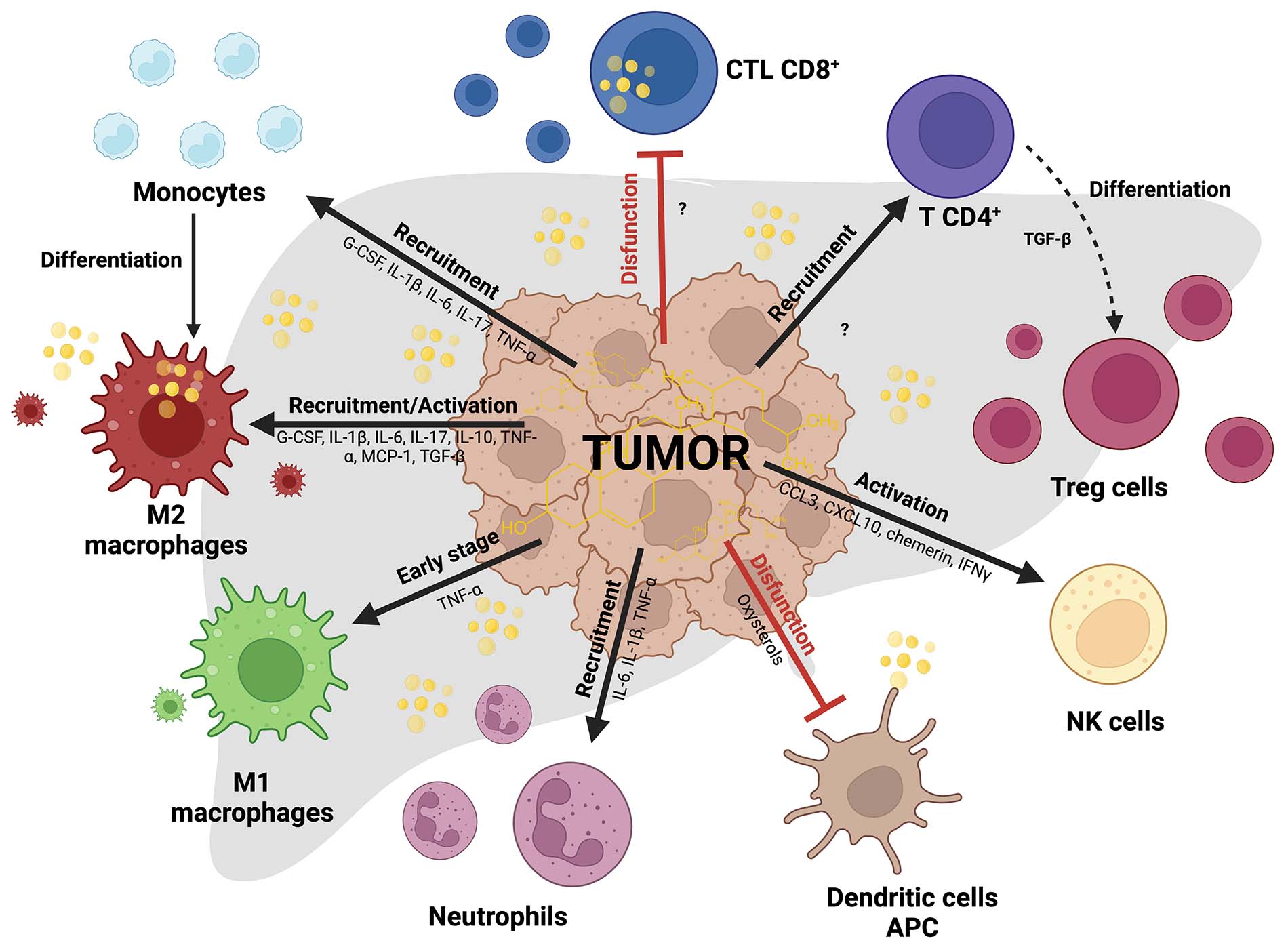
Immune cells in HCC tumors affecting cholesterol context. Differential effects of cholesterol in myeloid and lymphoid cells inside TIME in HCC. Black arrows indicate recruitment or activation, and flattened red lines indicate exhaustion or inactivity state leucocytes. M2 macrophages studied in ovarian cancer release cholesterol and provide aggressivity to the cancer cells. Cholesterol reduces cytotoxic activity in CD8+ T cells (CTL CD8+) through endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and affects antigen-presenting in dendritic cells (DC). In more cases, cholesterol promotes the recruitment and activation of different immune cells. Created with BioRender.com. CCL3: C-C motif chemokine ligand 3; G-CSF: granulocyte-colony stimulator factor; IFNγ: interferon gamma; MCP-1: monocyte chemoattractant protein-1