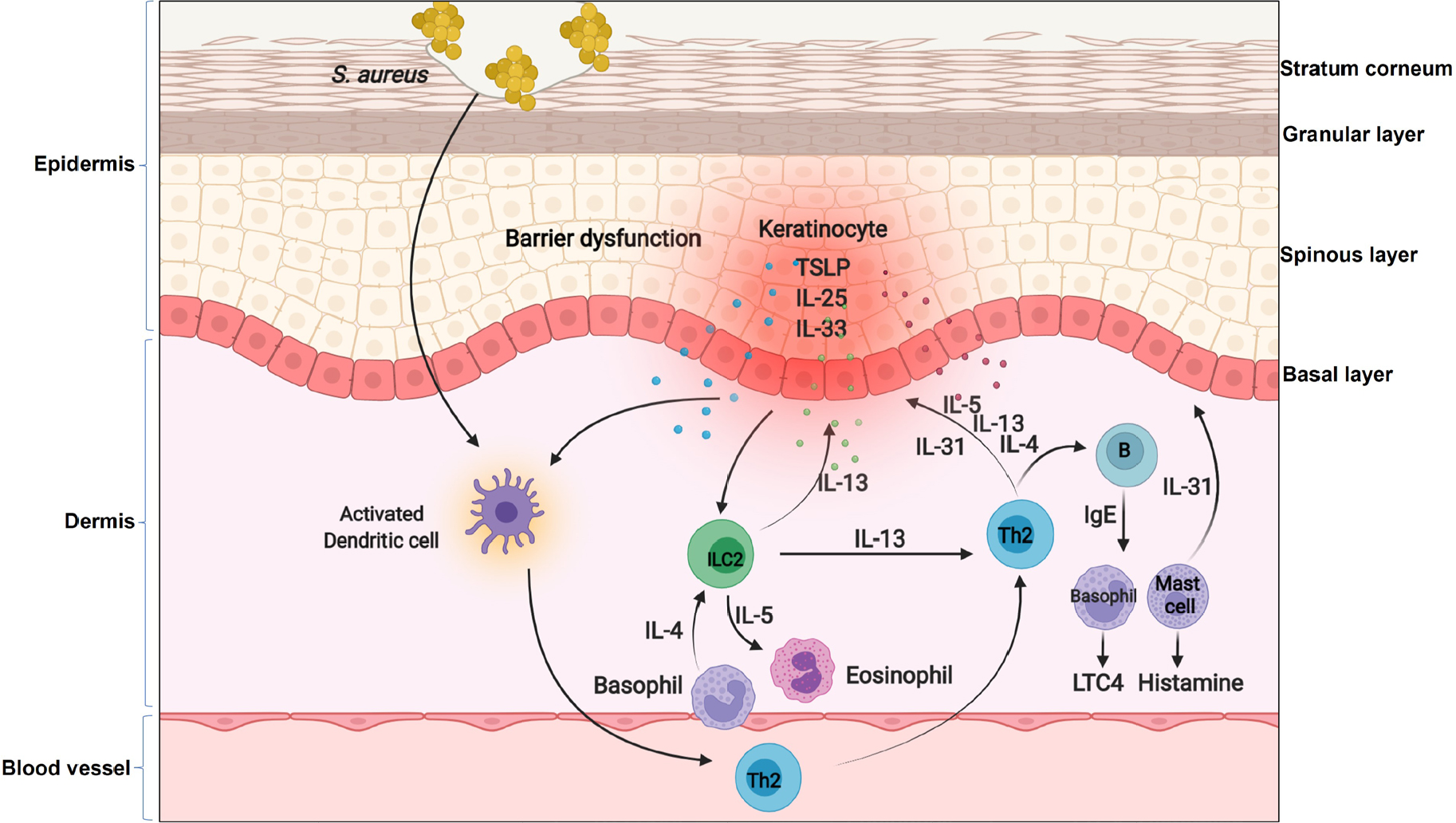
The inflammatory loop in AD. In the context of AD, keratinocytes produce cytokines such as TSLP, IL-25 and IL-33. These cytokines on one hand activate DCs to produce chemokines for recruiting Th2 cells and ILC2 into lesional skin, on the other hand directly active basophils to release IL-4 and then activate ILC2. Th2 cells and ILC2 produce IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13 to induce an immunoglobulin isotype switch to IgE in B cells, and then IgE triggers mast cells and basophils to release a diverse group of biologically active products including histamine and LTC4. Moreover, these Th2 cytokines can inhibit FLG expression in keratinocytes or further induce keratinocytes to produce TSLP. Furthermore, the genetic defects in keratinocytes impair skin barrier and facilitates Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) entry through the epidermal barrier. Penetrated S. aureus enables them to come direct contact with viable immune cells and enhances the expression of Th2 cytokines such as IL-4