-
 Special Issue Topic
Special Issue TopicCellular and Molecular Targets for NAFLD or MAFLD Treatments and Their Functions in Liver Fibrosis, Cirrhosis, and Cancer
Submission Deadline: January 31, 2025Guest Editors
Prof. Ming Yang E-Mail
Department of Surgery, University of Missouri, Columbia, United States
Research Keywords: NASH, liver fibrosis, liver cancer, gut microbiota, immunotherapy, drug targets, cancer treatment
Prof. Chunye Zhang E-Mail
Christopher S. Bond Life Sciences Center, University of Missouri, Columbia, United States
Research Keywords: Animal models, gut microbiota, drug discovery, molecular targets, virology, cancer therapy
About the Special Issue
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) or metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) becomes the most common chronic liver disease, affecting a quarter of the world population. A progressive form of NAFLD/MAFLD is non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) with the progression of liver inflammation and varying degrees of fibrosis, which may lead to liver cirrhosis and cancer, such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The prevalence of NASH is increasing due to a raising trend of obesity, diabetes, and metabolic related disease. However, there is no currently approved treatment for NAFLD/MAFLD. Infiltrated circulating immune cells or bone marrow-derived immune cells and liver resident immune cells such as macrophages and monocytes play important roles in the pathogenesis of these chronic liver diseases. Activation of molecular signaling pathways involved in liver inflammation, cell death, and fibrosis accounts for the progression of NAFLD/MAFLD to NASH, promoting cancer development and progression. Thus, it is essential to understand the underlying cellular and molecular mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of NAFLD or MAFLD, and their progression to the end-stage of liver disease. In addition, regulating these targets could prevent or reverse the disease progression. This special issue focuses on the "Cellular and molecular targets for NAFLD or MAFLD treatments and their functions in liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and cancer". Here, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the latest research and clinical findings in this field and provide potential therapeutic targets for NASH and liver cancer, as well as future research directions. We are collecting original research and review articles of basic and clinical studies from experts in the field to enhance our current understanding of the pathogenesis of NAFLD/MAFLD, NASH, and their mediated liver cancer development.
Keywords: NAFLD, MAFLD, NASH, fibrosis, liver cancer, cellular and molecular mechanisms, targets, treatments
Call for Papers
Published Articles
 An overview of pathogenesis of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver diseaseOpen AccessReviewSteatotic liver disease (SLD) has been known for a long time, but our understanding of this disease has remained poor until the past decade. Despite extensive research, our ability to comprehend the [...] Read more.Shahid Habib, Andrew JohnsonPublished: November 11, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. 2024;3:459–473
An overview of pathogenesis of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver diseaseOpen AccessReviewSteatotic liver disease (SLD) has been known for a long time, but our understanding of this disease has remained poor until the past decade. Despite extensive research, our ability to comprehend the [...] Read more.Shahid Habib, Andrew JohnsonPublished: November 11, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. 2024;3:459–473
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/edd.2024.00061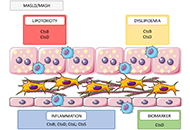 Searching for novel cellular targets for MASLD and HCC within the humble lysosomal cathepsinsOpen AccessReviewMetabolic-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and its pathological version, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), are becoming the main leading causes of chronic liver dise [...] Read more.Alejandro del Castillo-Cruz ... Anna MolesPublished: September 10, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. 2024;3:428–442
Searching for novel cellular targets for MASLD and HCC within the humble lysosomal cathepsinsOpen AccessReviewMetabolic-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and its pathological version, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), are becoming the main leading causes of chronic liver dise [...] Read more.Alejandro del Castillo-Cruz ... Anna MolesPublished: September 10, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. 2024;3:428–442
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/edd.2024.00059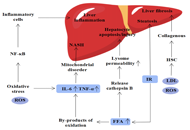 Therapeutic targets for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and their roles in hepatocellular carcinomaOpen AccessReviewMetabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is one of the most common chronic liver diseases. Over time, there has been a significant increase in the prevalence of MASLD. It has [...] Read more.Chenyu Wei ... Xianguang YangPublished: December 13, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. 2023;2:282–296
Therapeutic targets for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and their roles in hepatocellular carcinomaOpen AccessReviewMetabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is one of the most common chronic liver diseases. Over time, there has been a significant increase in the prevalence of MASLD. It has [...] Read more.Chenyu Wei ... Xianguang YangPublished: December 13, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. 2023;2:282–296
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/edd.2023.00031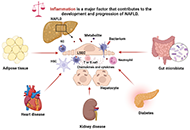 Molecular mechanisms of metabolic disease-associated hepatic inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitisOpen AccessReviewNon-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the leading chronic liver disease worldwide, with a progressive form of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). It may progress to advanced liver diseases, [...] Read more.Chunye Zhang ... Ming YangPublished: October 25, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. 2023;2:246–275
Molecular mechanisms of metabolic disease-associated hepatic inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitisOpen AccessReviewNon-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the leading chronic liver disease worldwide, with a progressive form of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). It may progress to advanced liver diseases, [...] Read more.Chunye Zhang ... Ming YangPublished: October 25, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. 2023;2:246–275
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/edd.2023.00029 -
-
Ongoing Special Issues
-
Completed Special Issues