From botany to bedside: a review of the health benefits of Lycium barbarum as a functional food
Native to East Asia and predominantly cultivated in regions such as the Ningxia Hui and Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Regions of China,
Lycium barbarum (
L. barbarum), commonly known as goji berry, has
[...] Read more.
Native to East Asia and predominantly cultivated in regions such as the Ningxia Hui and Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Regions of China, Lycium barbarum (L. barbarum), commonly known as goji berry, has a long history in traditional medicine and is gaining recognition in contemporary health research. This review provides a comprehensive exploration of its botanical characteristics, pharmacokinetics, and safety, alongside a critical evaluation of human clinical studies investigating its therapeutic potential. Key health benefits include immune modulation, antioxidative effects, mental health support, ocular health preservation, and metabolic and cardiovascular regulation. Furthermore, its role in addressing age-related macular degeneration and chronic conditions such as cancer and metabolic syndrome is highlighted. The bioactivity of L. barbarum is attributed to its rich composition of polysaccharides, carotenoids, flavonoids, and other bioactive compounds, which exhibit anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and metabolic-regulating properties. This review also examines the safety profile of L. barbarum, considering its side effects, toxicity, potential contamination, and interactions with medications, emphasising the importance of balancing its health-promoting properties with cautious consumption. Despite promising findings, gaps in the evidence base, including the need for larger, long-term, and rigorously controlled trials, remain significant barriers to clinical translation. By integrating traditional medicinal knowledge with modern scientific insights, this review underscores L. barbarum’s potential as a functional food and therapeutic agent. Its unique pharmacological properties and broad applicability position it as a valuable tool for health promotion and disease prevention, while highlighting areas requiring further research to optimise its safe and effective use.
Alois Berisha ... Tao Zhang
View:126
Download:12
Times Cited: 0
Native to East Asia and predominantly cultivated in regions such as the Ningxia Hui and Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Regions of China, Lycium barbarum (L. barbarum), commonly known as goji berry, has a long history in traditional medicine and is gaining recognition in contemporary health research. This review provides a comprehensive exploration of its botanical characteristics, pharmacokinetics, and safety, alongside a critical evaluation of human clinical studies investigating its therapeutic potential. Key health benefits include immune modulation, antioxidative effects, mental health support, ocular health preservation, and metabolic and cardiovascular regulation. Furthermore, its role in addressing age-related macular degeneration and chronic conditions such as cancer and metabolic syndrome is highlighted. The bioactivity of L. barbarum is attributed to its rich composition of polysaccharides, carotenoids, flavonoids, and other bioactive compounds, which exhibit anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and metabolic-regulating properties. This review also examines the safety profile of L. barbarum, considering its side effects, toxicity, potential contamination, and interactions with medications, emphasising the importance of balancing its health-promoting properties with cautious consumption. Despite promising findings, gaps in the evidence base, including the need for larger, long-term, and rigorously controlled trials, remain significant barriers to clinical translation. By integrating traditional medicinal knowledge with modern scientific insights, this review underscores L. barbarum’s potential as a functional food and therapeutic agent. Its unique pharmacological properties and broad applicability position it as a valuable tool for health promotion and disease prevention, while highlighting areas requiring further research to optimise its safe and effective use.
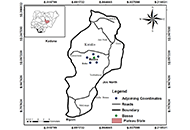 Carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic human health risk assessment of some vegetables irrigated with wastewater in Jos, Plateau State, NigeriaOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: There is growing concern on the use of contaminated and untreated water from industrial discharge for irrigation during the dry season farming in many parts of northern Nigeria. Industries e [...] Read more.Usman Bawa, Ahmad AbdulHameedPublished: January 22, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101068
Carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic human health risk assessment of some vegetables irrigated with wastewater in Jos, Plateau State, NigeriaOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: There is growing concern on the use of contaminated and untreated water from industrial discharge for irrigation during the dry season farming in many parts of northern Nigeria. Industries e [...] Read more.Usman Bawa, Ahmad AbdulHameedPublished: January 22, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101068 The challenges associated with a ketogenic diet: a narrative reviewOpen AccessReviewThe so-called ‘ketogenic diet’ aimed to limit energy derived from carbohydrates, has many variations which cause confusion in the literature and beyond. For ‘intractable’ epilepsy (when seiz [...] Read more.Xin Qi, Richard TesterPublished: January 16, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101065
The challenges associated with a ketogenic diet: a narrative reviewOpen AccessReviewThe so-called ‘ketogenic diet’ aimed to limit energy derived from carbohydrates, has many variations which cause confusion in the literature and beyond. For ‘intractable’ epilepsy (when seiz [...] Read more.Xin Qi, Richard TesterPublished: January 16, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101065 Spent coffee grounds as a sustainable coffee flavouring ingredient in muffinsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: United Nations calls for actions to meet future challenges, and industries and governments need to look for new solutions. Coffee is one of the largest industries in the world, and spent cof [...] Read more.Sina Breian Solberg, Svein Øivind SolbergPublished: January 17, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101066
Spent coffee grounds as a sustainable coffee flavouring ingredient in muffinsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: United Nations calls for actions to meet future challenges, and industries and governments need to look for new solutions. Coffee is one of the largest industries in the world, and spent cof [...] Read more.Sina Breian Solberg, Svein Øivind SolbergPublished: January 17, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101066 Assessing the price effects of African swine fever in the China marketOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: African swine fever is a viral disease that has affected the pig business in several nations worldwide. One of the most serious diseases affecting the hog business significantly influences C [...] Read more.Melissza SallingPublished: January 15, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101064
Assessing the price effects of African swine fever in the China marketOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: African swine fever is a viral disease that has affected the pig business in several nations worldwide. One of the most serious diseases affecting the hog business significantly influences C [...] Read more.Melissza SallingPublished: January 15, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101064 From botany to bedside: a review of the health benefits of Lycium barbarum as a functional foodOpen AccessReviewNative to East Asia and predominantly cultivated in regions such as the Ningxia Hui and Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Regions of China, Lycium barbarum (L. barbarum), commonly known as goji berry, has [...] Read more.Alois Berisha ... Tao ZhangPublished: January 25, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101070
From botany to bedside: a review of the health benefits of Lycium barbarum as a functional foodOpen AccessReviewNative to East Asia and predominantly cultivated in regions such as the Ningxia Hui and Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Regions of China, Lycium barbarum (L. barbarum), commonly known as goji berry, has [...] Read more.Alois Berisha ... Tao ZhangPublished: January 25, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101070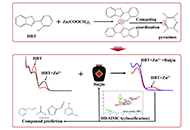 Rapid identification of high-temperature Daqu Baijiu with the same aroma type by UV-VIS sensor of HBT combined with Zn2+Open AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Baijiu adulteration has always been a hot spot of social concern, especially high-temperature Daqu Baijiu, because of its better flavor quality and high value, it faces a challenge from ille [...] Read more.Yanmei Zhu ... Haiyan FuPublished: January 22, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101067
Rapid identification of high-temperature Daqu Baijiu with the same aroma type by UV-VIS sensor of HBT combined with Zn2+Open AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Baijiu adulteration has always been a hot spot of social concern, especially high-temperature Daqu Baijiu, because of its better flavor quality and high value, it faces a challenge from ille [...] Read more.Yanmei Zhu ... Haiyan FuPublished: January 22, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101067 Sustainable alternative of palm wine analogue from different tiger nut milk-sugar syrup blends for local productionOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The unfermented pale-yellow exudates (“palm sap”) emerge from tapped unopened spathe of mostly oil palm (Elaeis guineensis) and raphia palm (Raphia hookeri). Besides, tiger nut milk (Kun [...] Read more.Adindu O. Onyeodili ... Raquel P.F. GuinéPublished: January 24, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101069
Sustainable alternative of palm wine analogue from different tiger nut milk-sugar syrup blends for local productionOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The unfermented pale-yellow exudates (“palm sap”) emerge from tapped unopened spathe of mostly oil palm (Elaeis guineensis) and raphia palm (Raphia hookeri). Besides, tiger nut milk (Kun [...] Read more.Adindu O. Onyeodili ... Raquel P.F. GuinéPublished: January 24, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101069