patients with tumors located in central position or at risk of hemorrhage. The identification of predictive biomarkers is an important goal of research to optimize the combined use of these agents.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2020.00008

Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) remains a major cause of chronic liver disease worldwide. Despite extensive studies, the heterogeneity of the risk factors as well as different disease mechanisms complicate the goals toward effective diagnosis and management. Recently, it has been shown that sex differences play a role in the prevalence and progression of NAFLD. In vitro, in vivo, and clinical studies revealed that the lower prevalence of NAFLD in premenopausal as compared to postmenopausal women and men is mainly due to the protective effects of estrogen and body fat distribution. It has been also described that males and females present differential pathogenic features in terms of biochemical profiles and histological characteristics. However, the exact molecular mechanisms for the gender differences that exist in the pathogenesis of NAFLD are still elusive. Lipogenesis, oxidative stress, and inflammation play a key role in the progression of NAFLD. For NAFLD, only a few studies characterized these mechanisms at the molecular level. Therefore, we aim to review the reported differential molecular mechanisms that trigger such different pathogenesis in both sexes. Differences in lipid metabolism, glucose homeostasis, oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis were discussed based on the evidence reported in recent publications. In conclusion, with this review, we hope to provide a new perspective for the development of future practice guidelines as well as a new avenue for the management of the disease.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) remains a major cause of chronic liver disease worldwide. Despite extensive studies, the heterogeneity of the risk factors as well as different disease mechanisms complicate the goals toward effective diagnosis and management. Recently, it has been shown that sex differences play a role in the prevalence and progression of NAFLD. In vitro, in vivo, and clinical studies revealed that the lower prevalence of NAFLD in premenopausal as compared to postmenopausal women and men is mainly due to the protective effects of estrogen and body fat distribution. It has been also described that males and females present differential pathogenic features in terms of biochemical profiles and histological characteristics. However, the exact molecular mechanisms for the gender differences that exist in the pathogenesis of NAFLD are still elusive. Lipogenesis, oxidative stress, and inflammation play a key role in the progression of NAFLD. For NAFLD, only a few studies characterized these mechanisms at the molecular level. Therefore, we aim to review the reported differential molecular mechanisms that trigger such different pathogenesis in both sexes. Differences in lipid metabolism, glucose homeostasis, oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis were discussed based on the evidence reported in recent publications. In conclusion, with this review, we hope to provide a new perspective for the development of future practice guidelines as well as a new avenue for the management of the disease.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2020.00005
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring NAFLD/NASH

Left ventricular ejection fraction is the critical parameter used for heart failure classification, decision making and assessing prognosis. It is defined as a volumetric ratio and is essentially a composite of arterial and ventricular elastances, but not intrinsic contractility. The clinician should be aware of its numerous limitations when measuring and reporting it. And make a step toward more insightful understanding of hemodynamics.
Left ventricular ejection fraction is the critical parameter used for heart failure classification, decision making and assessing prognosis. It is defined as a volumetric ratio and is essentially a composite of arterial and ventricular elastances, but not intrinsic contractility. The clinician should be aware of its numerous limitations when measuring and reporting it. And make a step toward more insightful understanding of hemodynamics.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2020.00006

Rational government of patient fluxes from primary care to hepatology clinic is a priority of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) research. Estimating pre-test probability of disease, risk of fibrosis progression, and exclusion of competing causes of liver disease must be addressed. Here we propose a novel taxonomic classification of NAFLD based on hepatic, pathogenic and systemic features of disease in the individual patient. The variable course of disease in any given patient remains a clinical enigma. Therefore, future studies will have to better characterize the role of genetic polymorphisms, family and personal history, diet, alcohol, physical activity and drugs as modifiers of the course of disease and clues to the early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. A better understanding of these, together with a taxonomic diagnosis, may prompt a more accurate personalization of care. For example, understanding the putative role of psycho-depression in NAFLD promises to revolutionize disease management in a proportion of cases. Similarly, sex differences in outcome and response to treatment are insufficiently characterized. More studies are awaited regarding those forms of NAFLD which occur secondary to endocrine derangements. The intersections between NAFLD and the lung must better be defined. These include the bi-directional associations of NAFLD and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and sleep apnoea syndrome, as well as the totally unexplored chapter of NAFLD and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Finally, the therapeutic roles of intermittent fasting and anticoagulation must be assessed. In conclusion, over the last 20 years, NAFLD has taught us a lot regarding the pathogenic importance of insulin resistance, the limitations of correcting this in the treatment of NAFLD, the root causes of diabetes and the metabolic syndrome, sex differences in disease and the role of nuclear receptors. However, the overwhelming COVID-19 pandemic is now expected to reset the priorities of public health.
Rational government of patient fluxes from primary care to hepatology clinic is a priority of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) research. Estimating pre-test probability of disease, risk of fibrosis progression, and exclusion of competing causes of liver disease must be addressed. Here we propose a novel taxonomic classification of NAFLD based on hepatic, pathogenic and systemic features of disease in the individual patient. The variable course of disease in any given patient remains a clinical enigma. Therefore, future studies will have to better characterize the role of genetic polymorphisms, family and personal history, diet, alcohol, physical activity and drugs as modifiers of the course of disease and clues to the early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. A better understanding of these, together with a taxonomic diagnosis, may prompt a more accurate personalization of care. For example, understanding the putative role of psycho-depression in NAFLD promises to revolutionize disease management in a proportion of cases. Similarly, sex differences in outcome and response to treatment are insufficiently characterized. More studies are awaited regarding those forms of NAFLD which occur secondary to endocrine derangements. The intersections between NAFLD and the lung must better be defined. These include the bi-directional associations of NAFLD and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and sleep apnoea syndrome, as well as the totally unexplored chapter of NAFLD and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Finally, the therapeutic roles of intermittent fasting and anticoagulation must be assessed. In conclusion, over the last 20 years, NAFLD has taught us a lot regarding the pathogenic importance of insulin resistance, the limitations of correcting this in the treatment of NAFLD, the root causes of diabetes and the metabolic syndrome, sex differences in disease and the role of nuclear receptors. However, the overwhelming COVID-19 pandemic is now expected to reset the priorities of public health.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2020.00007
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring NAFLD/NASH

Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is a common form of leukemia and is dependent on growth-promoting signaling via the B-cell receptor. The Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) is an important mediator of B-cell receptor signaling and the irreversible BTK inhibitor ibrutinib can trigger dramatic clinical responses in treated patients. However, emergence of resistance and toxicity are major limitations which lead to treatment discontinuation. There remains, therefore, a clear need for new therapeutic options. In this review, we discuss recent progress in the development of BTK-targeted proteolysis targeting chimeras (PROTACs) describing how such agents may provide advantages over ibrutinib and highlighting features of PROTACs that are important for the development of effective BTK degrading agents. Overall, PROTACs appear to be an exciting new approach to target BTK. However, development is at a very early stage and considerable progress is required to refine these agents and optimize their drug-like properties before progression to clinical testing.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is a common form of leukemia and is dependent on growth-promoting signaling via the B-cell receptor. The Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) is an important mediator of B-cell receptor signaling and the irreversible BTK inhibitor ibrutinib can trigger dramatic clinical responses in treated patients. However, emergence of resistance and toxicity are major limitations which lead to treatment discontinuation. There remains, therefore, a clear need for new therapeutic options. In this review, we discuss recent progress in the development of BTK-targeted proteolysis targeting chimeras (PROTACs) describing how such agents may provide advantages over ibrutinib and highlighting features of PROTACs that are important for the development of effective BTK degrading agents. Overall, PROTACs appear to be an exciting new approach to target BTK. However, development is at a very early stage and considerable progress is required to refine these agents and optimize their drug-like properties before progression to clinical testing.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2020.00009
This article belongs to the special issue Proteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC)

Aim:
To test if the impairment of mononuclear cell (MNC) migration in patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) is due to the reduction of the endoglin (ENG) receptor on the cell surface and oxidative stress.
Methods:
MNCs of HHT patients and normal controls were subjected to migration assay. Fractions of MNCs were pre-incubated with antibodies specific to HHT causative genes ENG [hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia type 1 (HHT1)] or activin receptor-like kinase 1 [ALK1, hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia type 2 (HHT2)], AMD3100 or Diprotin-A to block ENG, ALK1 C-X-C chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) or CD26 (increased in HHT1 MNCs) before migration assay. The MNCs were allowed to migrate toward stromal cell-derived factor-1α (SDF-1α) for 18 h. The expression of CXCR4, CD26, superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) and glutathione peroxidase 1 (GPX1) in MNCs and nitric oxide levels in the plasma were analyzed.
Results:
Compared to the controls, fewer HHT1 MNCs and similar number of HHT2 MNCs migrated toward SDF-1α. Diprotin-A pre-treatment improved HHT1 MNC-migration, but had no effect on normal and HHT2 MNCs. Pre-incubation with an anti-ENG antibody reduced the migration of normal MNCs. Diprotin-A did not improve the migration of ENG antibody pre-treated MNCs. Anti-ALK1 antibody had no effect on MNC-migration. AMD3100 treatment reduced normal and HHT MNC-migration. ENG mRNA level was reduced in HHT1 and HHT2 MNCs. ALK1 mRNA was reduced in HHT2 MNCs only. CD26 expression was higher in HHT1 MNCs. Pre-treatment of MNCs with anti-ENG or anti-ALK1 antibody had no effect on CD26 and CXCR4 expression. The expression of antioxidant enzymes, SOD1, was reduced in HHT1 MNCs, which was accompanied with an increase of ROS in HHT MNCs and nitric oxide in HHT1 plasma.
Conclusions:
Reduction of ENG receptor on MNC surface reduced monocyte migration toward SDF-1α independent of CD26 expression. Increased oxidative stress could alter HHT MNC migration behavior.
Aim:
To test if the impairment of mononuclear cell (MNC) migration in patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) is due to the reduction of the endoglin (ENG) receptor on the cell surface and oxidative stress.
Methods:
MNCs of HHT patients and normal controls were subjected to migration assay. Fractions of MNCs were pre-incubated with antibodies specific to HHT causative genes ENG [hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia type 1 (HHT1)] or activin receptor-like kinase 1 [ALK1, hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia type 2 (HHT2)], AMD3100 or Diprotin-A to block ENG, ALK1 C-X-C chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) or CD26 (increased in HHT1 MNCs) before migration assay. The MNCs were allowed to migrate toward stromal cell-derived factor-1α (SDF-1α) for 18 h. The expression of CXCR4, CD26, superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) and glutathione peroxidase 1 (GPX1) in MNCs and nitric oxide levels in the plasma were analyzed.
Results:
Compared to the controls, fewer HHT1 MNCs and similar number of HHT2 MNCs migrated toward SDF-1α. Diprotin-A pre-treatment improved HHT1 MNC-migration, but had no effect on normal and HHT2 MNCs. Pre-incubation with an anti-ENG antibody reduced the migration of normal MNCs. Diprotin-A did not improve the migration of ENG antibody pre-treated MNCs. Anti-ALK1 antibody had no effect on MNC-migration. AMD3100 treatment reduced normal and HHT MNC-migration. ENG mRNA level was reduced in HHT1 and HHT2 MNCs. ALK1 mRNA was reduced in HHT2 MNCs only. CD26 expression was higher in HHT1 MNCs. Pre-treatment of MNCs with anti-ENG or anti-ALK1 antibody had no effect on CD26 and CXCR4 expression. The expression of antioxidant enzymes, SOD1, was reduced in HHT1 MNCs, which was accompanied with an increase of ROS in HHT MNCs and nitric oxide in HHT1 plasma.
Conclusions:
Reduction of ENG receptor on MNC surface reduced monocyte migration toward SDF-1α independent of CD26 expression. Increased oxidative stress could alter HHT MNC migration behavior.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2020.00010

Aim:
Epigenetic variation of DNA methylation of the mu-opioid receptor gene (OPRM1) has been identified in the blood and saliva of individuals with opioid use disorder (OUD) and infants with neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome (NOWS). It is unknown whether epigenetic variation in OPRM1 exists within placental tissue in women with OUD and whether it is associated with NOWS outcomes. In this pilot study, the authors aimed to 1) examine the association between placental OPRM1 DNA methylation levels and NOWS outcomes, and 2) compare OPRM1 methylation levels in opioid-exposed versus non-exposed control placentas.
Methods:
Placental tissue was collected from eligible opioid (n = 64) and control (n = 29) women after delivery. Placental DNA was isolated and methylation levels at six cytosine-phosphate-guanine (CpG) sites within the OPRM1 promoter were quantified. Methylation levels were evaluated for associations with infant NOWS outcome measures: need for pharmacologic treatment, length of hospital stay (LOS), morphine treatment days, and treatment with two medications. Regression models were created and adjusted for clinical co-variates. Methylation levels between opioid and controls placentas were also compared.
Results:
The primary opioid exposures were methadone and buprenorphine. Forty-nine (76.6%) of the opioid-exposed infants required pharmacologic treatment, 10 (15.6%) two medications, and average LOS for all opioid-exposed infants was 16.5 (standard deviation 9.7) days. There were no significant associations between OPRM1 DNA methylation levels in the six CpG sites and any NOWS outcome measures. No significant differences were found in methylation levels between the opioid and control samples.
Conclusions:
No significant associations were found between OPRM1 placental DNA methylation levels and NOWS severity in this pilot cohort. In addition, no significant differences were seen in OPRM1 methylation in opioid versus control placentas. Future association studies examining methylation levels on a genome-wide level are warranted.
Aim:
Epigenetic variation of DNA methylation of the mu-opioid receptor gene (OPRM1) has been identified in the blood and saliva of individuals with opioid use disorder (OUD) and infants with neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome (NOWS). It is unknown whether epigenetic variation in OPRM1 exists within placental tissue in women with OUD and whether it is associated with NOWS outcomes. In this pilot study, the authors aimed to 1) examine the association between placental OPRM1 DNA methylation levels and NOWS outcomes, and 2) compare OPRM1 methylation levels in opioid-exposed versus non-exposed control placentas.
Methods:
Placental tissue was collected from eligible opioid (n = 64) and control (n = 29) women after delivery. Placental DNA was isolated and methylation levels at six cytosine-phosphate-guanine (CpG) sites within the OPRM1 promoter were quantified. Methylation levels were evaluated for associations with infant NOWS outcome measures: need for pharmacologic treatment, length of hospital stay (LOS), morphine treatment days, and treatment with two medications. Regression models were created and adjusted for clinical co-variates. Methylation levels between opioid and controls placentas were also compared.
Results:
The primary opioid exposures were methadone and buprenorphine. Forty-nine (76.6%) of the opioid-exposed infants required pharmacologic treatment, 10 (15.6%) two medications, and average LOS for all opioid-exposed infants was 16.5 (standard deviation 9.7) days. There were no significant associations between OPRM1 DNA methylation levels in the six CpG sites and any NOWS outcome measures. No significant differences were found in methylation levels between the opioid and control samples.
Conclusions:
No significant associations were found between OPRM1 placental DNA methylation levels and NOWS severity in this pilot cohort. In addition, no significant differences were seen in OPRM1 methylation in opioid versus control placentas. Future association studies examining methylation levels on a genome-wide level are warranted.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2020.00009
This article belongs to the special issue The Biological Basis of Substance Use Disorders

Aim:
Recent randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have tested the efficacy of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA) to specifically treat non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). We performed a meta-analysis of RCTs to investigate the efficacy of GLP-1 RAs for treatment of NAFLD or non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
Methods:
We systematically searched PubMed and ClinicalTrials.Gov databases utilizing specific terms to identify placebo-controlled or head-to-head RCTs (last research on March 1, 2020) involving NAFLD patients with the aim of evaluating the efficacy of GLP-1 RAs to treat NAFLD/NASH. Primary outcomes were changes in serum liver enzymes, liver fat content, or histologic resolution of NASH. Weighted mean differences (WMD) were used to test the differences between the treatment arms.
Results:
Overall, we found 7 placebo-controlled or head-to-head RCTs involving 472 middle-aged individuals (66% men; 77% with established diabetes) followed for a median of 16 weeks that have used liraglutide or exenatide to treat NAFLD on imaging (n = 6) or biopsy (n = 1). Compared to placebo or reference therapy, treatment with GLP-1 RAs decreased serum alanine aminotransferase [n = 7 studies; WMD: –8.77 IU/L, 95% confidence intervals (CI) –17.69 to 0.14 IU/L; I2 = 87.3%], gamma-glutamyltransferase levels (n = 4 studies; WMD: –10.17 IU/L, 95% CI –14.27 IU/L to –6.07 IU/L; I2 = 0%) and imaging-defined liver fat content (n = 4 studies; WMD: –6.23%, 95% CI –8.95% to –3.51%; I2 = 85.9%). In one RCT involving 55 patients with biopsy-proven NASH, a 48-week treatment with liraglutide also led to a greater histological resolution of NASH than placebo.
Conclusions:
GLP-1 RAs (mostly liraglutide) seem to be a promising treatment option for NAFLD or NASH.
Aim:
Recent randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have tested the efficacy of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA) to specifically treat non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). We performed a meta-analysis of RCTs to investigate the efficacy of GLP-1 RAs for treatment of NAFLD or non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
Methods:
We systematically searched PubMed and ClinicalTrials.Gov databases utilizing specific terms to identify placebo-controlled or head-to-head RCTs (last research on March 1, 2020) involving NAFLD patients with the aim of evaluating the efficacy of GLP-1 RAs to treat NAFLD/NASH. Primary outcomes were changes in serum liver enzymes, liver fat content, or histologic resolution of NASH. Weighted mean differences (WMD) were used to test the differences between the treatment arms.
Results:
Overall, we found 7 placebo-controlled or head-to-head RCTs involving 472 middle-aged individuals (66% men; 77% with established diabetes) followed for a median of 16 weeks that have used liraglutide or exenatide to treat NAFLD on imaging (n = 6) or biopsy (n = 1). Compared to placebo or reference therapy, treatment with GLP-1 RAs decreased serum alanine aminotransferase [n = 7 studies; WMD: –8.77 IU/L, 95% confidence intervals (CI) –17.69 to 0.14 IU/L; I2 = 87.3%], gamma-glutamyltransferase levels (n = 4 studies; WMD: –10.17 IU/L, 95% CI –14.27 IU/L to –6.07 IU/L; I2 = 0%) and imaging-defined liver fat content (n = 4 studies; WMD: –6.23%, 95% CI –8.95% to –3.51%; I2 = 85.9%). In one RCT involving 55 patients with biopsy-proven NASH, a 48-week treatment with liraglutide also led to a greater histological resolution of NASH than placebo.
Conclusions:
GLP-1 RAs (mostly liraglutide) seem to be a promising treatment option for NAFLD or NASH.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2020.00008
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus

Tanshinone is a herbal medicinal compound described in Chinese medicine, extracted from the roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza (Danshen). This family of compounds, including Tanshinone IIA and Tanshinone I, have shown remarkable potential as anti-cancer molecules, especially against breast, cervical, colorectal, gastric, lung, and prostate cancer cell lines, as well as leukaemia, melanoma, and hepatocellular carcinoma among others. Recent data has indicated that Tanshinones can modulate multiple molecular pathways such as PI3K/Akt, MAPK and JAK/STAT3, and exert their pharmacological effects against different malignancies. In addition, preclinical and clinical data, together with the safety profile of Tanshinones, encourage further applications of these compounds in cancer therapeutics. In this review article, the effect of Tanshinones on different cancers, challenges in their pharmacological development, and opportunities to harness their clinical potential have been documented.
Tanshinone is a herbal medicinal compound described in Chinese medicine, extracted from the roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza (Danshen). This family of compounds, including Tanshinone IIA and Tanshinone I, have shown remarkable potential as anti-cancer molecules, especially against breast, cervical, colorectal, gastric, lung, and prostate cancer cell lines, as well as leukaemia, melanoma, and hepatocellular carcinoma among others. Recent data has indicated that Tanshinones can modulate multiple molecular pathways such as PI3K/Akt, MAPK and JAK/STAT3, and exert their pharmacological effects against different malignancies. In addition, preclinical and clinical data, together with the safety profile of Tanshinones, encourage further applications of these compounds in cancer therapeutics. In this review article, the effect of Tanshinones on different cancers, challenges in their pharmacological development, and opportunities to harness their clinical potential have been documented.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2020.00010
This article belongs to the special issue Targeting Transcription Factors for Cancer Therapy

Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a substantial and growing problem worldwide and has become the second most common indication for liver transplantation as it may progress to cirrhosis and develop complications from portal hypertension primarily caused by advanced fibrosis and erratic tissue remodeling. However, elevated portal venous pressure has also been detected in experimental models of fatty liver and in human NAFLD when fibrosis is far less advanced and cirrhosis is absent. Early increases in intrahepatic vascular resistance may contribute to the progression of liver disease. Specific pathophenotypes linked to the development of portal hypertension in NAFLD include hepatocellular lipid accumulation and ballooning injury, capillarization of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells, enhanced contractility of hepatic stellate cells, activation of Kupffer cells and pro-inflammatory pathways, adhesion and entrapment of recruited leukocytes, microthrombosis, angiogenesis and perisinusoidal fibrosis. These pathological events are amplified in NAFLD by concomitant visceral obesity, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes and dysbiosis, promoting aberrant interactions with adipose tissue, skeletal muscle and gut microbiota. Measurement of the hepatic venous pressure gradient by retrograde insertion of a balloon-tipped central vein catheter is the current reference method for predicting outcomes of cirrhosis associated with clinically significant portal hypertension and guiding interventions. This invasive technique is rarely considered in the absence of cirrhosis where currently available clinical, imaging and laboratory correlates of portal hypertension may not reflect early changes in liver hemodynamics. Availability of less invasive but sufficiently sensitive methods for the assessment of portal venous pressure in NAFLD remains therefore an unmet need. Recent efforts to develop new biomarkers and endoscopy-based approaches such as endoscopic ultrasound-guided measurement of portal pressure gradient may help achieve this goal. In addition, cellular and molecular targets are being identified to guide emerging therapies in the prevention and management of portal hypertension.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a substantial and growing problem worldwide and has become the second most common indication for liver transplantation as it may progress to cirrhosis and develop complications from portal hypertension primarily caused by advanced fibrosis and erratic tissue remodeling. However, elevated portal venous pressure has also been detected in experimental models of fatty liver and in human NAFLD when fibrosis is far less advanced and cirrhosis is absent. Early increases in intrahepatic vascular resistance may contribute to the progression of liver disease. Specific pathophenotypes linked to the development of portal hypertension in NAFLD include hepatocellular lipid accumulation and ballooning injury, capillarization of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells, enhanced contractility of hepatic stellate cells, activation of Kupffer cells and pro-inflammatory pathways, adhesion and entrapment of recruited leukocytes, microthrombosis, angiogenesis and perisinusoidal fibrosis. These pathological events are amplified in NAFLD by concomitant visceral obesity, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes and dysbiosis, promoting aberrant interactions with adipose tissue, skeletal muscle and gut microbiota. Measurement of the hepatic venous pressure gradient by retrograde insertion of a balloon-tipped central vein catheter is the current reference method for predicting outcomes of cirrhosis associated with clinically significant portal hypertension and guiding interventions. This invasive technique is rarely considered in the absence of cirrhosis where currently available clinical, imaging and laboratory correlates of portal hypertension may not reflect early changes in liver hemodynamics. Availability of less invasive but sufficiently sensitive methods for the assessment of portal venous pressure in NAFLD remains therefore an unmet need. Recent efforts to develop new biomarkers and endoscopy-based approaches such as endoscopic ultrasound-guided measurement of portal pressure gradient may help achieve this goal. In addition, cellular and molecular targets are being identified to guide emerging therapies in the prevention and management of portal hypertension.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2020.00011
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring NAFLD/NASH

Immunotherapy has shifted the therapeutic landscape in thoracic cancers. However, assessment of biomarkers for patient selection and disease monitoring remain challenging, especially considering the lack of tissue sample availability for clinical and research purposes. In this scenario, liquid biopsy (LB), defined as the study and characterization of biomarkers in body fluids, represents a useful alternative strategy. In other malignancies such as colorectal cancer, breast cancer or melanoma, the potential of LB has been more extensively explored for monitoring minimal residual disease or response to treatment, and to investigate mechanisms of resistance to targeted agents. Even if various experiences have already been published about the applications of LB in immunotherapy in thoracic cancers, the standardization of methodology and assessment of its clinical utility is still pending. In this review, the authors will focus on the applications of LB in immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer, small cell lung cancer, and malignant pleural mesothelioma, describing available data and future perspectives.
Immunotherapy has shifted the therapeutic landscape in thoracic cancers. However, assessment of biomarkers for patient selection and disease monitoring remain challenging, especially considering the lack of tissue sample availability for clinical and research purposes. In this scenario, liquid biopsy (LB), defined as the study and characterization of biomarkers in body fluids, represents a useful alternative strategy. In other malignancies such as colorectal cancer, breast cancer or melanoma, the potential of LB has been more extensively explored for monitoring minimal residual disease or response to treatment, and to investigate mechanisms of resistance to targeted agents. Even if various experiences have already been published about the applications of LB in immunotherapy in thoracic cancers, the standardization of methodology and assessment of its clinical utility is still pending. In this review, the authors will focus on the applications of LB in immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer, small cell lung cancer, and malignant pleural mesothelioma, describing available data and future perspectives.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2020.00012
This article belongs to the special issue Liquid Biopsy in Thoracic Cancer

Poly-ADP-ribose polymerase inhibitors (PARP-I) represent one of the most attractive and promising class of biological agents studied both in relapsed ovarian cancer (OC) and in the advanced setting. The availability of this new class of drugs has changed the clinical management of OC ensuring an unprecedented advance in such an aggressive cancer. Three oral PARP-I are currently available: olaparib, niraparib and rucaparib. Another two are in active clinical exploration: veliparib and talazoparib. Here the authors report clinical data with PARP-I with a particular emphasis on the phase II and III trials that support PARP-I approval by regulatory agencies in OC patients.
Poly-ADP-ribose polymerase inhibitors (PARP-I) represent one of the most attractive and promising class of biological agents studied both in relapsed ovarian cancer (OC) and in the advanced setting. The availability of this new class of drugs has changed the clinical management of OC ensuring an unprecedented advance in such an aggressive cancer. Three oral PARP-I are currently available: olaparib, niraparib and rucaparib. Another two are in active clinical exploration: veliparib and talazoparib. Here the authors report clinical data with PARP-I with a particular emphasis on the phase II and III trials that support PARP-I approval by regulatory agencies in OC patients.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2020.00011

Pooled prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) globally is about 25%. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) with advanced fibrosis has been linked with substantial morbidity and mortality, without having to-date any licensed treatment. C-C chemokine receptor (CCR) antagonists have been investigated as candidates for the treatment of NASH. Inhibition of CCR2 is expected to mitigate hepatic inflammation, through reducing the activation of Kupffer cells, as well as the infiltration of monocytes and macrophages into the liver. Inhibition of CCR5 is expected to mitigate hepatic fibrogenesis, through impairing the activation of hepatic stellate cells, as well as to mitigate hepatic inflammation, through impairing the activation of Kupffer cells and macrophages. Cenicriviroc (CVC) is the first in class, dual inhibitor of CCR2 and CCR5. After exhibiting favorable results in animal models, CVC was shown to be beneficial in NASH patients with more severe fibrosis at a phase 2b trial (CENTAUR) and is currently at a phase 3 clinical trial (AURORA). Apart from CVC, other CCR5 mono-antagonists, such as maraviroc, are under evaluation in clinical trials with human immunodeficiency virus patients with NAFLD. The aim of this review was to summarize existing evidence on CVC and other CCR antagonists in NASH patients, primarily focusing on their clinical efficacy and safety.
Pooled prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) globally is about 25%. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) with advanced fibrosis has been linked with substantial morbidity and mortality, without having to-date any licensed treatment. C-C chemokine receptor (CCR) antagonists have been investigated as candidates for the treatment of NASH. Inhibition of CCR2 is expected to mitigate hepatic inflammation, through reducing the activation of Kupffer cells, as well as the infiltration of monocytes and macrophages into the liver. Inhibition of CCR5 is expected to mitigate hepatic fibrogenesis, through impairing the activation of hepatic stellate cells, as well as to mitigate hepatic inflammation, through impairing the activation of Kupffer cells and macrophages. Cenicriviroc (CVC) is the first in class, dual inhibitor of CCR2 and CCR5. After exhibiting favorable results in animal models, CVC was shown to be beneficial in NASH patients with more severe fibrosis at a phase 2b trial (CENTAUR) and is currently at a phase 3 clinical trial (AURORA). Apart from CVC, other CCR5 mono-antagonists, such as maraviroc, are under evaluation in clinical trials with human immunodeficiency virus patients with NAFLD. The aim of this review was to summarize existing evidence on CVC and other CCR antagonists in NASH patients, primarily focusing on their clinical efficacy and safety.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2020.00012
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring NAFLD/NASH

The currently ongoing coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) pandemic has affected globally human health and economy. Research in progress has shown facts associated with this disease and raised questions relevant for disease control and prevention. In this perspective, the collaboration between science and art in visual communication using the artwork “Enseñanza” (“Teaching”) contributes to the representation of the lessons learned from COVID-19 and the way forward. To advance preparedness for current and future pandemics, the authors propose to address international collaborations, support to science, access to food supplies and health services, sustainable development and a “One Health” approach searching a balanced interaction of humanity with nature and a more holistic approach to disease prevention and control.
The currently ongoing coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) pandemic has affected globally human health and economy. Research in progress has shown facts associated with this disease and raised questions relevant for disease control and prevention. In this perspective, the collaboration between science and art in visual communication using the artwork “Enseñanza” (“Teaching”) contributes to the representation of the lessons learned from COVID-19 and the way forward. To advance preparedness for current and future pandemics, the authors propose to address international collaborations, support to science, access to food supplies and health services, sustainable development and a “One Health” approach searching a balanced interaction of humanity with nature and a more holistic approach to disease prevention and control.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2020.00016

Cancer remains the second leading cause of mortality globally. In combating cancer, conventional chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy are administered as first-line therapy. However, these are usually accompanied with adverse side effects that decrease the quality of patient’s lives. As such, natural bioactive compounds have gained an attraction in the scientific and medical community as evidence of their anticancer properties and attenuation of side effects mounted. In particular, quassinoids have been found to exhibit a plethora of inhibitory activities such as anti-proliferative effects on tumor development and metastasis. Recently, bruceine D, a quassinoid isolated from the shrub Brucea javanica (L.) Merr. (Simaroubaceae), has come under immense investigation on its antineoplastic properties in various human cancers including pancreas, breast, lung, blood, bone, and liver. In this review, we have highlighted the antineoplastic effects of bruceine D and its mode of actions in different tumor models.
Cancer remains the second leading cause of mortality globally. In combating cancer, conventional chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy are administered as first-line therapy. However, these are usually accompanied with adverse side effects that decrease the quality of patient’s lives. As such, natural bioactive compounds have gained an attraction in the scientific and medical community as evidence of their anticancer properties and attenuation of side effects mounted. In particular, quassinoids have been found to exhibit a plethora of inhibitory activities such as anti-proliferative effects on tumor development and metastasis. Recently, bruceine D, a quassinoid isolated from the shrub Brucea javanica (L.) Merr. (Simaroubaceae), has come under immense investigation on its antineoplastic properties in various human cancers including pancreas, breast, lung, blood, bone, and liver. In this review, we have highlighted the antineoplastic effects of bruceine D and its mode of actions in different tumor models.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2020.00013
This article belongs to the special issue Targeting Transcription Factors for Cancer Therapy

Diabetes and cancer are widespread worldwide and the number of subjects presenting both diseases increased over the years. The management of cancer patients having diabetes represents a challenge not only because of the complexity and heterogeneity of these pathologies but also for the lack of standardised clinical guidelines. The diagnosis of cancer is traumatizing and monopolizes the attention of both patients and caregivers. Thus, pre-existent or new-onset diabetes can be overshadowed thus increasing the risk for short- and long-term adverse events. Moreover, drugs used for each disease can interfere with the clinical course of the concomitant disease, making challenging the management of these patients. Over the years, this issue has become more relevant because of the increased patients’ life expectancy due to the improved efficacy of diabetes and cancer therapies.
The purpose of this review is to highlight what is known and what should be taken into consideration to optimise the clinical management of patients with diabetes and cancer. Due to the complexity of these diseases, a multidisciplinary, shared approach, including all the protagonists involved, is necessary to improve patients’ quality of life and lifespan.
Diabetes and cancer are widespread worldwide and the number of subjects presenting both diseases increased over the years. The management of cancer patients having diabetes represents a challenge not only because of the complexity and heterogeneity of these pathologies but also for the lack of standardised clinical guidelines. The diagnosis of cancer is traumatizing and monopolizes the attention of both patients and caregivers. Thus, pre-existent or new-onset diabetes can be overshadowed thus increasing the risk for short- and long-term adverse events. Moreover, drugs used for each disease can interfere with the clinical course of the concomitant disease, making challenging the management of these patients. Over the years, this issue has become more relevant because of the increased patients’ life expectancy due to the improved efficacy of diabetes and cancer therapies.
The purpose of this review is to highlight what is known and what should be taken into consideration to optimise the clinical management of patients with diabetes and cancer. Due to the complexity of these diseases, a multidisciplinary, shared approach, including all the protagonists involved, is necessary to improve patients’ quality of life and lifespan.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2020.00013
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus

The prevalence of nonalcoholic or more recently re-defined metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) is rapidly growing worldwide. It is characterized by hepatic fat accumulation exceeding 5% of liver weight not attributable to alcohol consumption. MAFLD refers to an umbrella of conditions ranging from simple steatosis to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis which may finally progress to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. MAFLD is closely related to components of the metabolic syndrome and to environmental factors. In addition to the latter, genetic predisposition plays a key role in MAFLD pathogenesis and strictly contributes to its progressive forms. The candidate genes which have been related to MAFLD hereditability are mainly involved in lipids remodeling, lipid droplets assembly, lipoprotein packaging and secretion, de novo lipogenesis, and mitochondrial redox status. In the recent years, it has emerged the opportunity to translate the genetics into clinics by aggregating the genetic variants mostly associated with MAFLD in polygenic risk scores. These scores might be used in combination with metabolic factors to identify those patients at higher risk to develop more severe liver disease and to schedule an individual therapeutic approach.
The prevalence of nonalcoholic or more recently re-defined metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) is rapidly growing worldwide. It is characterized by hepatic fat accumulation exceeding 5% of liver weight not attributable to alcohol consumption. MAFLD refers to an umbrella of conditions ranging from simple steatosis to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis which may finally progress to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. MAFLD is closely related to components of the metabolic syndrome and to environmental factors. In addition to the latter, genetic predisposition plays a key role in MAFLD pathogenesis and strictly contributes to its progressive forms. The candidate genes which have been related to MAFLD hereditability are mainly involved in lipids remodeling, lipid droplets assembly, lipoprotein packaging and secretion, de novo lipogenesis, and mitochondrial redox status. In the recent years, it has emerged the opportunity to translate the genetics into clinics by aggregating the genetic variants mostly associated with MAFLD in polygenic risk scores. These scores might be used in combination with metabolic factors to identify those patients at higher risk to develop more severe liver disease and to schedule an individual therapeutic approach.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2020.00015
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring NAFLD/NASH

Lung cancer represents the world’s most common cause of cancer death. In recent years, we moved from a generic therapeutic strategy to a personalized approach, based on the molecular characterization of the tumor. In this view, liquid biopsy is becoming an important tool for assessing the progress or onset of lung disease. Liquid biopsy is a non-invasive procedure able to isolate circulating tumor cells, tumor educated platelets, exosomes and free circulating tumor DNA from body fluids. The characterization of these liquid biomarkers can help to choose the therapeutic strategy for each different case. In this review, the authors will analyze the main aspects of lung cancer and the applications currently in use focusing on the benefits associated with this approach for predicting the prognosis and monitoring the clinical conditions of lung cancer disease.
Lung cancer represents the world’s most common cause of cancer death. In recent years, we moved from a generic therapeutic strategy to a personalized approach, based on the molecular characterization of the tumor. In this view, liquid biopsy is becoming an important tool for assessing the progress or onset of lung disease. Liquid biopsy is a non-invasive procedure able to isolate circulating tumor cells, tumor educated platelets, exosomes and free circulating tumor DNA from body fluids. The characterization of these liquid biomarkers can help to choose the therapeutic strategy for each different case. In this review, the authors will analyze the main aspects of lung cancer and the applications currently in use focusing on the benefits associated with this approach for predicting the prognosis and monitoring the clinical conditions of lung cancer disease.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2020.00015
This article belongs to the special issue Liquid Biopsy in Thoracic Cancer