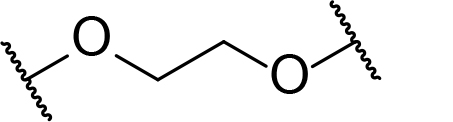
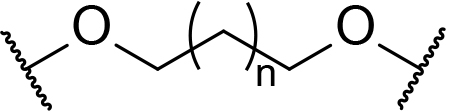
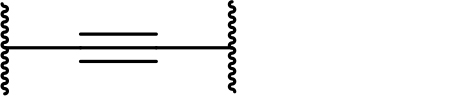
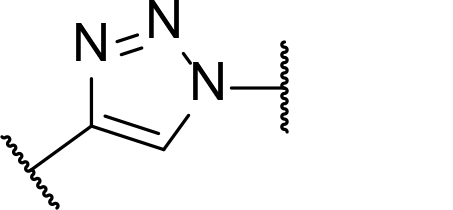
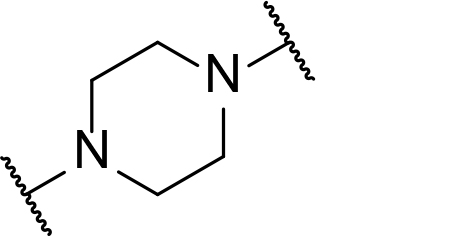
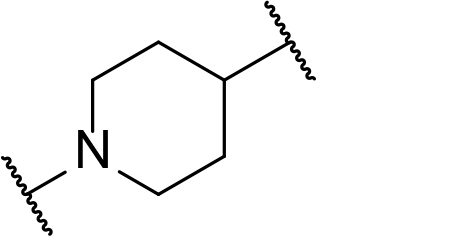
Occurrence of selected linker motifs in the Maple database of published degrader structures. Wavy lines indicate attachment to other linker motifs, protein-binding ligands, or connecting functional groups. Since many PROTACs combine more than one structural motifs into their linkers therefore these percentages sum to more than 100
All authors contributed to the conception and organisation of this review. RT prepared the first draft of the manuscript, and all authors contributed to the writing and development of additional sections. All authors contributed to manuscript revision and approved the submitted version.
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
This work was supported by AstraZeneca with a CASE award, and the EPSRC with a CASE Conversion grant (EP/R513325/1). AstraZeneca approved the final submitted version of the manuscript. The industrial supervisor/author (CF), together with the other authors, contributed to the design, writing, proof-reading and submission of this review.
© The Author(s) 2020.