Affiliation:
1State Key Laboratory of Microbial Metabolism, School of Life Sciences & Biotechnology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
2Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
ORCID: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8030-2401
Affiliation:
1State Key Laboratory of Microbial Metabolism, School of Life Sciences & Biotechnology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
ORCID: https://orcid.org/0009-0005-5073-2626
Affiliation:
1State Key Laboratory of Microbial Metabolism, School of Life Sciences & Biotechnology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
Email: weiding@sjtu.edu.cn
Affiliation:
2Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
Email: qizhang@sioc.ac.cn
ORCID: https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8135-2221
Explor Drug Sci. 2024;2:190–202 DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eds.2024.00042
Received: October 17, 2023 Accepted: December 25, 2023 Published: April 19, 2024
Academic Editor: Xuechen Li, The University of Hong Kong, China
The article belongs to the special issue Bioactive Peptides discovery and development
Cyclophane-containing peptides comprise an important group of macrocyclic peptides with unique structural properties and pharmaceutical relevance. Darobactin A is a ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide (RiPP) antibiotic, which features an unusual biscyclophane moiety formed via the class-defining ether crosslink in addition to a carbon-carbon (C-C) crosslink. Because darobactin-like peptides (daropeptides) are widespread in nature, further exploration of these emerging RiPP natural products featuring ether crosslinked cyclophane could facilitate the discovery and development of new bioactive peptides. This perspective provides updated insights into the biosynthesis and classification of daropeptides, highlighting the potential to manipulate daropeptide maturases to access novel bioactive peptide cyclophanes.
Cyclophane-containing peptide occupies a unique structural niche among macrocyclic peptides of pharmaceutical interest [1–4]. Unlike other linkers commonly used for peptide macrocycle construction, the intrinsic ring strain imposed by the hydrophobic cyclophane linker restricts the free rotation of the aryl-tethered side chains [5]. This property not only creates molecular complexity through planar/axial chirality but also induces rigid scaffolds with specific stereo-orientation to meet various functional demands in biological systems. Historically, the non-ribosomal peptide (NRP) pathway represents the major source of bioactive peptide cyclophanes [3]. One such example is the antimicrobial glycopeptide vancomycin discovered in the 1950s, which has been used clinically as an antibiotic of last resort and profoundly benefited human health and society [6]. In recent years, ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides (RiPPs) have emerged as a new source of naturally occurring peptide cyclophanes [7–9]. The cyclophane-containing RiPPs have been increasingly discovered in bacteria [10–19], fungi [20, 21], and plants [22, 23], and many of these compounds possess novel ring connectivity and topology that underpins equally diverse biological activities [24]. Moreover, these RiPP pathways offer a diverse set of cyclophane synthases that are dedicated biocatalysts for in trans polypeptide macrocyclization and are of important bioengineering application potential [25–28]. As RiPP natural products represent a valuable yet still underexplored reservoir of cyclophane biochemistry, further investigation of the hidden structure-function relationships and biosynthetic potential of RiPP-derived cyclophanes could offer new impetus in the development of bioactive peptides.
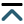
Darobactin A serves as a compelling example of how cyclophane formation within ribosomal peptides can yield highly valuable pharmaceutical compounds [29]. This compound is a heptapeptide isolated from Photorhabdus khanni in 2019, which exhibits potent and broad-spectrum activity against a wide panel of Gram-negative pathogens [29]. Darobactin A consists of two fused three-residue cyclophane units, which are formed via an ether crosslink adjoining Trp1-C7 and Trp3-Cβ, and a carbon-carbon (C-C) crosslink adjoining Trp3-C6 and Lys5-Cβ, respectively (Figure 1A). The unique biscyclophane structure forms a rigid β-strand, allowing the compound to selectively bind to and inhibit the lateral gate of BamA mainly through backbone interaction [30, 31]. BamA is the central unit of the bacterial β-barrel assembly machinery (BAM) complex [32, 33], which is universally present in Gram-negative bacteria and responsible for the folding and insertion of outer membrane proteins (OMPs). Recent years have witnessed increasing (peptide) antibiotics that target Gram-negative bacteria by functioning as BAM inhibitors with diverse modes of action [11, 34–38], darobactin A stands out as it not only demonstrates the lateral gate of BamA as a hotspot druggable site to combat Gram-negative infection but delivers a new antibiotic drug lead with novel peptidyl biscyclophane scaffold and ring connectivity [39].
Darobactin A and its unique biscyclophane biosynthesis. A. Organization of dar biosynthetic gene cluster (BGC) and biosynthesis of darobactin A. The transporter-related gene (e.g., darBCD) are not colored for clarity; B. reaction scheme highlighting the substrate-controlled cyclophane formation in daropeptide maturase, as illustrated herein by darobactin biosynthesis. Ω: aromatic residue; X: non-aromatic residue; the white circles in the peptide structure: a shorthand of the amino acid side chain or extended peptide main skeleton
Note. Adapted with permission from “Substrate-controlled catalysis in the ether cross-link-forming radical SAM enzymes,” by Ma S, Xi W, Wang S, Chen H, Guo S, Mo T, et al. J Am Chem Soc. 2023;145:22945–53 (https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.3c04355). © 2023 American Chemical Society.
The pharmaceutical significance of darobactin has continued to spur investigations on biosynthetic chemistry toward its biogenesis. While a similar C-C crosslink has been found for several cyclophane-containing RiPPs [9, 40], the ether crosslinked cyclophane in darobactin A was highly unique and had no structural counterparts in nature prior to its discovery. Moreover, biosynthesis of both ether crosslink and C-C crosslink in darobactin A is unprecedented in biochemistry, which has manifested nature’s ingenuity in achieving molecular diversity of ribosomal peptides through post-translational modifications. Interestingly, recent genome mining studies have revealed that darobactin A belongs to a larger class of RiPP natural products, now referred to as darobactin-like peptide (daropeptide), which is characterized by the unique three-residue cyclophanes with ether cross-linkage [41, 42]. Further exploration of this emerging RiPP class and its biosynthetic capacity holds great promise to facilitate the discovery and development of new bioactive macrocyclic peptides. This perspective provides a brief and updated insight into the biosynthesis, classification, and widespread occurrence of daropeptides. Also highlighted is the potential to leverage daropeptide biosynthetic chemistry to access a diverse range of peptide cyclophanes. The readers are directed to a recent review that details the chemical synthesis and biosynthesis of darobactin A [43].
Similar to other RiPP natural products, darobactin A is biosynthesized from gene-encoded precursor peptides, which are matured by post-translational modifications and trimmed by proteolysis (Figure 1A). In addition to the precursor peptide DarA, the BGC of darobactin A (dar) also encodes three transporter-related proteins DarBCD and a radical S-adenosylmethionine (rSAM) enzyme DarE. The functions of these proteins involved in darobactin biogenesis have been comprehensively dissected through heterologous expression and metabolic engineering efforts in Escherichia coli (E. coli) [29, 41, 44]. While DarBCD are not assigned to a biosynthetic role and their exact functions in darobactin biogenesis await further investigation, DarE has been verified to be responsible for the formation of the biscyclophane structure in DarA [41, 44]. Removal of the leader and follower peptide in the modified DarA to produce mature darobactin A is likely catalyzed by unknown proteases encoded outside of the BGC [41, 44].
The unusual biscyclophane modification involves two remarkable biochemical processes in DarE catalysis (Figure 1B). First, the ether crosslink in darobactin A is de novo synthesized by taking an exogenous source of oxygen, which is unprecedented in rSAM enzymology. Second, DarE also forms a chemically distinct C-C crosslink besides the ether crosslink, raising questions regarding the mechanism of regio- and chemo-selectivity in DarE catalysis. Decrypting the mechanism for ether crosslink formation and the control of chemo-selectivity underlying the multifunctionality of DarE is critical to understanding the enzymology of DarE, which paves the way for biosynthetic application of this versatile cyclophane synthase.
The rSAM enzymes constitute the largest enzyme superfamily that catalyze impressively diverse and chemically demanding reactions [45–48]. These enzymes utilize a strictly conserved [4Fe-4S] cluster ligated by three Cys residues to reductively cleave the cofactor S-adenosylmethionine (SAM). The resulting 5’-deoxyadenosyl (dAdo) radical then abstracts a hydrogen (H)-atom from the substrate to initiate subsequent biotransformations [49, 50]. Because the [4Fe-4S] cluster of rSAM enzymes is prone to oxidative deconstruction, this superfamily of enzymes are generally highly sensitive to oxygen (O2) and are believed to function only anaerobically in vitro. Surprisingly, in vitro studies of DarE revealed that the ether crosslinking activity can only be fully reconstituted in the presence of O2 additionally supplemented in the reaction [42, 51]. Furthermore, 18O labeling assays have demonstrated that O2 is the source of oxygen in the ether crosslink [42, 51]. These results have demonstrated DarE is an unprecedented rSAM oxygenase that can utilize O2 as a co-substrate, which suggests a significant change in the paradigm of the rSAM enzymology. Note that heavy-oxygen water (H218O) labeling assays in DarE-catalyzed reaction can lead to deceptive 18O-incorporation into the ether crosslinked product, which likely results from the non-specific solvent exchange with the still unclear mechanism [41, 42].
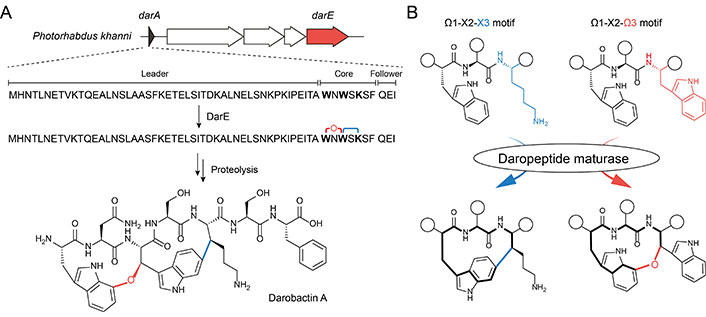
An intriguing question lies in how a single DarE enzyme achieves the synthesis of two cyclophane moieties with distinct chemo- and regio-selectivity (i.e. a western ether crosslink tethering through Trp1-C7 and an eastern C-C crosslink tethering through Trp3-C6). Recently, bioinformatics and substrate mutagenesis analysis on PasB (vide infra), an ortholog of DarE, provided the first insight into the intriguing substrate-controlled reactivity of these remarkable enzymes [42]. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that DarE, PasB, and other ether crosslink-forming rSAM enzymes have evolved from the same ancestor with anaerobic sulfatase maturating enzymes (anSMEs) and three-residue cyclophane-forming enzymes (3-CyFEs) (Figure 2A) [42]. anSMEs e.g., AtsB [52] catalyze the conversion of Cys/Ser to formylglycine (FGly) during the maturation of sulfatase, while 3-CyFEs e.g., SjiB [53] acts on the class-defining Ω1-X2-X3 substrate motif of triceptide precursors to afford three-residue cyclophane. Enzyme promiscuity within this unique sequence-function space has been previously observed, where the cyclophane synthase SjiB can also act like an anSME to convert the native X3 substrate (i.e. Ser) to produce FGly and aminomalonate, and the partition of the two reactions is under substrate-control [53]. In DarE catalysis, the C-C crosslink is notably installed in a Ω1-X2-X3 substrate motif (i.e. Trp3-Ser4-Lys5 motif in darobactin A) that is identical to the natural substrate of 3-CyFEs [10, 15, 53, 54], suggesting the different catalytic outcomes of DarE are similarly governed by the substrate sequence.
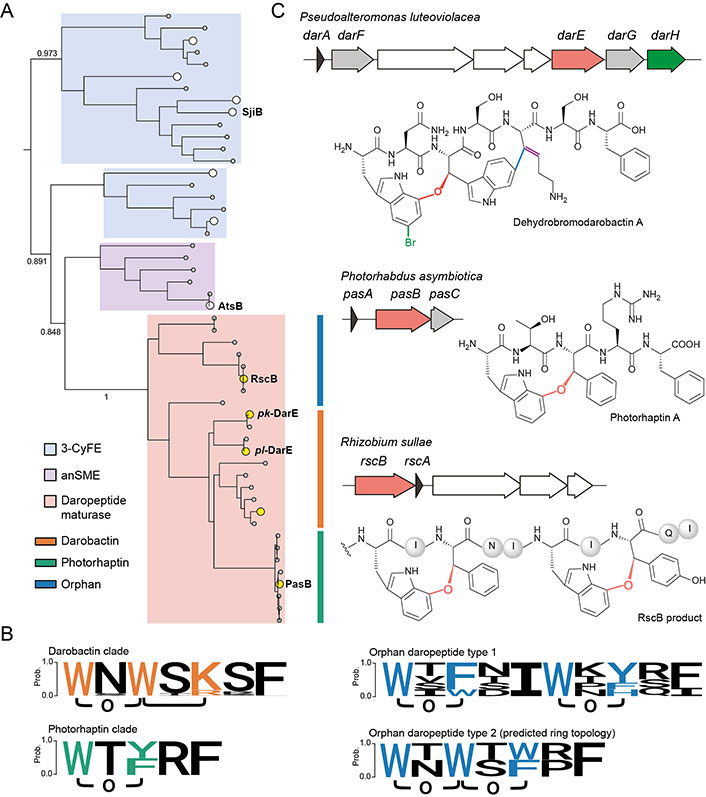
Biosynthetic diversity of daropeptide family. A. Phylogenetic analysis and subfamily classification of daropeptide maturases. The daropeptide maturases are likely evolved from the same ancestor with 3-CyFE (e.g., SjiB) and anSME (e.g., AtsB). The characterized enzymes that have also been discussed in this perspective are highlighted in white (for 3-CyFE and anSME) and in yellow (for daropeptide maturase) while their uncharacterized homologs are in grey. Key bootstrap values are indicated; B. the known and predicted ring topologies of cyclophane systems in different daropeptide clades. The logo of darobactin clade encompasses the core peptide sequences of darobactin A–F and dehydrobromodarobactin. The logo of the photorhaptin clade includes photorhaptin A. The logo of orphan daropeptide type 1 include RscB product. The ring topology of orphan daropeptide type 2 is predicted from the bioinformatic analysis in reference [42]; C. BGCs and structures of the newly characterized daropeptides. The transporter-related genes are colored in white. Genes encoding new tailoring enzymes (i.e. DarF, DarG, and PasC) with still uncharacterized functions are colored collectively in grey
Note. Adapted with permission from “Substrate-controlled catalysis in the ether cross-link-forming radical SAM enzymes,” by Ma S, Xi W, Wang S, Chen H, Guo S, Mo T, et al. J Am Chem Soc. 2023;145:22945–53 (https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.3c04355). © 2023 American Chemical Society.
These bioinformatic analyses have suggested an intriguing substrate-controlled catalysis in DarE and PasB, during which these enzymes catalyze ether crosslink formation upon the Ω1-X2-Ω3 substrate motif and C-C crosslink formation upon an Ω1-X2-X3 substrate motif (Figure 1B) [42]. Such a proposal is supported by a mutagenesis effort, in which a DarA Ω3-to-X3 mutant (i.e. DarA-W1K) was converted to a product featuring an eastern C-C crosslink (instead of the original ether crosslink) by DarE [42]. Furthermore, comprehensive substrate-activity investigations on PasB have also demonstrated Ω1-X2-Ω3 and Ω1-X2-X3 substrate motifs direct the formation of ether crosslink and C-C crosslink, respectively, suggesting substrate-controlled catalysis is likely ubiquitous in other rSAM enzymes within this unique sequence-function space. This unusual catalytic property likely results from the distinct stability of the Ω3/X3-Cβ radical intermediates generated from rSAM chemistry. Moreover, these discoveries have suggested that the distinct use of Trp-C7 or C6 for the formation of different crosslinks in darobactin A is likely a compromise resulting from the preorganization of a reaction intermediate in the same enzyme active site, in which 14-membered cyclophane was uniformly formed regardless of the chemical nature of crosslink [42].
Recently, parallel research has comprehensively dissected the substrate-activity relationship in DarE catalysis by using a panel of DarA variants resulting from saturating mutagenesis, which has also pointed to the conclusion that DarE-catalyzed reaction is indeed under substrate-control [55]. Quantum mechanical calculation of the plausible DarA biosynthetic intermediates has demonstrated the distinct stability of the Ω3/X3-Cβ radical intermediates controls the ether/C-C crosslink formation, respectively [55]. Molecular docking studies demonstrate the different preferences of Trp-indole regio-selectivity during ether/C-C crosslink installation [55].
The O2-dependent ether crosslink and the substrate-controlled cyclophane chemotypes have enabled a mechanistic hypothesis for the unusual biscyclophane formation in darobactin A detailed in references [42, 51, 55]. The dAdo radical generated at the rSAM (4Fe-4S) cluster of DarE abstracts the pro-R Hβ of Trp3 to afford a Trp3-Cβ radical. Likely stabilized by radical delocalization in the aromatic moiety, the Trp3-Cβ radical undergoes an intermolecular reaction with O2, and the resulting intermediate attacks on Trp1 to furnish the western ether crosslink. The second dAdo radical generated at the rSAM (4Fe-4S) cluster of DarE then abstracts the pro-R Hβ of Lys5 to afford a Lys5-Cβ radical. In contrast to the Trp3-Cβ radical that is stable enough for coupling with O2, this radical directly adds to the Trp1 to afford the eastern C-C crosslink. Although further studies await to examine in detail the many aspects of the proposed mechanism, the snapshots of its unusual enzymology gained thus far have clearly demonstrated how DarE creates chemically and biosynthetically unprecedented peptide cyclophanes.
Concomitant to the discovery of darobactin A, a series of darobactin A analogs (e.g., darobactin B-F) containing substitutions on non-crosslinked residues have been revealed in various γ-proteobacteria, including strains of the genera Photorhabdus, Yersinia, and Vibrio (Figure 2B) [29]. Due to their high structural similarities in the characteristic biscyclophane scaffold, these analogs in general exhibit antibacterial activities and modes of action in a way similar to darobactin A [29, 56, 57]. Notably, darobactin B, an analog with a heptapeptide sequence WNWTKRF, displays even more potent activity than darobactin A against several clinically important strains, including Acinetobacter baumannii isolates [57]. These facts have demonstrated the non-crosslinked residues within the biscyclophane scaffold have a significant impact on biological activity [57]. Precursor engineering efforts for non-natural darobactin production allow the systematic assessment of the contribution of different non-crosslinked residues to antibacterial activity and results in non-natural darobactins with more potent activities [58–60], notably including darobactin 22 [59], which has a heptapeptide sequence WNWTKRW and possesses 128-fold increased activity as compared to darobactin A.
More recently, novel darobactin A derivatives harboring Trp1-bromination or Lys5-dehydration, or both, namely bromodarobactin A, dehydrodarobactin A, and bromodehydrodarobactin A, have been identified from marine Pseudoalteromonas luteoviolacea (Figure 2C) [61]. Likely owing to their additional modifications, these derivatives exhibit solubility and plasma protein binding ability different from darobactin A and are found more active than darobactin A. The BGCs of these variants contain additional biosynthetic proteins DarFGH, among which DarH was verified to act as a flavin-dependent halogenase (PF13738) with a novel structural fold for Trp1-C5 bromination [61]. DarF belongs to mod_HExxH family (TIGR04267) that is suggestive of peptidase activity while DarG has been annotated as a transporter-related (TIGR02204) protein [42, 61]. However, the exact functions of the two proteins remain unknown and require further studies. It also remains to be investigated how the Lys5 in these variants is desaturated.
Besides the darobactin A and its variants, the BGCs of other ether crosslinked three-residue cyclophane-containing RiPP (daropeptide) are also rich in nature (Figure 2B) [41, 42]. One prevalent daropeptide subfamily, dubbed as photorhaptin owing to their exclusive occurrence in strains of the genus Photorhabdus, are derived from precursor peptides with single three-residue substrate motif Ω1-X2-Ω3. Functional characterization of one such BGC (pas) from Photorhabdus asymbiotica revealed that the rSAM enzyme PasB installs a single ether crosslink in the precursor peptide PasA in an atroposelective manner [42]. Moreover, the unknown E. coli proteases can also process the modified PasA in vivo to release photorhaptin A, the ether crosslink-containing pentapeptide (Figure 2C). Because photorhaptin BGCs invariantly encode a general control non-repressible 5 (GCN5)-related N-acetyltransferases (GNAT) family acyltransferase [62], e.g., PasC [42], with as-yet unknown function, photorhaptin A may be further modified by PasC and the structure and bioactivity of the mature product awaits further investigation.
In addition to photorhaptin, orphan daropeptides with precursor peptides harboring two Ω1-X2-Ω3 substrate motifs have been found across diverse symbiotic or terrestrial bacteria, including Rhizobium, Sodalis, Devosia, Myxococcus and Martelella et al (Figure 2B) [42]. A preliminary study on an orphan daropeptide BGC (rsc) with discrete substrate motifs (i.e. orphan daropeptide type 1) (Figure 2B) from Rhizobium sullae revealed that the rSAM enzyme RscB installs two ether crosslinks upon precursor peptide RscA, which likely proceeds in a two-step distributive manner and in a direction from C-terminal to N-terminal (Figure 2C) [42]. Because detailed structure elucidation of the RscB product was impeded by the extremely low yield of conversion, further investigation is needed for the characterization of the mature product derived from rsc and evaluation of its biological function.
In addition, orphan daropeptides with fused Ω1-X2-Ω3 substrate motifs (i.e. orphan daropeptide type 2) (Figure 2B) have been predicted from the compiled dataset from the genome mining study [42]. Based on the established substrate-activity relationship of daropeptide maturase (Figure 1B), these novel daropeptides are expected to harbor biscyclophane scaffold that resembles darobactin but is solely furnished by two ether crosslinks instead of C-C crosslink. Despite such a natural product remains currently being uncharacterized, a recent study has demonstrated the production of a darobactin variant that features diether crosslink-forged biscyclophane through DarA mutagenesis [55]. These results have suggested the broad diversity of ring topology enabled by daropeptide maturares [55].
The discovery of hidden daropeptide maturases from different clades (Figure 2A) also provides a fascinating opportunity to investigate their mechanism of catalysis through comparative analysis. Mechanistic studies on the new daropeptide maturase PasB revealed that it also introduces ether crosslink from O2, suggesting the ability of O2 utilization for ether crosslink construction is universal in all daropeptide maturases [42]. Meanwhile, the fact that photorhaptin and the RscB product do not contain C-C crosslink as found in darobactin but are solely modified with one or two ether crosslinks, led to the finding of the substrate-controlled catalysis in these rSAM enzymes [42], as has also been discussed in the previous section. The substrate scope of DarE and PasB is broad, which can catalyze ether crosslinks in diverse Ω1-X2-Ω3-type substrate motifs, and C-C crosslinks in diverse Ω1-X2-X3-type substrate motifs [42, 55]. These results suggest the intrinsically high substrate tolerance of these enzymes, setting the stage for synthesizing macrocyclic peptides bearing diverse cyclophanes [42, 55]. Furthermore, inspired by the close phylogenic relationship between daropeptide maturase and anSMEs (Figure 2A), PasB has been verified to act on a Ω1-X2-S3 substrate motif to produce a Ser-derived FGly residue [42], an aldehyde-containing amino acid amenable to bioorthogonal chemistry-enabled late-stage diversification [63, 64]. Similar Ser oxidation activity was also observed for DarE [55]. These results showcase the remarkably diverse post-translational modification enabled by daropeptide maturaes, which can be harnessed for future chemical biology and biotechnology applications in terms of polypeptide structural diversification.
Because of their unique structural features and biochemical properties, cyclophane-containing peptides have been historically a focal point for synthetic chemists and pharmacologists [3, 9, 65]. Various synthetic methodologies have been developed for or applied to peptide cyclophane synthesis, with the palladium-catalyzed directing group-assisted intramolecular Csp3-H arylation reactions being a general strategy [66, 67], and Larock heteroannulation most frequently applied in the case of Trp-centered peptide cyclophane [68], including the total synthesis of darobactin [69, 70]. Nevertheless, the strained nature of peptide cyclophanes has imposed synthetic challenges in terms of chemo-/stereo-/regio-selectivities within the complex polypeptide scaffolds, rendering the canonical C-H functionalization route for cyclophane construction chemically challenging. The discovery of cyclophane-containing peptide natural products not only provides novel bioactive compounds with intricate cyclophane structures but also unveils new biocatalysts well-suited for peptide cyclophane construction, providing an alternative way to access these synthetically challenging peptide macrocycles [3].
With the advance of genome sequencing techniques and the advent of new genome mining tools, RiPPs constitute a rapidly emerging superfamily of peptide natural products that have drawn particular attention in recent decades, particularly in the context of in silico BGC discovery and post-translational enzymology studies [71–73]. Perhaps the most distinguished feature in RiPP biosynthesis as compared to NRPs lies in their genetically encoded peptide substrates and impressively diverse peptide modifications installed by various trans-acting and catalytically promiscuous biosynthetic enzymes. These merits permit a high level of biosynthetic flexibility and adaptability that make RiPP biosynthetic systems an ideal chemoenzymatic platform for devising structurally complex polypeptides [74]. When combined with genetic code expansion techniques or high-throughput screening (HTS) methods, such as saturating mutagenesis and various genetically encoded library (GEL) techniques, RiPP biosynthetic chemistries hold great promise in peptide bioengineering and the discovery of bioactive macrocyclic peptides [25, 26, 75–77].
In recent years, two dominant biosynthetic origins of bioactive cyclophane-containing RiPPs have emerged, which are distinguished by their chemotypes and biosynthetic origins [9, 78, 79]. One is the Csp2-Csp2 (i.e. biaryl) crosslinked cyclophane [78], which is typically introduced by cytochrome P450 enzymes, while the other is the Csp2-Csp3 (i.e. monoaryl) crosslinked cyclophanes [9, 79], typically introduced by the rSAM enzymes. In addition, crosslinks involving endogenous heteroatom, e.g., Csp2-N or Csp3-N crosslink [11, 18, 19, 80], have also been found, demonstrating the immense biosynthetic potential of the RiPP cyclophane synthases. As a recent addition to the already impressive collection of cyclophanes, daropeptides, characterized by their unique ether (i.e. Csp2-O-Csp3) crosslinks, have undoubtedly marked a brand-new chemical space in peptide cyclophane. The discovery of daropeptides has also expanded the scope of rSAM enzymology by demonstrating the ability to utilize exogenous O2 [51]. Furthermore, the substrate-controlled catalysis in the daropeptide maturase demonstrates the great opportunity to manipulate cyclophane chemotypes through RiPP precursor engineering [53].
Due to its catalytic robustness in mediating C-H bond activation reactions, the P450 enzymes are among the most studied and promising biocatalysts that have been commonly used for various biotechnological applications, including enzyme engineering and biocatalytic synthesis. In contrast, the rSAM enzymes are comparatively intractable owing to their O2-sensitivity, often low catalytic turnover number, and difficulties in rSAM enzyme engineering. However, in light of the vast diversity of reactions catalyzed by rSAM enzymes that have passed through the natural selection barriers [47], as illustrated herein by the discovery of rSAM oxygenases in daropeptide maturation, one may expect the biotechnological applications of rSAM enzymology in RiPP engineering to happen soon.
Despite these progresses, the unusual catalytic pathway of these rSAM oxygenases may hinder their broader biocatalytic applications in peptide engineering, unless a more deepened and comprehensive understanding is achieved. These include but are not limited to 1) the detailed mechanisms by which the O2 is specifically incorporated into the Ω1-X2-Ω3 (not Ω1-X2-X3) substrate for ether crosslink construction, 2) the detailed mechanisms by which the enzymes integrate O2 into the catalytic cycle, 3) tolerance and the ways for maintenance of O2 concentration in the biocatalytic synthesis of these enzymes, 4) the precise mode of recognition through which these enzymes recruit and interact with the polypeptide substrate, including identifying the minimal elements (e.g., minimal substrate sequence and length) required for cyclophane installation, and 5) the essential factors that may result in the ability of daropeptide maturaes to form multiple cyclophane rings, and the ways to devise polycyclophane units with desired ring topology. Given the pioneering efforts in engineering daropeptide derivatives for enhanced bioactivity [57–60], the established total synthesis methodology [68, 69], and the availability of high-throughput BAM assay [81], it can be expected that further manipulation of daropeptide maturases via substrate-controlled catalysis and protein engineering may facilitate the establishment of new platforms to generate chemically and topologically diverse peptide cyclophanes with novel bioactivities (e.g., more potent BAM inhibitor), utilizing chemoenzymatic synthesis and HTS techniques.
3-CyFEs: three-residue cyclophane-forming enzymes
anSMEs: anaerobic sulfatase maturating enzymes
BAM: β-barrel assembly machinery
BGC: biosynthetic gene cluster
C-C: carbon-carbon
dAdo: 5’-deoxyadenosyl
FGly: formylglycine
O2: oxygen
RiPP: ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide
rSAM: radical S-adenosylmethionine
SM: Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing. SG: Writing—review & editing. WD and QZ: Conceptualization, Writing—review & editing. All authors contributed to manuscript revision, discussion, and approved the submitted version.
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
This work is supported by grants from the National Key Research and Development Program [2018Y F A0900402, 2021YFA0910501]; the National Natural Science Foundation of China [31870050, 32270070, U22A20451]; the funding of innovative research team of high-level local universities in Shanghai and a key laboratory program of the Education Commission of Shanghai Municipality [ZDSYS14005]; West Light Foundation of the Chinese Academy of Sciences [xbzg-zdsys-202105]. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Copyright: © The Author(s) 2024. This is an Open Access article licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, for any purpose, even commercially, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Qiushi Chen ... Xuechen Li
Ping Zeng ... Lanhua Yi
Shoko Tanaka ... Kohei Sato
Feliciana Real-Fernandez ... Paolo Rovero
Chloé O. Sebilleau, Steven J. Sucheck
Qian Zhang ... Chunqiu Zhang
Yanyan Liao, Xuefeng Jiang
Qian Wang ... Shiyu Chen
Jarais Fontaine, Jianfeng Cai
Oscar Noya ... Sandra Losada