An overview of pathogenesis of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
Steatotic liver disease (SLD) has been known for a long time, but our understanding of this disease has remained poor until the past decade. Despite extensive research, our ability to comprehend the
[...] Read more.
Steatotic liver disease (SLD) has been known for a long time, but our understanding of this disease has remained poor until the past decade. Despite extensive research, our ability to comprehend the etiopathogenesis and natural course of SLD is far from the desired level of comprehension. This is required to develop a universally effective novel therapeutic agent. This review aims to concisely elaborate the conceptual approach and advancement in the understanding of global disease burden and etiopathogenic process, identifying the gaps and the pathophysiologic mechanism behind developing novel therapeutic agents. We searched two major databases, PubMed and Google Scholar, to identify publications related to the abovementioned topics. All publications, including original papers, reviews, and commentaries, were reviewed. Findings: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is not limited to obese individuals, rather, it may develop in any individual independent of weight. Visceral adiposity is strongly associated with MASLD and subsequent risks of cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and cardiovascular disease. MASLD is associated with diabetes mellitus independent of underlying pathogenic mechanisms, and there is a bidirectional connection between MASLD and diabetes mellitus, making the situation quite challenging. Not all patients with MASLD exhibit atherogenic dyslipidemia and thus do not have a higher risk of cardiovascular disease. The overlap of these metabolic risk factors is not straightforward. There is a differential contribution of these risk factors based on age, gender, race, ethnicity, alcohol consumption, and microbiota composition. Poor dietary habits and lifestyle directly affect the microbiota, modulators, and mediators, thereby affecting the final biochemical processes leading to steatosis, steatohepatitis, fibrosis, and oncogenesis. In conclusion, MASLD is a complex and pathogenically heterogeneous disease with significant interpatient variation in the natural course and outcome. Understanding the precise mechanism of variability is the key gap and a limiting factor in the development of a novel therapeutic agent.
Shahid Habib, Andrew Johnson
View:105
Download:8
Times Cited: 0
Steatotic liver disease (SLD) has been known for a long time, but our understanding of this disease has remained poor until the past decade. Despite extensive research, our ability to comprehend the etiopathogenesis and natural course of SLD is far from the desired level of comprehension. This is required to develop a universally effective novel therapeutic agent. This review aims to concisely elaborate the conceptual approach and advancement in the understanding of global disease burden and etiopathogenic process, identifying the gaps and the pathophysiologic mechanism behind developing novel therapeutic agents. We searched two major databases, PubMed and Google Scholar, to identify publications related to the abovementioned topics. All publications, including original papers, reviews, and commentaries, were reviewed. Findings: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is not limited to obese individuals, rather, it may develop in any individual independent of weight. Visceral adiposity is strongly associated with MASLD and subsequent risks of cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and cardiovascular disease. MASLD is associated with diabetes mellitus independent of underlying pathogenic mechanisms, and there is a bidirectional connection between MASLD and diabetes mellitus, making the situation quite challenging. Not all patients with MASLD exhibit atherogenic dyslipidemia and thus do not have a higher risk of cardiovascular disease. The overlap of these metabolic risk factors is not straightforward. There is a differential contribution of these risk factors based on age, gender, race, ethnicity, alcohol consumption, and microbiota composition. Poor dietary habits and lifestyle directly affect the microbiota, modulators, and mediators, thereby affecting the final biochemical processes leading to steatosis, steatohepatitis, fibrosis, and oncogenesis. In conclusion, MASLD is a complex and pathogenically heterogeneous disease with significant interpatient variation in the natural course and outcome. Understanding the precise mechanism of variability is the key gap and a limiting factor in the development of a novel therapeutic agent.
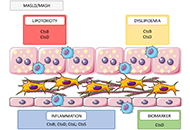 Searching for novel cellular targets for MASLD and HCC within the humble lysosomal cathepsinsOpen AccessReviewMetabolic-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and its pathological version, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), are becoming the main leading causes of chronic liver dise [...] Read more.Alejandro del Castillo-Cruz ... Anna MolesPublished: September 10, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. 2024;3:428–442
Searching for novel cellular targets for MASLD and HCC within the humble lysosomal cathepsinsOpen AccessReviewMetabolic-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and its pathological version, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), are becoming the main leading causes of chronic liver dise [...] Read more.Alejandro del Castillo-Cruz ... Anna MolesPublished: September 10, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. 2024;3:428–442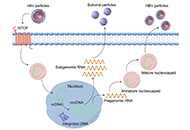 Hepatitis B virus: modes of transmission, immune pathogenesis, and research progress on therapeutic vaccinesOpen AccessReviewHepatitis B virus (HBV) infection affects 262 million people worldwide, leading to over 820,000 deaths annually. The reason HBV has been a persistent issue for decades is that it is a non-cytopathic [...] Read more.Chunzheng Li ... Xianguang YangPublished: October 14, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. 2024;3:443–458
Hepatitis B virus: modes of transmission, immune pathogenesis, and research progress on therapeutic vaccinesOpen AccessReviewHepatitis B virus (HBV) infection affects 262 million people worldwide, leading to over 820,000 deaths annually. The reason HBV has been a persistent issue for decades is that it is a non-cytopathic [...] Read more.Chunzheng Li ... Xianguang YangPublished: October 14, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. 2024;3:443–458 An overview of pathogenesis of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver diseaseOpen AccessReviewSteatotic liver disease (SLD) has been known for a long time, but our understanding of this disease has remained poor until the past decade. Despite extensive research, our ability to comprehend the [...] Read more.Shahid Habib, Andrew JohnsonPublished: November 11, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. 2024;3:459–473
An overview of pathogenesis of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver diseaseOpen AccessReviewSteatotic liver disease (SLD) has been known for a long time, but our understanding of this disease has remained poor until the past decade. Despite extensive research, our ability to comprehend the [...] Read more.Shahid Habib, Andrew JohnsonPublished: November 11, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. 2024;3:459–473