Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Medicine and USF Health Byrd Alzheimer’s Research Institute, Morsani College of Medicine, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL 33612, USA
Email: vuversky@usf.edu
ORCID: https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4037-5857
Explor Immunol. 2022;2:731–748 DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ei.2022.00079
Received: June 01, 2022 Accepted: August 05, 2022 Published: October 31, 2022
Academic Editor: Dominique J. Charron, Hospital Saint Louis, France
The article belongs to the special issue Old and New Paradigms in Viral Vaccinology
The absence of advancement in finding efficient vaccines for several human viruses, such as hepatitis C virus (HCV), human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1), and herpes simplex viruses (HSVs) despite 30, 40, and even 60 years of research, respectively, is unnerving. Among objective reasons for such failure are the highly glycosylated nature of proteins used as primary vaccine targets against these viruses and the presence of neotopes and cryptotopes, as well as high mutation rates of the RNA viruses HCV and HIV-1 and the capability to establish latency by HSVs. However, the lack of success in utilization of the structure-based reverse vaccinology for these viruses is likely to be related to the presence of highly flexible and intrinsically disordered regions in human antibodies (Abs) and the major immunogens of HIV-1, HCV, and HSVs, their surface glycoproteins. This clearly calls for moving from the rational structure-based vaccinology to the unstructural vaccinology based on the utilization of tools designed for the analysis of disordered and flexible proteins, while looking at intrinsically disordered viral antigens and their interactions with intrinsically disordered/flexible Abs.
Among the various techniques utilized by rational vaccine design the special place is given to the structure-based reverse vaccinology [1, 2] that uses information from the crystallographic structure of a complex between a neutralizing monoclonal antibody (mAb) and a complementary epitope to rationally design better antigens capable of acting as vaccine immunogens. This computational methodology, which utilizes docking and molecular modeling, is deeply rooted in the knowledge of the high-resolution structures of the pathogenic proteins and the antigen-antibody (Ab) complexes and is expected to reconstruct epitopes capable of mAb binding. In the corresponding experiments, a process similar to the rational drug design is used, where the structure of a highly neutralizing mAb serves as a template, to which modeled epitopes are docked to design molecules with high potential for the selective binding to and specific inhibition of the biological activity of the mAb [3]. It is expected that such computationally reconstructed antigens, which are “rationally” designed to fit the mAb, would have desired antigenic properties and induce polyclonal Abs with the neutralizing potential similar to that of the mAb used as a template for designing the antigen.
In an alternative approach, instead of rationally designing epitopes using docking-based structural modeling, computational approaches are used to predict potential antigens that are located on the surface of the pathogens and that could serve as vaccine candidates. Since it is likely that antigens are present in any protein from a pathogenic microorganism, specialized computational tools can be used to predict them. Based on these premises, the corresponding in silico techniques are used to search entire proteomes of query microbial pathogens (bacteria, fungi, and viruses) for potential antigens [1, 2]. Thus found potent antigens are further studied by the means of structural vaccinology to find and characterize potential structural epitopes. A crucial step that follows these computational analyses is experimental validation of the ability of found antigens to elicit immunity in animal models [4, 5].
There are many examples of the successful utilization of the reverse vaccinology tools for the identification of the novel vaccine antigens and for the improvement of the safety and antigenicity of vaccine antigens [1–5]. Among those are the highly potent vaccine candidates designed using the detailed structural knowledge of the viral fusion mechanisms and structural analysis of the glycoprotein from the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) [6] and the spike protein from the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) [7]. The structure-guided design and high-throughput in vitro assays were successfully used to discover the broadly neutralizing Abs (bNAbs) against the dengue envelope protein and influenza hemagglutinin stalk [8–10]. Linear and discontinuous human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) epitopes grafted onto the computationally designed scaffolds represent an impressive illustration of the successful utilization of the rational structure-based vaccinology, where structural information pertaining to the existing bNAbs-antigen complexes was utilized in the development of the designer antigens [11, 12]. A culmination of the success of this strategy was given by the remarkable speed of the vaccine development against the causative agent of current coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), where the fertile soil was created by the aggregation of three decades of scientific research in the fields of reverse vaccinology, structural vaccinology, synthetic biology, and vaccine adjuvants [13, 14].
However, despite many success stories, these promising technologies have serious limitations. The founding principles of the structure-based rational design in general and the rational structural vaccinology in particular are rooted in the consideration of protein-ligand, protein-nucleic acid, protein-protein, and antigen-Ab complexes as rigid, motionless structures with steric “lock-and-key”-type complementarity to each other. However, this is clearly an oversimplification, as biological molecules are not akin to crystals, being instead pliable entities characterized by conformational fluctuations of different amplitudes happening at multiple time-scales. Therefore, protein-based interactions rely on the mutual adjustments of the partners via coordinated induced complementarity and fit; i.e., are better described by the flexible keys and adjustable locks model [15]. Therefore, binding site is not fixed in space and time, being instead a relational entity. This means that the specific features of a binding site are not solely defined by the independently determined unique/rigid three-dimensional (3D)-structure of a protein, but show relational association with a particular partner. In other words, binding sites of all the partners involved in the complex formation are engaged in mutual tuning, the scale of which can vary from rather minimal structural adjustments to global binding-induced folding. Unfortunately, these important aspects are mostly ignored in structure-based rational design, and rational structural vaccinology continues to rely on known 3D-structures of Abs and antigens. However, as it is shown in this article, many antigens are not suitable for such structure-based analysis as they either contain noticeable levels of intrinsic disorder or at least are characterized by high conformational plasticity. Furthermore, antigen-binding sites of Abs are flexible/disordered themselves. These important observations clearly indicate that intrinsic disorder and structural flexibility of antigens and Abs cannot be ignored and future vaccine design should include techniques of unstructural biology. It is very likely that the past inability (or unwillingness) to consider and apply these aspects of unstructural vaccinology is at least in part responsible for the absence of advancement in finding efficient vaccines for several human viruses, such as hepatitis C virus (HCV), HIV-1, and herpes simplex viruses (HSVs) despite 30, 40, and even 60 years of research, respectively. To illustrate these points, this article represents an overview of the intrinsic disorder status of the surface glycoproteins, which are considered as major antigens of these three viruses, and discusses conformational flexibility of Abs.
HIV-1, a causative agent of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), is a small enveloped RNA virus with genome of 9.75 kb. It belongs to the genus Lentivirus within the family of Retroviridae, subfamily Orthoretrovirinae [16]. HIV genome consists of two copies of noncovalently linked, unspliced, positive-sense single-stranded RNAs (ssRNA+) that contains nine genes encoding fifteen viral proteins [17] which are enclosed within the core of the virus particle. The surface of the HIV-1 is decorated by 14 trimeric spikes formed by the envelope protein (Env) heterodimers of the gp41 and gp120 glycoproteins, which originate as a result of the cleavage of the full-length gp160 protein by a protease and which serve as the major immunogens of HIV-1 [18, 19].
The HIV/AIDS epidemic continues to be one of the major global health threats, and in 2020, 38 million people were living with HIV, 1.5 million people became newly infected with HIV, and 680,000 people died from AIDS-related diseases [20]. Although significant progress is reached in the development of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) that can reduce the risk of AIDS and transmission of HIV [21], the medications are expensive, and access to treatment remains a substantial barrier, especially in low- and medium-income countries. Therefore, a prophylactic vaccine represents an important means in attempts to end the epidemics. However, the search for the efficient anti-HIV vaccine utilizing various approaches including structure-based reverse vaccinology has spanned nearly four decades without much success [22–28], although several broadly neutralizing anti-HIV-1 Abs were found [29, 30].
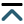
The high glycosylation levels of the HIV surface are taken as one of the most probable explanations for these failures to find an efficient anti-HIV vaccine. In fact, HIV is known as the most glycosylated virus [31], and glycans constitute half of the mass of the only surface HIV-1 protein, the Env protein [32]. This is illustrated by Figure 1A and 1B showing the extent of the dynamic glycan shield of this protein, which efficiently covers almost the entire protein, making it almost inaccessible to neutralizing Abs [33]. As discussed below (see section HCV), similar situation is observed for the HCV envelope glycoproteins E1 and E2, which are also heavily glycosylated (see Figure 1C, 1D, and 1E).
Dynamic glycan shield of viral surface glycoproteins. (A) Single snapshot of the modeled natively glycosylated structure of the soluble HIV-1 Env trimer, BG505 SOSIP.664 gp140, with each glycan taking up a particular conformation; (B) cumulative shielding effect over time due to the dynamic nature of the glycans. Plot shows one hundred randomly selected models from the 1,000-structure ensemble (plots A and B are modified from [33]); (C) schematic representation of the N-glycosylation sites on HCV envelope glycoproteins E1 and E2, where the relative position of the glycosylation site in the sequence is indicated with the letter “N” followed by a number. The numbers in brackets represent the position of the glycosylation sites according to the HCV genotype 1a consensus sequence (GenBank: AF009606.1). Sites conserved across all HCV genotypes are shown in red. Genotype-specific E1 glycans are shown in orange. E2 N-glycans are conserved across most genotypes, with the exception of genotype 1b (E2N5) and genotypes 3 and 6 (E2N7), which are shown in yellow. (D) and (E) glycan shielding of the HCV E2 glycoprotein. N-glycans are extensively shielding the CD81 binding loop and antigenic domains of E2 (D), whereas there are fewer shielding effects on the non-antigenic face of E2 (E). (plots C, D, and E are adopted from [34]). HVR1: Hyper variable region 1; CD81: CD81 binding loop; TMD: transmembrane domain
Note. Figure 1A and 1B are adapted from “Quantification of the resilience and vulnerability of HIV-1 native glycan shield at atomistic detail,” by Chakraborty S, Berndsen ZT, Hengartner NW, Korber BT, Ward AB, Gnanakaran S. iScience. 2020;23:101836 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2020.101836). CC BY; figure 1C, 1D and 1E are adapted from “Hepatitis C virus glycan-dependent interactions and the potential for novel preventative strategies,” by LeBlanc EV, Kim Y, Capicciotti CJ, Colpitts CC. Pathogens. 2021;10:685 (https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10060685). CC BY.
Another reason for the difficulty to develop a vaccine is the presence of neotopes (or neo-antigenic sites, which do not exist in the viral protein monomers but are formed as a result of conformational changes induced in the protein by the intersubunit interactions or some other means) in the HIV-1 gp120 trimers, where they are rather common [35–43]. There are several anti-HIV-1 Abs that can recognize neotopes. An illustrative example of such Abs is given by a highly strain-specific mAb 2902 Ab directed to a neotope of the Env protein [44, 45], which uses its 21-residue-long complementarity determining region (CDR) H3 loop (one of the six CDRs that form paratopes of Abs, see below) protruding from the paratope surface to recognize a neotope comprising portions of the V2 and V3 loops of the Env protein [46, 47]. Among other examples of Env neotope recognizing Abs are PG9 and PG16 mAbs, which also recognize a V2/V3 neotope and are capable of neutralization of ∼80% of primary HIV-1 isolates [40, 42, 48], with the neotope recognized by PG9 representing a β-strand and two glycans organized in a canyon-like structure, which accommodates the long CDR H3 loop of mAb PG9 [49].
Importantly, pathogens might also contain cryptotopes or cryptic epitopes, which are potential antigenic sites hidden by surface subunits in the quaternary structure of protein complexes or within the 3D-structures, or epitopes normally existing in a low-affinity binding conformation. Such cryptotopes become displayed only after the dissociation of protein complexes or due to structural changes in a protein. An example of the cryptotope in HIV-1 is given by a capsid protein p24, for which it was shown that the affinity of an anti-p24 mAb can be dramatically increased by chemical modification of the lysine residues of rp24 with different amounts of maleic anhydride [50]. Another example of HIV-1 cryptotopes is given by the gp120 neutralization epitopes, which become exposed upon gp120-CD4 binding [51]. Despite the fact that B-cell response to neotopes and cryptotopes may be of high immunological relevance [52, 53], unfortunately, neither neotopes nor cryptotopes attracted sufficient attention from researchers. As a result, only a few cryptotopes have been identified so far on flaviviruses [54], HCV [55], HIV [51], and influenza viruses [56, 57]. Furthermore, as it was rightly pointed out [36], the utilization of structure-based design for finding or reconstructing neotopes (and, as a matter of fact, for finding or reconstructing cryptotopes) is challenging if not impossible task, as these would involve working with the highly dynamic systems, which are transiently populated and accessible only for a limited time.
Other difficulties in the search for the HIV vaccine were attributed to the high mutation rate of this virus due to the utilization of the error-prone polymerase for replication [26–28]. As a result, infected persons are characterized by a high degree of HIV genetic variability and typically contain a complex mixture of heterogeneous strains, “quasispecies” [58]. Finally, in the HIV infection, the immune response is mostly generated against the highly variable immunodominant epitopes, such as the V1, V2, and V3 loops of the envelope glycoprotein gp160, and such immune response does not provide protection against diverse HIV strains [4].
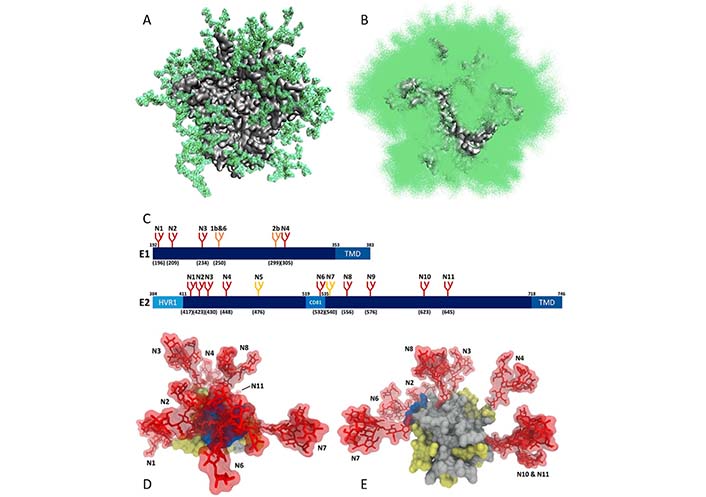
What is completely neglected in these considerations is the potential role of intrinsic disorder and structural flexibility, which can further contribute to the ability of HIV-1 to evade the immune response by generating another level of the flexible shield in this virus. The disorder profile of the envelope glycoprotein gp160 from the HIV-1 group M subtype B (isolate HXB2) is shown in Figure 2A. This protein, after the removal of the 33-residue-long signal peptide and before the furin-mediated cleavage in the trans-Golgi to generate the surface protein gp120 (residues 1–479) and transmembrane protein gp41 (residues 480–824), exists as an 824-residue-long surface protein.
Intrinsic disorder predisposition of HIV-1 surface glycoprotein gp160 (A) and the HCV glycoproteins E2 (B) and E1 (C). Disorder profiles are generated using the RIDAO platform designed to aggregate the results from a number of well-known disorder predictors, such as PONDR® VL3 [59], PONDR® VLXT [60], PONDR® FIT [61], PONDR® VLS2 [62], IUPred2 (Short), and IUPred2 (Long) [63–65]. Dotted lines show the disordered threshold of 0.5 that separates ordered residues [predicted disorder scores (PDS) < 0.5] and intrinsically disordered residues (PDS ≥ 0.5). Based on their PDS values, ordered residues are further subdivided to highly ordered [PDS (0.15) and flexible (0.15 ≤ PDS < 0.5)]. Locations of functional regions and sites of N-glycosylation in all three proteins are shown by colored boxes and dark brown ticks. σMDP: mean disorder prediction; CD4: CD4-binding loop; IGH526: region capable of binding to the cross-neutralizing Ab IGH526; IUP2(L): IUPred2 (long); IUP2(S): IUPred2 (short); PONDR-FIT: PONDR® FIT; V1, V2, V3, V4, and V5: variable regions V1 through V5 of the gp120; VL3: PONDR® VL3; VLXT: PONDR® VLXT; VSL2B: PONDR® VSL2
Glycoprotein gp120 contains variable regions V1 through V5 (residues 98–122, 123–160, 260–293, 348–373, and 416–426), which are the most genetically diverse regions of the entire HIV-1 genome, as well as a CD4-binding loop (residues 327–337). As shown in Figure 2A, all these functional regions of gp120 as well as the site of the gp160 cleavage by cellular furin or furin-like proteases and all N-linked glycosylation sites are located within or in the close proximity to the intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs). This indicates that intrinsic disorder is crucial for the function of gp120 and gp41. This also emphasizes that the local disorder of the polypeptide backbone, being combined with the structural flexibility of glycans, might generate a dramatic increase in the efficiency and space coverage of the resulting glycan-IDR shield. In other words, the impressive flexibility and space coverage of the glycan-only shield proposed based on the molecular dynamics simulation experiments [33] are noticeably underestimated, since the local protein flexibility and disorder were not taken into account.
Ignoring intrinsic disorder further complicates the application of structure-based reverse vaccinology to the development of the gp120-based vaccine. It was pointed out that to generate “crystallizable” variants, various short forms of this protein are typically used instead of the full-length gp120 protein, where some disordered and/or flexible regions are removed [66]. Curiously, even these truncated forms of the gp120 core were shown to be characterized by noticeable structural variability, as between 20% and 30% of each structurally characterized gp120 core form contained some unique structural features, not seen in other forms [66]. All these observations clearly indicate that intrinsic disorder in the viral antigens should be taken into account.
HCV is an enveloped, single-stranded, ssRNA+ virus [67]. This member of the genus Hepacivirus in the family Flaviviridae is a small RNA virus with a 9,600-nucleotide-long genome [68] encoding polyprotein precursor of ∼3,100 amino acids, which is subsequently processed to ten HCV proteins by the action of viral and cellular proteases [69]. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) [70], HCV chronically infects 58 million people worldwide, with about 1.5 million new infections occurring per year. Furthermore, HCV continues to be a leading cause of liver-related mortality worldwide, causing 333,000, 499,000, and 704,000 deaths in 1990, 2010, and 2013, respectively [71–73]. Despite serious efforts of multiple researchers worldwide, a hunt for the vaccines against this virus, which was identified in 1989 (i.e., more than 30 years ago), continues to be mostly unsuccessful. One of the major reasons why the development of an HCV vaccine has proven challenging is given by high genetic diversification of this virus. In fact, one can find seven major HCV genotypes (1–7), each differing by 30% in nucleotide sequence [74], which are further subdivided into 86 subtypes with 15% sequence variation [75]. Most vaccines aiming at raising neutralizing Abs against the HCV target its envelope glycoproteins E1 (or gp35) and E2 (or gp70), which form E1–E2 dimer in the host-derived lipid membrane of the HCV envelope. These transmembrane proteins are heavily glycosylated (see Figure 1C), and Figure 1D and 1E clearly show that the E2 glycoprotein is covered by the dense glycan shield, which makes its potential epitopes poorly accessible to the neutralizing Abs. Furthermore, a hypervariable region of the E2 protein (residues 1–27) is believed to shield the more conserved epitopes of this protein from neutralizing Abs [76]. Importantly, this hypervariable region, as well as N-linked glycosylation sites is predicted to be disordered (see Figure 2B), providing further support to the importance of the conformational flexibility for the efficiency of the glycan-IDR shield. Similarly, in the E1 glycoprotein, sites of the N-linked glycosylation and the antigenic region capable of binding to the cross-neutralizing Ab IGH526 [77] are predicted to be disordered or flexible (see Figure 2C).
HSV-1 and HSV-2 are enveloped viruses from the human Herpesviridae family, which have relatively large, double-stranded, linear DNA genome. This genome is encased within a capsid, contains at least 74 genes, and encodes at least 84 unique proteins [78]. HSV-1 and HSV-2 cause a prevalent sexually transmitted infection, which is manifested in orofacial cold sores, severe ocular disease and blindness, and genital ulcers. As of 2016, 13.2% and 66.6% of the global population aged 15–49 were living with HSV-2 and HSV-1 infections, respectively [79, 80]. An important feature of HSV-1 and HSV-2 shared with other alphaherpes viruses is their ability to infect neurons and establish latency in the trigeminal ganglionic and dorsal root neurons, respectively [81]. Diseases caused by HSV are incurable, difficult to prevent, and clearly require efficient HSV vaccine, which does not exist yet despite more than 60 years of research [81–83].
HSV-1 and HSV-2 entry to the host cells via fusion of the viral envelope with the host plasma membranes. Entry of the HSVs is a complex process that involves a set of 12 surface viral glycoproteins (gB, gC, gD, gE, gG, gH, gI, gJ, gK, gL, gM, and gN), with fusion alone requiring at least five proteins, gB (the sole fusogenic viral glycoprotein), gD (defines HSV entry by binding to one of its many cell surface receptors), gH/gL heterodimer (absolutely required for viral entry) [84, 85], and gK (plays accessory roles in controlling gB-mediated membrane fusion) [81, 86]. Remaining surface glycoproteins have other roles: gC is responsible for adsorption to cell-surface heparan sulfate and provides a shield against neutralizing Abs that interfere with gB-gD, gB-gH/gL, or gD-gH/gL interactions [85], the gE/gI heterodimer is required for the cell-to-cell spread of the virus [87], gG is a chemokine-binding protein found in HSV-2 only [88], gJ is located in membranes of Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, and endosome and acts as an activator of viral protein expression and virus production and spread [89], gM is important for virion assembly and egress, interacts with gN, and controls the correct incorporation of gH/gL into virion membrane [90], whereas gN partners with gM to modulate the viral fusion machinery [91].
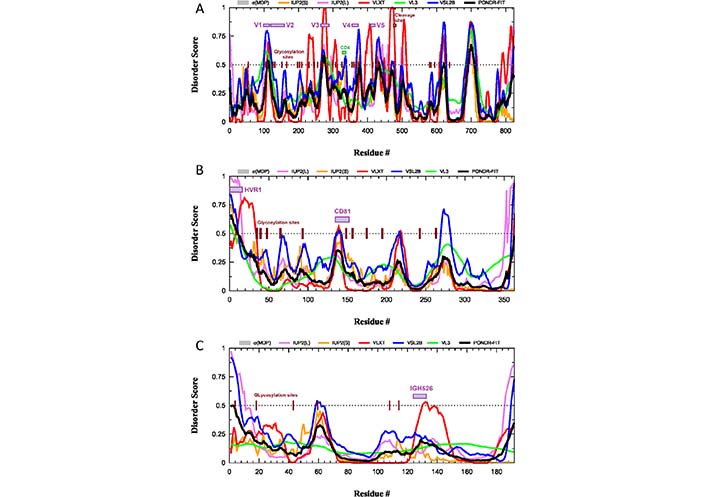
Since these 12 glycoproteins are located on the surface of the viral particle and play a crucial role in viral entry, they serve attractive targets for vaccine development. In line with this idea, gD from HSV-2 was recently used in the design of a multi-epitope protein vaccine against sexually transmitted diseases caused by infection with HSV, human papillomavirus, and Chlamydia trachomatis [92]. Similarly, gE, gB, and gD from HSV-1 were used to design polyvalent subunit vaccines in a recent study that utilized reverse vaccinology and bioinformatics (note, these three candidates were selected from nine envelope glycoproteins, gM, gH, gI, gE, gB, gL, gD, gK, and gC) [93]. The same group of authors used the tools of reverse vaccinology and immunoinformatics to develop several polyvalent subunit vaccines against multiple strains of HSV-1 and HSV-2, targeting the gE, gB, and gD [94]. An obvious step in reverse vaccinology is the utilization of the antigen structure. As shown in Figures 3 and 4, all 12 surface glycoproteins are predicted to contain high levels of intrinsic disorder and based on their disorder content can be arranged as follows: gG > gN > gE > gI > gC > gL > gJ > gB > gM > gH > gD > gK, with disorder content ranging from > 70% in gG to ∼10% in gK. It is also seen that 50%, 31%, and 25% residues in gE, gB, and gD used in the aforementioned reverse vaccinology experiments are predicted as intrinsically disordered.
Intrinsic disorder status of 12 surface glycoproteins from HSV-1. The disorder predisposition of 12 glycoproteins from human HSV-1 (strain 17) based on disorder score and percent of disordered residues. Larger values of each parameter indicate increasing disorder. Color blocks show regions in which one can find mostly ordered (blue and light blue), moderately disordered (pink and light pink), or mostly disordered (red) proteins. If the two parameters agree, the corresponding part of the background is dark (blue or pink), whereas light blue and light pink reflect areas in which only one of these criteria applies
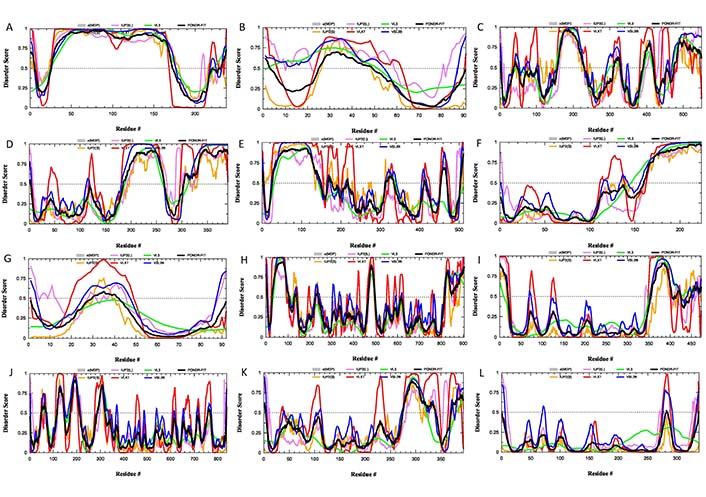
Intrinsic disorder status of 12 surface glycoproteins from HSV-1. Per-residue disorder profiles of the individual glycoproteins from HSV-1: (A) gG (UniProt ID: P06484); (B) gN (UniProt ID: O09800); (C) gE (UniProt ID: P04488); (D) gI (UniProt ID: P06487); (E) gC (UniProt ID: P10228); (F) gL (UniProt ID: P10185); (G) gJ (UniProt ID: P06480); (H) gB (UniProt ID: P10211); (I) gM (UniProt ID: P04288); (J) gH (UniProt ID: P06477); (K) gD (UniProt ID: Q69091); (L) gK (UniProt ID P68331)
These observations raise a question on the robustness and validity of structures used for the reverse vaccinology based on any HSV glycoprotein. Once again, many important functional features of HSV glycoproteins and their N-glycosylation sites overlap or are located within or in close proximity to IDRs. This not only indicates the functional importance of intrinsic disorder in these proteins but emphasizes once again the potential role of intrinsic disorder in establishing a flexible glycan-IDR shield protecting potential epitopes from neutralizing Abs.
Another side of the dynamic antigen-Ab dances is given by the highly flexible structure of Abs. Details of this structural flexibility were discussed in a recent opinion article dedicated to the analysis of the bottlenecks of the anti-HIV vaccine development [66]. Brief summary of the related considerations is presented below. Structural dynamics of the immunoglobulin G (IgG), which is an illustrative example of five different classes of Abs, IgM, IgD, IgG, IgA, and IgE that all have comparable structural organization, go well beyond the structural malleability of this Y-shaped molecule provided by the flexible linkers between the antigen-binding fragments (Fab) (arms) and the constant fragment (Fc) (stem), which by itself represents a major reason for the dearth of the resolved crystal structures of the full-length immunoglobulins. In fact, due to this high conformational flexibility of hinges connecting Fab fragments with the Fc fragment Abs exist as highly dynamic conformational ensembles and the known crystal Ab structures represent “snapshots” of these ensembles [95]. The next level of structural flexibility is given by the conformational dynamics of the Ab discontinuous “active sites”, which are formed by the 50–70 hypervariable residues containing paratopes (binding sub-sites with chemical and structural complementary to the epitopes) built from the short stretches of residues located on six CDRs [L1, L2, L3 on the light (L) chain and H1, H2, and H3 on the heavy (H) chain] [96].
Although the antigen-binding sites of anti-protein Abs are typically relatively flat, the H3 loops located in the center of the binding sites are often extended in human Abs [95, 97–99] providing them with the capability to embed into the canyons and clefts on the antigen surface [95, 100]. Furthermore, these H3 loops in human Abs are characterized by a very broad spectrum of distinctive structural features containing on average 10 times more unique conformations than the other loops, as evidenced by the comprehensive analysis of known 3D-structures of human Abs [101]. This structural polymorphism reflects highly flexible if not disordered nature of this region in solution. This hypothesis is supported by the results of the intrinsic disorder predisposition analysis of both H and L chains of a typical IgG, according to which CDRs are predicted to be either flexible or disordered (i.e., as regions with the PDS ≥ 0.5 and 0.15 ≤ PDS < 0.5, respectively) (see Figure 5).
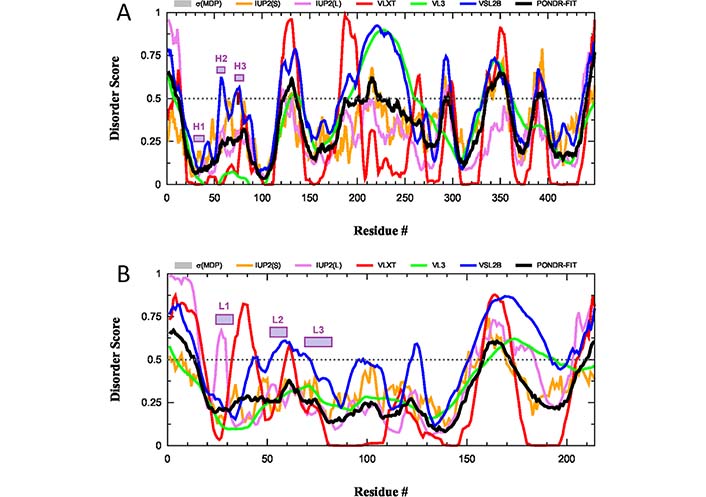
Intrinsic disorder predisposition of H and L chains of a typical human IgG. (A) Intrinsic disorder profile of human immunoglobulin gamma-1 H chain (UniProt ID: P0DOX5); (B) intrinsic disorder profile of human immunoglobulin gamma-1 L chain (UniProt ID: P0DOX7). Positions of CDRs in each chain are shown by colored boxes
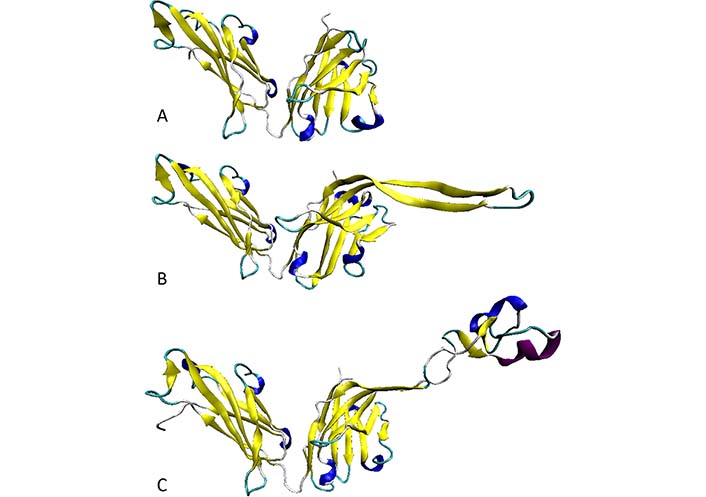
Furthermore, analysis of several anti-HIV Abs of human or bovine origin [66] revealed that the length of the H3 loop can vary in a very broad range, from 4 residues in a non-neutralizing HIV Ab 13H11 [protein databank (PDB) ID: 3MO1] to 16 residues in a broadly reactive and potent HIV-1 neutralizing human Ab PG9 (PDB ID: 3U1S; [49]), and to 60 residues in a potent HIV-1 bNAb NC-Cow1 (PDB ID: 6OO0; [102]) (see Figure 6A, 6B, and 6C, respectively). As shown in Figure 6C, the exceptionally long CDR H3 of the NC-Cow1 bNAb is folded into a particular structure representing a mini domain (knob) on an extended stalk [102]. This is a very important feature that allows the efficient binding of the Fab NC-Cow1 to the HIV Env trimer BG505 SOSIP, where knob on the stalk “navigates through the dense glycan shield on Env to target a small footprint on the gp120 CD4 receptor binding site with no contact of the other CDRs to the rest of the Env trimer” [102]. Furthermore, it seems that the length of a CDR H3 loop correlates with the neutralization potential of a given Ab, as bNAbs are typically characterized by the long CDR H3 loops [103, 104]. The high neutralization potential of these Abs is defined by the capability of their long CDR H3 loops to breach the dense glycan shield of HIV Env thereby ensuring the access to the protein surface of this viral glycoprotein [104, 105]. Since extra-long CDR H3 loops can protrude up to 40 Å above the tips of the other CDR loops [102], the “knob on an extended stalk” structure of an extra-long CDR H3 acts as a perfect “penetrator” capable of navigating through the glycan shield on Env. Since the CDR H3 loops of different Abs were all predicted to be flexible or disordered with the degree of disorderedness being increasing with the length of the H3 loop, it is likely that the neutralizing efficiency of bNAbs is driven by the intrinsic disorder. Therefore, it is likely that the structures reported for this region in different Abs represent snapshots of dynamic conformational ensembles, with some observed structures being stabilized (or even induced) by the Ab interaction with the antigens or by the crystal lattice. All these observations are in line with the important hypothesis that the functionality of the Abs depends on conformational flexibility and intrinsic disorder (at least of their long H3 loops). Furthermore, although many anti-HIV-1 Abs have been found to possess long CDR H3 regions [46, 106–108], it is unclear at the moment how one can induce such Abs containing long CDR H3 by immunization [36].
The lack of success in finding efficient vaccines for HCV, HIV, and HSV despite 30, 40, and even 60 years of research is daunting. Although HIV, HCV, and HSV belong to different viral families, they have some similarities, such as the appearance of the quaternary structure-dependent neotopes and the high glycosylation degree of their surface proteins, which are used as primary vaccine targets as they are essential to viral fusion with the cell membrane and can contribute to immune system evasion. On the other hand, HIV and HCV, being RNA viruses, are characterized by high mutation rates, whereas the evolution of HSVs (which are DNA viruses) is slow. Furthermore, the capability of HSVs to establish latency contributes to the challenges associated with the anti-HSV vaccine development, as “an effective vaccine must not only prevent active clinical disease but ideally latent infection as well” [79].
Curiously, many of these seemingly structure-related features are in fact deeply intertwined with intrinsic disorder and structural flexibility. For example, quaternary structure, the formation of which is associated with the appearance of neotopes, is often linked to binding-induced folding, where flexible or disordered regions of protomers undergo transition to a more ordered state as a result of oligomerization or complex formation. This suggests connection of such binding-induced folding to the origin of at least some of the neotopes. Catalyzed protein posttranslational modifications in general and glycosylation in particular are frequently happening within disordered and flexible regions [48, 109]. As it was emphasized in this article, the fact that glycosylation most often happens within disordered regions can be related to the creation of a highly mobile glycan-IDR shield providing high efficiency and space coverage needed for the establishing efficient protection of viral epitopes from the neutralizing Abs. Furthermore, flexible or disorder regions are targeted by mutations more frequently than ordered domains, suggesting that disorder/flexibility plays a role in the viral evolution as well.
All these observations and considerations bring serious doubts about the overall applicability of the rational structural vaccinology computational methods. These concerns are further elaborated and enhanced by an important fact that when the proteins interact, they often undergo mutual adaptation and induced fit/folding [36, 110–112], indicating that epitopes and paratopes are fuzzy binding sites devoid of clear-cut structural boundaries [113]. As a result, the structures of the binding sites in the unbound molecules may dramatically differ from the static structures of antigen-Ab complexes used in the rational structural vaccinology [113–116]. Furthermore, since neither Abs nor antigens have static rigid structures, the attempts of using rational structure-based design for the development of (at least) HIV, HCV, and HSV vaccines are rather spurious. In fact, due to the presence of intrinsic disorder and high structural flexibility, Abs and antigens are located within the passage to the dark proteome that comprises mostly disordered/flexible proteins not amenable to the traditional experimental structure determination by existing means and inaccessible to homology modeling [117]. Curiously, since antigen-binding sites of Abs are flexible/disordered themselves, it seems that the immune system follows the “if you can’t fight them join them” principle and “fights fire with fire” by utilizing intrinsic disorder/structural flexibility of Abs to overcome intrinsic disorder-based “invisibility” of viral antigens.
These are very important considerations that cannot be ignored. We should stop playing with the motionless toys, as the reality is much more complex than static picture drawn by classic “lock-and-key” model. In fact, it is even more complex than an intricate interplay of the “flexible keys and adjustable locks”. It is time for the emergence of unstructural vaccinology, where the phenomenon of intrinsic disorder is taken into account while thinking about novel approaches for designing vaccines against “flexible” viruses that act as dynamic “shape-shifters” [28]. In other words, we need to start using experimental and computational tools designed for the analysis of disordered and flexible proteins, while looking at intrinsically disordered viral antigens and their interactions with intrinsically disordered/flexible Abs. Regrettably, despite the obvious need to move away from the rational structural vaccinology and corresponding computational and experimental methods, the transition to the unstructural or non-structure-based vaccinology is not even started yet. This is illustrated by the fact that the literature on unstructural vaccinology is non-existent. Although in PubMed, one can find almost 1,000 papers dedicated to the structural vaccinology, the search for “unstructural vaccinology” retrieved no results. The situation is not improved if “non-structure-based vaccinology” is used as a search term. Although papers containing the phrase “non-structural vaccinology” were not found in PubMed as well, there were 36 hits, when the database was searched for “non-structural AND vaccinology”. Unfortunately, all retrieved papers were dedicated to vaccinology targeting non-structural viral proteins.
3D: three-dimensional
Abs: antibodies
AIDS: acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
bNAbs: broadly neutralizing Abs
CD4: CD4-binding loop
CDR: complementarity determining region
Env: envelope protein
Fab: antigen-binding fragments
H: heavy
HCV: hepatitis C virus
HIV: human immunodeficiency virus
HIV-1: human immunodeficiency virus type 1
HSVs: herpes simplex viruses
IDRs: intrinsically disordered regions
IgG: immunoglobulin G
L: light
mAb: monoclonal antibody
PDB: protein databank
PDS: predicted disorder scores
The author contributed solely to the work.
The author declares that he has no conflicts of interest.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Copyright: © The Author(s) 2022. This is an Open Access article licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, for any purpose, even commercially, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Marc H.V. Van Regenmortel
Christine Jacomet
Brent Brown ... Ingo Fricke
Chittaranjan Baruah ... Bhabesh Deka
Brent Brown ... Enrique Chacon-Cruz
Om Saswat Sahoo ... Subhradip Karmakar
Mikolaj Raszek ... Alberto Rubio-Casillas
Ankit Kumar ... Vijay Mishra
Yulia Desheva ... Irina Isakova-Sivak