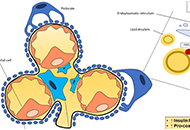
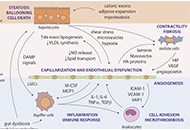
-
Exploration of Medicine
eISSN: 2692-3106EiC: Lindsay A. Farrer, USAFrequency: Continuous PublicationAPC: $2,000 per article (See APC Waivers and Discounts)Publishing Model: Open AccessPeer Review Model: Single BlindIndexing & Archiving: Scopus, Google Scholar, DOAJ, CAS, Dimensions, Portico, etc. The journal is also the member of COPE.Articles Right ventricular echocardiographic parameters predict severe sleep apnea syndrome in patients with heart failureOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The study aimed to determine which right ventricle echocardiography parameters were associated with severe sleep apnea syndrome in heart failure patients with sleep apnea syndrome. Meth [...] Read more.
Right ventricular echocardiographic parameters predict severe sleep apnea syndrome in patients with heart failureOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The study aimed to determine which right ventricle echocardiography parameters were associated with severe sleep apnea syndrome in heart failure patients with sleep apnea syndrome. Meth [...] Read more.Aim:
The study aimed to determine which right ventricle echocardiography parameters were associated with severe sleep apnea syndrome in heart failure patients with sleep apnea syndrome.
Methods:
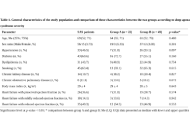
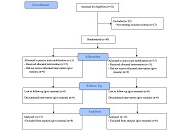
A cross-sectional monocentric study was conducted, including 85 patients with stable heart failure. All patients underwent home respiratory polygraphy and transthoracic echocardiography with evaluation of the right ventricular echocardiographic parameters and sleep apnea syndrome severity.
Results:
The average age of the population was 69 years. The median left ventricular ejection fraction was 38% (33; 52). Sleep apnea syndrome was diagnosed in 71 patients (83.5%), with obstructive sleep apnea in 50 patients (58.8%) and central sleep apnea in 21 patients (24.7%). Severe sleep apnea syndrome was observed in 31% (n = 22) of patients. In the univariate analysis, right ventricle Tei index with a cutoff value > 0.50 (OR = 3; 95% CI = 1.06–8.56; p = 0.035), right ventricle fractional area change < 40 (OR = 4; 95% CI = 1.38–11; p = 0.09) and right ventricle free wall longitudinal strain with a cut-off value > –17 (OR = 3.5; 95% CI = 1.15–9.41; p = 0.002) increased the risk of having severe sleep apnea syndrome. In the multivariate analysis, the right ventricle free wall longitudinal strain was the only independent predictor for severe sleep apnea syndrome [hazard ratio (HR) = 0.892; 95% CI = 0.816–0.979; p = 0.036].
Conclusions:
Right ventricle free wall longitudinal strain seems to be a strong predictor of severe sleep apnea syndrome in patients with stable chronic heart failure and sleep apnea syndrome.
Saoussen Antit ... Lilia ZakhamaPublished: April 23, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001311
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001311Aim:
The study aimed to determine which right ventricle echocardiography parameters were associated with severe sleep apnea syndrome in heart failure patients with sleep apnea syndrome.
Methods:
A cross-sectional monocentric study was conducted, including 85 patients with stable heart failure. All patients underwent home respiratory polygraphy and transthoracic echocardiography with evaluation of the right ventricular echocardiographic parameters and sleep apnea syndrome severity.
Results:
The average age of the population was 69 years. The median left ventricular ejection fraction was 38% (33; 52). Sleep apnea syndrome was diagnosed in 71 patients (83.5%), with obstructive sleep apnea in 50 patients (58.8%) and central sleep apnea in 21 patients (24.7%). Severe sleep apnea syndrome was observed in 31% (n = 22) of patients. In the univariate analysis, right ventricle Tei index with a cutoff value > 0.50 (OR = 3; 95% CI = 1.06–8.56; p = 0.035), right ventricle fractional area change < 40 (OR = 4; 95% CI = 1.38–11; p = 0.09) and right ventricle free wall longitudinal strain with a cut-off value > –17 (OR = 3.5; 95% CI = 1.15–9.41; p = 0.002) increased the risk of having severe sleep apnea syndrome. In the multivariate analysis, the right ventricle free wall longitudinal strain was the only independent predictor for severe sleep apnea syndrome [hazard ratio (HR) = 0.892; 95% CI = 0.816–0.979; p = 0.036].
Conclusions:
Right ventricle free wall longitudinal strain seems to be a strong predictor of severe sleep apnea syndrome in patients with stable chronic heart failure and sleep apnea syndrome.
 Long-term neurological and otolaryngological sequelae of COVID-19: a retrospective studyOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: COVID-19, a multisystemic syndrome caused by SARS-CoV-2, often results in long-term complications collectively referred to as long COVID. This study explores the persistence of neurological [...] Read more.
Long-term neurological and otolaryngological sequelae of COVID-19: a retrospective studyOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: COVID-19, a multisystemic syndrome caused by SARS-CoV-2, often results in long-term complications collectively referred to as long COVID. This study explores the persistence of neurological [...] Read more.Aim:
COVID-19, a multisystemic syndrome caused by SARS-CoV-2, often results in long-term complications collectively referred to as long COVID. This study explores the persistence of neurological and otolaryngological symptoms in patients two years after acute infection, with a focus on gender differences and variant-specific effects.
Methods:
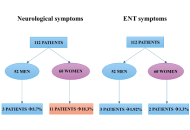
A retrospective follow-up was conducted in January 2024 on 112 patients who had been hospitalized for COVID-19. Patients completed a questionnaire assessing the persistence of neuropsychiatric, otolaryngological, and systemic symptoms.
Results:
Findings reveal that 18.3% of women reported persistent neuropsychiatric symptoms, such as memory deficits, depression, and concentration issues, compared to 5.7% of men. Otolaryngological symptoms, including anosmia and ageusia, largely resolved, with only 4.5% reporting persistent issues. Symptom persistence was more common in older individuals, women, smokers, and those with severe acute-phase illness. Neuropsychiatric symptoms remain prominent, underscoring the need for targeted long-term care.
Conclusions:
Vaccination significantly reduces the risk and severity of long COVID, particularly neuropsychiatric symptoms, emphasizing its role in mitigating the long-term burden of SARS-CoV-2. Future research should explore biomolecular markers and imaging techniques to better understand and address these long-term sequelae.
Wael Abu Ruqa ... Antonio MinniPublished: April 21, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001310
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001310
This article belongs to the special issue Emerging Infectious DiseasesAim:
COVID-19, a multisystemic syndrome caused by SARS-CoV-2, often results in long-term complications collectively referred to as long COVID. This study explores the persistence of neurological and otolaryngological symptoms in patients two years after acute infection, with a focus on gender differences and variant-specific effects.
Methods:
A retrospective follow-up was conducted in January 2024 on 112 patients who had been hospitalized for COVID-19. Patients completed a questionnaire assessing the persistence of neuropsychiatric, otolaryngological, and systemic symptoms.
Results:
Findings reveal that 18.3% of women reported persistent neuropsychiatric symptoms, such as memory deficits, depression, and concentration issues, compared to 5.7% of men. Otolaryngological symptoms, including anosmia and ageusia, largely resolved, with only 4.5% reporting persistent issues. Symptom persistence was more common in older individuals, women, smokers, and those with severe acute-phase illness. Neuropsychiatric symptoms remain prominent, underscoring the need for targeted long-term care.
Conclusions:
Vaccination significantly reduces the risk and severity of long COVID, particularly neuropsychiatric symptoms, emphasizing its role in mitigating the long-term burden of SARS-CoV-2. Future research should explore biomolecular markers and imaging techniques to better understand and address these long-term sequelae.
 Cytocompatibility and bone regeneration potential of chitosan-thiocolchicoside-lauric acid nanogel with insights into zebrafish toxicologyOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The present study explored the bone regeneration potential of chitosan-thiocolchicoside-lauric (CTL) nanogel using MG-63 cell lines. The cytocompatibility of CTL nanogel was also studied usi [...] Read more.
Cytocompatibility and bone regeneration potential of chitosan-thiocolchicoside-lauric acid nanogel with insights into zebrafish toxicologyOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The present study explored the bone regeneration potential of chitosan-thiocolchicoside-lauric (CTL) nanogel using MG-63 cell lines. The cytocompatibility of CTL nanogel was also studied usi [...] Read more.Aim:
The present study explored the bone regeneration potential of chitosan-thiocolchicoside-lauric (CTL) nanogel using MG-63 cell lines. The cytocompatibility of CTL nanogel was also studied using osteoblast-like cells (MG-63 cell lines) and zebrafish embryos.
Methods:
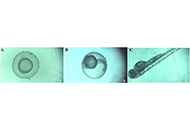
The effect of CTL nanogel on the metabolic and wound-healing activity of MG-63 cells was investigated in the present study. The alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and bone sialoprotein (BSP) activity of CTL nanogel-treated MG-63 cells were assessed using ELISA. RUNX2, ALP, BSP, and COL1A1 gene expression in MG-63 cells were also investigated after treatment with CTL nanogel. Hatching rates and viability of zebrafish embryos treated with different CTL nanogel concentrations were studied. Any developmental toxicity of embryos after treatment with CTL nanogel was also investigated.
Results:
There was no significant reduction in the proliferation of MG-63 cells when treated with 5–20 μL/mL of CTL nanogel in the MTT assay (p < 0.05). No prominent morphological changes or nuclear abnormalities were found in the MG-63 cells when treated with various concentrations of CTL nanogel compared to the control group. Invitro scratch wound healing assay showed excellent migration of cells and, hence, showed the excellent wound healing ability of CTL nanogel. ELISA showed significant ALP and BSP activity of CTL nanogel-treated MG-63 cells. RUNX2, ALP, BSP, and COL1A1 gene expression in MG-63 cells after treatment with CTL nanogel were significantly increased compared to the control group (p < 0.05). The hatching and viability rates of the embryos increased as the nanogel concentrations decreased, with the highest hatching rate observed at a 5 µL concentration. Developmental toxicity, such as spinal cord bent, tail bent, or yolk sac oedema, was not observed after treatment with CTL nanogel in zebrafish embryos.
Conclusions:
CTL nanogel can be used in treating bone defects and helping wound healing. The study also suggests that CTL nanogel had a concentration-dependent effect on zebrafish embryos’ viability and hatching rates only in very high concentrations.
Ameena Mustafa ... Giuseppe MinerviniPublished: April 21, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001309
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001309Aim:
The present study explored the bone regeneration potential of chitosan-thiocolchicoside-lauric (CTL) nanogel using MG-63 cell lines. The cytocompatibility of CTL nanogel was also studied using osteoblast-like cells (MG-63 cell lines) and zebrafish embryos.
Methods:
The effect of CTL nanogel on the metabolic and wound-healing activity of MG-63 cells was investigated in the present study. The alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and bone sialoprotein (BSP) activity of CTL nanogel-treated MG-63 cells were assessed using ELISA. RUNX2, ALP, BSP, and COL1A1 gene expression in MG-63 cells were also investigated after treatment with CTL nanogel. Hatching rates and viability of zebrafish embryos treated with different CTL nanogel concentrations were studied. Any developmental toxicity of embryos after treatment with CTL nanogel was also investigated.
Results:
There was no significant reduction in the proliferation of MG-63 cells when treated with 5–20 μL/mL of CTL nanogel in the MTT assay (p < 0.05). No prominent morphological changes or nuclear abnormalities were found in the MG-63 cells when treated with various concentrations of CTL nanogel compared to the control group. Invitro scratch wound healing assay showed excellent migration of cells and, hence, showed the excellent wound healing ability of CTL nanogel. ELISA showed significant ALP and BSP activity of CTL nanogel-treated MG-63 cells. RUNX2, ALP, BSP, and COL1A1 gene expression in MG-63 cells after treatment with CTL nanogel were significantly increased compared to the control group (p < 0.05). The hatching and viability rates of the embryos increased as the nanogel concentrations decreased, with the highest hatching rate observed at a 5 µL concentration. Developmental toxicity, such as spinal cord bent, tail bent, or yolk sac oedema, was not observed after treatment with CTL nanogel in zebrafish embryos.
Conclusions:
CTL nanogel can be used in treating bone defects and helping wound healing. The study also suggests that CTL nanogel had a concentration-dependent effect on zebrafish embryos’ viability and hatching rates only in very high concentrations.
 Breath analysis using FTIR spectroscopyOpen AccessReviewBreath analysis is a relatively new topic of study that has a lot of potential for both therapeutic and scientific applications. The volatile organic compounds (VOCs) found in breath are created int [...] Read more.
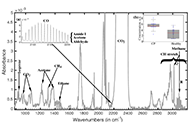
Breath analysis using FTIR spectroscopyOpen AccessReviewBreath analysis is a relatively new topic of study that has a lot of potential for both therapeutic and scientific applications. The volatile organic compounds (VOCs) found in breath are created int [...] Read more.Breath analysis is a relatively new topic of study that has a lot of potential for both therapeutic and scientific applications. The volatile organic compounds (VOCs) found in breath are created internally by the body due to environmental interactions, gut and air passage bacteria, and metabolites of ingested precursors. Breath analysis may help diagnose disorders linked to changes in breath composition, according to several recent research. An analytical technique that shows promise for the metabolic examination of breath is infrared spectroscopy. Chemical substances found in exhaled human breath can be used to diagnose illnesses, determine physiological states, or evaluate environmental exposure. Exhaled breath (EB) is the perfect biological fluid because it is nearly limitless and causes little to no discomfort for the patient, which promotes collaboration. Furthermore, EB can be sampled without requiring medical professionals or privacy, and it usually doesn’t produce infectious waste (despite airborne infections), which makes breath analysis a desirable method for a variety of applications. Breath analysis is a non-invasive method that solely uses the volatile composition of the EB to characterize the bloodstream and airways’ volatile content, which indicates the state and condition of the entire body’s metabolism. The absorption strength of the metabolites is still very modest, though, because EB contains minimal amounts of them. Several of the most recent uses of infrared spectroscopy for breath analysis, published between 2020 and 2024, are presented in this study.
Andrei A. Bunaciu, Hassan Y. Aboul-EneinPublished: April 17, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001308
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001308Breath analysis is a relatively new topic of study that has a lot of potential for both therapeutic and scientific applications. The volatile organic compounds (VOCs) found in breath are created internally by the body due to environmental interactions, gut and air passage bacteria, and metabolites of ingested precursors. Breath analysis may help diagnose disorders linked to changes in breath composition, according to several recent research. An analytical technique that shows promise for the metabolic examination of breath is infrared spectroscopy. Chemical substances found in exhaled human breath can be used to diagnose illnesses, determine physiological states, or evaluate environmental exposure. Exhaled breath (EB) is the perfect biological fluid because it is nearly limitless and causes little to no discomfort for the patient, which promotes collaboration. Furthermore, EB can be sampled without requiring medical professionals or privacy, and it usually doesn’t produce infectious waste (despite airborne infections), which makes breath analysis a desirable method for a variety of applications. Breath analysis is a non-invasive method that solely uses the volatile composition of the EB to characterize the bloodstream and airways’ volatile content, which indicates the state and condition of the entire body’s metabolism. The absorption strength of the metabolites is still very modest, though, because EB contains minimal amounts of them. Several of the most recent uses of infrared spectroscopy for breath analysis, published between 2020 and 2024, are presented in this study.
 Joint mobilization strategies for chronic ankle instability: comparing active and passive approaches in a randomized controlled trialOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study aimed to evaluate the differential effects of active joint mobilization (AJM) versus traditional passive joint mobilization (PJM) in individuals with chronic ankle instability. We [...] Read more.
Joint mobilization strategies for chronic ankle instability: comparing active and passive approaches in a randomized controlled trialOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study aimed to evaluate the differential effects of active joint mobilization (AJM) versus traditional passive joint mobilization (PJM) in individuals with chronic ankle instability. We [...] Read more.Aim:
This study aimed to evaluate the differential effects of active joint mobilization (AJM) versus traditional passive joint mobilization (PJM) in individuals with chronic ankle instability. We hypothesized that the integration of active components may yield superior outcomes through enhanced proprioceptive feedback and neuromuscular recruitment patterns.
Methods:
In this single-blind, parallel-group randomized controlled trial, thirty participants with chronic ankle instability were randomly assigned to either AJM (n = 15) or PJM (n = 15) groups. Interventions were administered by certified physical therapists three times per week for four weeks, with each session lasting 10 minutes. Primary outcome measures included the Cumberland Ankle Instability Tool (CAIT) and dorsiflexion range of motion (DFROM). Secondary outcomes focused on neuromuscular control parameters including joint position sense (JPS) and static balance, assessed at baseline and post-intervention.
Results:
Both groups demonstrated significant within-group improvements in multiple parameters. The PJM group showed significant improvements in CAIT (p < 0.001), DFROM (p < 0.001), and JPS (p < 0.01). Similarly, the AJM group exhibited significant improvements in CAIT (p < 0.01), DFROM (p < 0.001), and JPS (p < 0.001). Between-group comparison revealed no significant differences in any outcome measures (p > 0.05).
Conclusions:
Both AJM and PJM demonstrated effectiveness in improving functional ankle stability, range of motion, and proprioceptive function in individuals with chronic ankle instability. While both techniques can serve as viable therapeutic approaches, the slightly larger effect sizes observed in AJM for DFROM and proprioceptive function suggest potential additional benefits of active components (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04630899).
Hyunjoong Kim ... Mingyun KoPublished: April 17, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001307
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001307Aim:
This study aimed to evaluate the differential effects of active joint mobilization (AJM) versus traditional passive joint mobilization (PJM) in individuals with chronic ankle instability. We hypothesized that the integration of active components may yield superior outcomes through enhanced proprioceptive feedback and neuromuscular recruitment patterns.
Methods:
In this single-blind, parallel-group randomized controlled trial, thirty participants with chronic ankle instability were randomly assigned to either AJM (n = 15) or PJM (n = 15) groups. Interventions were administered by certified physical therapists three times per week for four weeks, with each session lasting 10 minutes. Primary outcome measures included the Cumberland Ankle Instability Tool (CAIT) and dorsiflexion range of motion (DFROM). Secondary outcomes focused on neuromuscular control parameters including joint position sense (JPS) and static balance, assessed at baseline and post-intervention.
Results:
Both groups demonstrated significant within-group improvements in multiple parameters. The PJM group showed significant improvements in CAIT (p < 0.001), DFROM (p < 0.001), and JPS (p < 0.01). Similarly, the AJM group exhibited significant improvements in CAIT (p < 0.01), DFROM (p < 0.001), and JPS (p < 0.001). Between-group comparison revealed no significant differences in any outcome measures (p > 0.05).
Conclusions:
Both AJM and PJM demonstrated effectiveness in improving functional ankle stability, range of motion, and proprioceptive function in individuals with chronic ankle instability. While both techniques can serve as viable therapeutic approaches, the slightly larger effect sizes observed in AJM for DFROM and proprioceptive function suggest potential additional benefits of active components (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04630899).
 Inflammatory mediators in nasal secretion in patients with bronchial asthma and allergic rhinitis with or without polyposis and hypertrophic sinonasal mucosaOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The pathogenetic mechanisms and predictors of the development of polyposis and hypertrophy of the sinonasal mucosa (SM) in patients with chronic allergic airway inflammation have not been cl [...] Read more.
Inflammatory mediators in nasal secretion in patients with bronchial asthma and allergic rhinitis with or without polyposis and hypertrophic sinonasal mucosaOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The pathogenetic mechanisms and predictors of the development of polyposis and hypertrophy of the sinonasal mucosa (SM) in patients with chronic allergic airway inflammation have not been cl [...] Read more.Aim:
The pathogenetic mechanisms and predictors of the development of polyposis and hypertrophy of the sinonasal mucosa (SM) in patients with chronic allergic airway inflammation have not been clearly established. The concentration of inflammatory biomarkers in nasal secretions was determined in children and adolescents with a combined course of bronchial asthma (BA) and allergic rhinitis (AR) in the absence or presence of polyposis and hypertrophy of the SM.
Methods:
A single-centre observational cross-sectional pilot study was conducted. 93 patients with BA aged 8 to 17 years were studied. Total Nasal Symptom Score (TNSS), sinonasal symptoms (SNOT-22), and peak nasal inspiratory flow (PNIF) were assessed. Concentrations of eosinophil cationic protein (ECP), interleukin 4 (IL-4), IL-1, total immunoglobulin E (IgE), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in nasal secretions were determined.
Results:
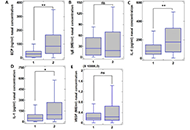
The levels of ECP, IL-4, and IL-1 in nasal secretions were statistically significantly higher in patients with the presence of polyposis and hypertrophic SM than in those without, amounting to 83.1 [31.4; 166.8] ng/mL for ECP vs. 29.5 [5.3; 49.9] ng/mL, P < 0.001, for IL-4 174.6 [68.6; 325.5] pg/mL vs. 79.5 [42.8; 146.01] pg/mL, P = 0.004, for IL-1 98.7 [33.7; 267.5] pg/mL and 48.8 [9.01; 108.2] pg/mL, P = 0.025. There were no statistically significant differences in IgE and VEGF levels in nasal secretions, all P > 0.05. Parameters such as ECP, IL-4, and IL-1 were found to be significant predictors of polyposis and hypertrophy in the formation of SM.
Conclusions:
In patients with a combined course of BA and AR, the presence of polyposis and hypertrophy of SM is associated with higher levels of ECP, IL-4, and IL-1 in nasal secretion. This may indicate that pathological remodelling of SM is associated with both the intensity of allergic inflammation and its relationship with local activation of innate immunity.
Svetlana Viktorovna Krasilnikova ... Nailya Iskhakovna KubyshevaPublished: April 17, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001306
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001306Aim:
The pathogenetic mechanisms and predictors of the development of polyposis and hypertrophy of the sinonasal mucosa (SM) in patients with chronic allergic airway inflammation have not been clearly established. The concentration of inflammatory biomarkers in nasal secretions was determined in children and adolescents with a combined course of bronchial asthma (BA) and allergic rhinitis (AR) in the absence or presence of polyposis and hypertrophy of the SM.
Methods:
A single-centre observational cross-sectional pilot study was conducted. 93 patients with BA aged 8 to 17 years were studied. Total Nasal Symptom Score (TNSS), sinonasal symptoms (SNOT-22), and peak nasal inspiratory flow (PNIF) were assessed. Concentrations of eosinophil cationic protein (ECP), interleukin 4 (IL-4), IL-1, total immunoglobulin E (IgE), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in nasal secretions were determined.
Results:
The levels of ECP, IL-4, and IL-1 in nasal secretions were statistically significantly higher in patients with the presence of polyposis and hypertrophic SM than in those without, amounting to 83.1 [31.4; 166.8] ng/mL for ECP vs. 29.5 [5.3; 49.9] ng/mL, P < 0.001, for IL-4 174.6 [68.6; 325.5] pg/mL vs. 79.5 [42.8; 146.01] pg/mL, P = 0.004, for IL-1 98.7 [33.7; 267.5] pg/mL and 48.8 [9.01; 108.2] pg/mL, P = 0.025. There were no statistically significant differences in IgE and VEGF levels in nasal secretions, all P > 0.05. Parameters such as ECP, IL-4, and IL-1 were found to be significant predictors of polyposis and hypertrophy in the formation of SM.
Conclusions:
In patients with a combined course of BA and AR, the presence of polyposis and hypertrophy of SM is associated with higher levels of ECP, IL-4, and IL-1 in nasal secretion. This may indicate that pathological remodelling of SM is associated with both the intensity of allergic inflammation and its relationship with local activation of innate immunity.
 A large-scale survey of cannabis use for sleep: preferred products and perceived effects in comparison to over-the-counter and prescription sleep aidsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Cannabis use for sleep-related problems is on the rise; however, little is known about the cannabis products people are using for sleep or the perceived effects of cannabis in comparison to [...] Read more.
A large-scale survey of cannabis use for sleep: preferred products and perceived effects in comparison to over-the-counter and prescription sleep aidsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Cannabis use for sleep-related problems is on the rise; however, little is known about the cannabis products people are using for sleep or the perceived effects of cannabis in comparison to [...] Read more.Aim:
Cannabis use for sleep-related problems is on the rise; however, little is known about the cannabis products people are using for sleep or the perceived effects of cannabis in comparison to more conventional sleep aids. Therefore, the aim of this study was to examine the products cannabis users prefer to use for sleep as well as their experiences with cannabis relative to more conventional sleep aids.
Methods:
De-identified archival data from a Strainprint® survey of 1,216 individuals who use cannabis for sleep were analyzed.
Results:
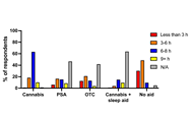
Participants predominantly reported smoking joints or vaping flower as their methods of administration, and seeking tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD), and the terpene myrcene in the cannabis they use for sleep. Only a small minority reported using cannabis in conjunction with conventional sleep aids. Comparisons of the self-reported effects of cannabis to conventional sleep aids revealed that participants reported feeling more refreshed, focused, better able to function, fewer headaches, and less nausea the morning after using cannabis for sleep than after using more conventional sleep aids or no sleep aids. However, they indicated they were more sleepy, anxious, and irritable in the mornings following the use of cannabis relative to other sleep aids. Participants were more likely to report red eyes and thirst and less likely to report nausea, anxiety, paranoia, and racing heart as side effects of cannabis relative to other sleep aids.
Conclusions:
Knowledge gained from this survey will provide health professionals with a better understanding of why people are using cannabis for sleep and may help guide future more controlled research.
Amanda Stueber, Carrie CuttlerPublished: October 25, 2023 Explor Med. 2023;4:709–719
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2023.00171
This article belongs to the special issue Beyond Weed: Clinical Applications of Cannabis and CannabinoidsAim:
Cannabis use for sleep-related problems is on the rise; however, little is known about the cannabis products people are using for sleep or the perceived effects of cannabis in comparison to more conventional sleep aids. Therefore, the aim of this study was to examine the products cannabis users prefer to use for sleep as well as their experiences with cannabis relative to more conventional sleep aids.
Methods:
De-identified archival data from a Strainprint® survey of 1,216 individuals who use cannabis for sleep were analyzed.
Results:
Participants predominantly reported smoking joints or vaping flower as their methods of administration, and seeking tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD), and the terpene myrcene in the cannabis they use for sleep. Only a small minority reported using cannabis in conjunction with conventional sleep aids. Comparisons of the self-reported effects of cannabis to conventional sleep aids revealed that participants reported feeling more refreshed, focused, better able to function, fewer headaches, and less nausea the morning after using cannabis for sleep than after using more conventional sleep aids or no sleep aids. However, they indicated they were more sleepy, anxious, and irritable in the mornings following the use of cannabis relative to other sleep aids. Participants were more likely to report red eyes and thirst and less likely to report nausea, anxiety, paranoia, and racing heart as side effects of cannabis relative to other sleep aids.
Conclusions:
Knowledge gained from this survey will provide health professionals with a better understanding of why people are using cannabis for sleep and may help guide future more controlled research.
 The potential anti-cancer effects of melatonin on breast cancerOpen AccessReviewMelatonin is the primary hormone of the pineal gland that is secreted at night. It regulates many physiological functions, including the sleep-wake cycle, gonadal activity, free radical scavenging, [...] Read more.
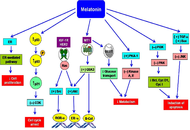
The potential anti-cancer effects of melatonin on breast cancerOpen AccessReviewMelatonin is the primary hormone of the pineal gland that is secreted at night. It regulates many physiological functions, including the sleep-wake cycle, gonadal activity, free radical scavenging, [...] Read more.Melatonin is the primary hormone of the pineal gland that is secreted at night. It regulates many physiological functions, including the sleep-wake cycle, gonadal activity, free radical scavenging, immunomodulation, neuro-protection, and cancer progression. The precise functions of melatonin are mediated by guanosine triphosphate (GTP)-binding protein (G-protein) coupled melatonin receptor 1 (MT1) and MT2 receptors. However, nuclear receptors are also associated with melatonin activity. Circadian rhythm disruption, shift work, and light exposure at night hamper melatonin production. Impaired melatonin level promotes various pathophysiological changes, including cancer. In our modern society, breast cancer is a serious problem throughout the world. Several studies have been indicated the link between low levels of melatonin and breast cancer development. Melatonin has oncostatic properties in breast cancer cells. This indolamine advances apoptosis, which arrests the cell cycle and regulates metabolic activity. Moreover, melatonin increases the treatment efficacy of cancer and can be used as an adjuvant with chemotherapeutic agents.
Naba Kumar Das, Saptadip SamantaPublished: February 25, 2022 Explor Med. 2022;3:112–127
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2022.00078Melatonin is the primary hormone of the pineal gland that is secreted at night. It regulates many physiological functions, including the sleep-wake cycle, gonadal activity, free radical scavenging, immunomodulation, neuro-protection, and cancer progression. The precise functions of melatonin are mediated by guanosine triphosphate (GTP)-binding protein (G-protein) coupled melatonin receptor 1 (MT1) and MT2 receptors. However, nuclear receptors are also associated with melatonin activity. Circadian rhythm disruption, shift work, and light exposure at night hamper melatonin production. Impaired melatonin level promotes various pathophysiological changes, including cancer. In our modern society, breast cancer is a serious problem throughout the world. Several studies have been indicated the link between low levels of melatonin and breast cancer development. Melatonin has oncostatic properties in breast cancer cells. This indolamine advances apoptosis, which arrests the cell cycle and regulates metabolic activity. Moreover, melatonin increases the treatment efficacy of cancer and can be used as an adjuvant with chemotherapeutic agents.
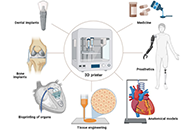
 3D printing in biomedicine: advancing personalized care through additive manufacturingOpen AccessReviewThe integration of three-dimensional (3D) printing techniques into the domains of biomedical research and personalized medicine highlights the evolving paradigm shifts within contemporary healthcare [...] Read more.
3D printing in biomedicine: advancing personalized care through additive manufacturingOpen AccessReviewThe integration of three-dimensional (3D) printing techniques into the domains of biomedical research and personalized medicine highlights the evolving paradigm shifts within contemporary healthcare [...] Read more.The integration of three-dimensional (3D) printing techniques into the domains of biomedical research and personalized medicine highlights the evolving paradigm shifts within contemporary healthcare. This technological advancement signifies potential breakthroughs in patient-specific therapeutic interventions and innovations. This systematic review offers a critical assessment of the existing literature, elucidating the present status, inherent challenges, and prospective avenues of 3D printing in augmenting biomedical applications and formulating tailored medical strategies. Based on an exhaustive literature analysis comprising empirical studies, case studies, and extensive reviews from the past decade, pivotal sectors including tissue engineering, prosthetic development, drug delivery systems, and customized medical apparatuses are delineated. The advent of 3D printing provides precision in the fabrication of patient-centric implants, bio-structures, and devices, thereby mitigating associated risks. Concurrently, it facilitates the ideation of individualized drug delivery paradigms to optimize therapeutic outcomes. Notwithstanding these advancements, issues concerning material biocompatibility, regulatory compliance, and the economic implications of avant-garde printing techniques persist. To fully harness the transformative potential of 3D printing in healthcare, collaborative endeavors amongst academicians, clinicians, industrial entities, and regulatory bodies are paramount. With continued research and innovation, 3D printing is poised to redefine the trajectories of biomedical science and patient-centric care. The paper aims to justify the research objective of whether to what extent the integration of 3D printing technology in biomedicine enhances patient-specific treatment and contributes to improved healthcare outcomes.
Kalyani Pathak ... Barbie BorthakurPublished: December 29, 2023 Explor Med. 2023;4:1135–1167
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2023.00200
This article belongs to the special issue Exploration of 3D and 4D Printing in the Biomedical and Personalized Medicine Fields: Merits and ChallengesThe integration of three-dimensional (3D) printing techniques into the domains of biomedical research and personalized medicine highlights the evolving paradigm shifts within contemporary healthcare. This technological advancement signifies potential breakthroughs in patient-specific therapeutic interventions and innovations. This systematic review offers a critical assessment of the existing literature, elucidating the present status, inherent challenges, and prospective avenues of 3D printing in augmenting biomedical applications and formulating tailored medical strategies. Based on an exhaustive literature analysis comprising empirical studies, case studies, and extensive reviews from the past decade, pivotal sectors including tissue engineering, prosthetic development, drug delivery systems, and customized medical apparatuses are delineated. The advent of 3D printing provides precision in the fabrication of patient-centric implants, bio-structures, and devices, thereby mitigating associated risks. Concurrently, it facilitates the ideation of individualized drug delivery paradigms to optimize therapeutic outcomes. Notwithstanding these advancements, issues concerning material biocompatibility, regulatory compliance, and the economic implications of avant-garde printing techniques persist. To fully harness the transformative potential of 3D printing in healthcare, collaborative endeavors amongst academicians, clinicians, industrial entities, and regulatory bodies are paramount. With continued research and innovation, 3D printing is poised to redefine the trajectories of biomedical science and patient-centric care. The paper aims to justify the research objective of whether to what extent the integration of 3D printing technology in biomedicine enhances patient-specific treatment and contributes to improved healthcare outcomes.
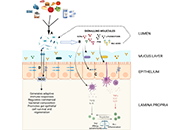
 The gut microbiome and the immune systemOpen AccessReviewThe human body contains trillions of microbes which generally live in symbiosis with the host. The interaction of the gut microbiome with elements of the host immune system has far-reaching effects [...] Read more.
The gut microbiome and the immune systemOpen AccessReviewThe human body contains trillions of microbes which generally live in symbiosis with the host. The interaction of the gut microbiome with elements of the host immune system has far-reaching effects [...] Read more.The human body contains trillions of microbes which generally live in symbiosis with the host. The interaction of the gut microbiome with elements of the host immune system has far-reaching effects in the development of normal gut and systemic immune responses. Disturbances to this intricate relationship may be responsible for a multitude of gastrointestinal and systemic immune mediated diseases. This review describes the development of the gut microbiome and its interaction with host immune cells in both health and disease states.
Tenzin Choden, Nathaniel Aviv CohenPublished: May 31, 2022 Explor Med. 2022;3:219–233
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2022.00087The human body contains trillions of microbes which generally live in symbiosis with the host. The interaction of the gut microbiome with elements of the host immune system has far-reaching effects in the development of normal gut and systemic immune responses. Disturbances to this intricate relationship may be responsible for a multitude of gastrointestinal and systemic immune mediated diseases. This review describes the development of the gut microbiome and its interaction with host immune cells in both health and disease states.
 Cannabis use in cancer patients: acute and sustained associations with pain, cognition, and quality of lifeOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Given the myriad of negative sequalae associated with cancer and its treatment, the palliative use of cannabis by cancer patients is increasingly of special interest. This research sought to e [...] Read more.
Cannabis use in cancer patients: acute and sustained associations with pain, cognition, and quality of lifeOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Given the myriad of negative sequalae associated with cancer and its treatment, the palliative use of cannabis by cancer patients is increasingly of special interest. This research sought to e [...] Read more.Aim:
Given the myriad of negative sequalae associated with cancer and its treatment, the palliative use of cannabis by cancer patients is increasingly of special interest. This research sought to explore associations of acute and sustained use of legal market edible cannabis products on pain, cognition, and quality of life in a group of cancer patients.
Methods:
In this observational study, cancer patients completed a baseline appointment, a two-week ad libitum cannabis use period, and an acute administration appointment that included assessments before cannabis use, one-hour post-use, and two-hour post-use. Participants completed self-report questionnaires related to the primary outcomes and the Stroop task as a measure of objective cognitive function.
Results:
Twenty-five participants [mean (standard deviation, SD) age = 54.3 years (15.6); 13 females (52.0%)] completed all study appointments and were included in the analysis. Sustained cannabis use was associated with improvements in pain intensity, pain interference, sleep quality, subjective cognitive function, and reaction times in the Stroop task, but no change in general quality of life was observed. High levels of cannabidiol (CBD) use during the two-week ad libitum use period was associated with steeper improvements in pain intensity and sleep quality. Participants reported improvements in pain intensity and increased feelings of subjective high after acute use. High levels of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) use during the acute administration appointment was associated with steeper increases in feelings of subjective high. Improvements in pain were associated with improvements in subjective cognitive function.
Conclusions:
This observational study is among the first of its kind to examine associations between legal market, palliative cannabis use, and subjective and objective outcomes among cancer patients. These early findings concerning pain intensity, sleep quality, and cognitive function can help to inform future, fully powered studies of this important topic (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03617692).
Gregory Giordano ... Angela D. BryanPublished: April 26, 2023 Explor Med. 2023;4:254–271
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2023.00138
This article belongs to the special issue Beyond Weed: Clinical Applications of Cannabis and CannabinoidsAim:
Given the myriad of negative sequalae associated with cancer and its treatment, the palliative use of cannabis by cancer patients is increasingly of special interest. This research sought to explore associations of acute and sustained use of legal market edible cannabis products on pain, cognition, and quality of life in a group of cancer patients.
Methods:
In this observational study, cancer patients completed a baseline appointment, a two-week ad libitum cannabis use period, and an acute administration appointment that included assessments before cannabis use, one-hour post-use, and two-hour post-use. Participants completed self-report questionnaires related to the primary outcomes and the Stroop task as a measure of objective cognitive function.
Results:
Twenty-five participants [mean (standard deviation, SD) age = 54.3 years (15.6); 13 females (52.0%)] completed all study appointments and were included in the analysis. Sustained cannabis use was associated with improvements in pain intensity, pain interference, sleep quality, subjective cognitive function, and reaction times in the Stroop task, but no change in general quality of life was observed. High levels of cannabidiol (CBD) use during the two-week ad libitum use period was associated with steeper improvements in pain intensity and sleep quality. Participants reported improvements in pain intensity and increased feelings of subjective high after acute use. High levels of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) use during the acute administration appointment was associated with steeper increases in feelings of subjective high. Improvements in pain were associated with improvements in subjective cognitive function.
Conclusions:
This observational study is among the first of its kind to examine associations between legal market, palliative cannabis use, and subjective and objective outcomes among cancer patients. These early findings concerning pain intensity, sleep quality, and cognitive function can help to inform future, fully powered studies of this important topic (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03617692).
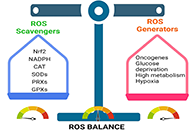
 Reactive oxygen species in cancer progression and its role in therapeuticsOpen AccessReviewThe redox status in pathogenesis is critically regulated by careful balance between the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and their elimination. Increased ROS level above the cellular tole [...] Read more.
Reactive oxygen species in cancer progression and its role in therapeuticsOpen AccessReviewThe redox status in pathogenesis is critically regulated by careful balance between the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and their elimination. Increased ROS level above the cellular tole [...] Read more.The redox status in pathogenesis is critically regulated by careful balance between the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and their elimination. Increased ROS level above the cellular tolerability threshold results in apoptotic or necrotic cell death. ROS belongs to a group of highly reactive compounds that have evolved to play key roles in cellular signaling pathways. It’s widely assumed that a reasonable amount of ROS is essential for a variety of biological processes. Elevated levels of ROS are known to cause various pathologic conditions like neurological disorders, cardiovascular conditions, inflammation, autoimmunity, and cancer. ROS is well known to initiate and assist in progression of tumor by promoting proliferation and survival of cancer cells and thus facilitates pro-tumorigenic signaling in tumor microenvironment. As cancer cells become more resilient to the effects of ROS manipulating drugs, increased antioxidant capacity attenuates their susceptibility to cancer treatment. Excessive environmental stress, on the other hand, can cause cancer cells to die. This review summarizes various molecular mechanisms including the role of checkpoint inhibitors that can be harnessed to develop effective therapeutic strategies for targeting ROS related signaling in cancer.
Ranjeet Singh, Partha Pratim MannaPublished: February 22, 2022 Explor Med. 2022;3:43–57
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2022.00073
This article belongs to the special issue Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in Pathophysiological ConditionsThe redox status in pathogenesis is critically regulated by careful balance between the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and their elimination. Increased ROS level above the cellular tolerability threshold results in apoptotic or necrotic cell death. ROS belongs to a group of highly reactive compounds that have evolved to play key roles in cellular signaling pathways. It’s widely assumed that a reasonable amount of ROS is essential for a variety of biological processes. Elevated levels of ROS are known to cause various pathologic conditions like neurological disorders, cardiovascular conditions, inflammation, autoimmunity, and cancer. ROS is well known to initiate and assist in progression of tumor by promoting proliferation and survival of cancer cells and thus facilitates pro-tumorigenic signaling in tumor microenvironment. As cancer cells become more resilient to the effects of ROS manipulating drugs, increased antioxidant capacity attenuates their susceptibility to cancer treatment. Excessive environmental stress, on the other hand, can cause cancer cells to die. This review summarizes various molecular mechanisms including the role of checkpoint inhibitors that can be harnessed to develop effective therapeutic strategies for targeting ROS related signaling in cancer.
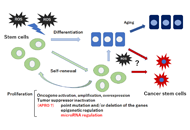
 Reactive oxygen species may influence on the crossroads of stemness, senescence, and carcinogenesis in a cell via the roles of APRO family proteinsOpen AccessPerspectiveExcessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) may cause oxidative stress which is involved in aging and in the pathogenesis of various human diseases. Whereas unregulated levels of the ROS may be harmful, regulated basal level of ROS is [...] Read more.
Reactive oxygen species may influence on the crossroads of stemness, senescence, and carcinogenesis in a cell via the roles of APRO family proteinsOpen AccessPerspectiveExcessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) may cause oxidative stress which is involved in aging and in the pathogenesis of various human diseases. Whereas unregulated levels of the ROS may be harmful, regulated basal level of ROS is [...] Read more.Excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) may cause oxidative stress which is involved in aging and in the pathogenesis of various human diseases. Whereas unregulated levels of the ROS may be harmful, regulated basal level of ROS is even necessary to support cellular functions as a second messenger for homeostasis under physiological conditions. Therefore, redox medicine could develop as a new therapeutic concept for human health-benefits. Here, we introduce the involvement of ROS on the crossroads of stemness, senescence, and carcinogenesis in a stem cell and cancer cell biology. Amazingly, the anti-proliferative (APRO) family anti-proliferative proteins characterized by immediate early growth responsive genes may also be involved in the crossroads machinery. The biological functions of APRO proteins (APROs) seem to be quite intricate, however, which might be a key modulator of microRNAs (miRNAs). Given the crucial roles of ROS and APROs for pathophysiological functions, upcoming novel therapeutics should include vigilant modulation of the redox state. Next generation of medicine including regenerative medicine and/or cancer therapy will likely comprise strategies for altering the redox environment with the APROs via the modulation of miRNAs as well as with the regulation of ROS of cells in a sustainable manner.
Yuka Ikeda ... Satoru MatsudaPublished: October 31, 2021 Explor Med. 2021;2:443–454
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2021.00062
This article belongs to the special issue Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in Pathophysiological ConditionsExcessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) may cause oxidative stress which is involved in aging and in the pathogenesis of various human diseases. Whereas unregulated levels of the ROS may be harmful, regulated basal level of ROS is even necessary to support cellular functions as a second messenger for homeostasis under physiological conditions. Therefore, redox medicine could develop as a new therapeutic concept for human health-benefits. Here, we introduce the involvement of ROS on the crossroads of stemness, senescence, and carcinogenesis in a stem cell and cancer cell biology. Amazingly, the anti-proliferative (APRO) family anti-proliferative proteins characterized by immediate early growth responsive genes may also be involved in the crossroads machinery. The biological functions of APRO proteins (APROs) seem to be quite intricate, however, which might be a key modulator of microRNAs (miRNAs). Given the crucial roles of ROS and APROs for pathophysiological functions, upcoming novel therapeutics should include vigilant modulation of the redox state. Next generation of medicine including regenerative medicine and/or cancer therapy will likely comprise strategies for altering the redox environment with the APROs via the modulation of miRNAs as well as with the regulation of ROS of cells in a sustainable manner.
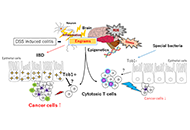
 A budding concept with certain microbiota, anti-proliferative family proteins, and engram theory for the innovative treatment of colon cancerOpen AccessPerspectiveInflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a multifactorial chronic disease. Patients with IBD have an increased risk of developing colorectal cancer which has become a major health concern. IBD might exer [...] Read more.
A budding concept with certain microbiota, anti-proliferative family proteins, and engram theory for the innovative treatment of colon cancerOpen AccessPerspectiveInflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a multifactorial chronic disease. Patients with IBD have an increased risk of developing colorectal cancer which has become a major health concern. IBD might exer [...] Read more.Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a multifactorial chronic disease. Patients with IBD have an increased risk of developing colorectal cancer which has become a major health concern. IBD might exert a role of engrams for making the condition of specific inflammation in the gut. Dysregulation of immune cells induced by the command of engrams might be crucial in the pathogenesis of damages in gut epithelium. The anti-proliferative (APRO) family of anti-proliferative proteins characterized by immediate early responsive gene-products that might be involved in the machinery of the carcinogenesis in IBD. Herein, it is suggested that some probiotics with specific bacteria could prevent the development and/or progression of the IBD related tumors. In addition, consideration regarding the application of studying APRO family proteins for the comprehension of IBD related tumors has been presented. It is hypothesized that overexpression of Tob1, a member of APRO family proteins, in the epithelium of IBD could suppress the function of adjacent cytotoxic immune cells possibly via the paracrine signaling.
Yuka Ikeda ... Satoru MatsudaPublished: October 27, 2022 Explor Med. 2022;3:468–478
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2022.00108
This article belongs to the special issue The Role of Gut Microbiota and its Metabolites in Gastrointestinal DiseasesInflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a multifactorial chronic disease. Patients with IBD have an increased risk of developing colorectal cancer which has become a major health concern. IBD might exert a role of engrams for making the condition of specific inflammation in the gut. Dysregulation of immune cells induced by the command of engrams might be crucial in the pathogenesis of damages in gut epithelium. The anti-proliferative (APRO) family of anti-proliferative proteins characterized by immediate early responsive gene-products that might be involved in the machinery of the carcinogenesis in IBD. Herein, it is suggested that some probiotics with specific bacteria could prevent the development and/or progression of the IBD related tumors. In addition, consideration regarding the application of studying APRO family proteins for the comprehension of IBD related tumors has been presented. It is hypothesized that overexpression of Tob1, a member of APRO family proteins, in the epithelium of IBD could suppress the function of adjacent cytotoxic immune cells possibly via the paracrine signaling.
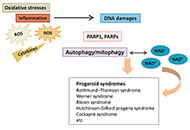
 Roles of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 and mitophagy in progeroid syndromes as well as physiological ageingOpen AccessReviewProgeroid syndromes are characterized by clinical signs of premature ageing, which may contain several diseases such as Werner syndrome, Bloom syndrome, Rothmund-Thomson syndrome, Hutchinson-Gilford [...] Read more.
Roles of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 and mitophagy in progeroid syndromes as well as physiological ageingOpen AccessReviewProgeroid syndromes are characterized by clinical signs of premature ageing, which may contain several diseases such as Werner syndrome, Bloom syndrome, Rothmund-Thomson syndrome, Hutchinson-Gilford [...] Read more.Progeroid syndromes are characterized by clinical signs of premature ageing, which may contain several diseases such as Werner syndrome, Bloom syndrome, Rothmund-Thomson syndrome, Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome, and Cockayne syndrome. These disorders may also exhibit some pathological involvements reminiscent of primary mitochondrial diseases. Emerging evidence has linked mitochondria even to physiological ageing. In addition, alterations in the maintenance pathway of mitochondria have been also deliberated as relevant in age-related diseases. In particular, mitophagy and its regulatory pathway might be key process for the homeostasis of mitochondria. Therefore, chronic DNA damage and/or the activation of poly[adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-ribose] polymerase 1 (PARP1) could be a threat to the mitochondrial alterations. The PARP1 is an enzyme responding to the DNA damage, which might be also involved in the mitophagy. Interestingly, the PARP1 has been reported to play an important role in the longevity of lifespan, which has attracted growing attention with the social development. This review may provide a rationalized overview of the involvement of mitochondrial oxidative stresses in genetically defined accelerated ageing, progeroid syndromes, physiological ageing, and/or age-related diseases for the innovative therapeutic approaches.
Naoko Suga ... Satoru MatsudaPublished: October 31, 2023 Explor Med. 2023;4:822–838
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2023.00180
This article belongs to the special issue Determinants of Exceptional LongevityProgeroid syndromes are characterized by clinical signs of premature ageing, which may contain several diseases such as Werner syndrome, Bloom syndrome, Rothmund-Thomson syndrome, Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome, and Cockayne syndrome. These disorders may also exhibit some pathological involvements reminiscent of primary mitochondrial diseases. Emerging evidence has linked mitochondria even to physiological ageing. In addition, alterations in the maintenance pathway of mitochondria have been also deliberated as relevant in age-related diseases. In particular, mitophagy and its regulatory pathway might be key process for the homeostasis of mitochondria. Therefore, chronic DNA damage and/or the activation of poly[adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-ribose] polymerase 1 (PARP1) could be a threat to the mitochondrial alterations. The PARP1 is an enzyme responding to the DNA damage, which might be also involved in the mitophagy. Interestingly, the PARP1 has been reported to play an important role in the longevity of lifespan, which has attracted growing attention with the social development. This review may provide a rationalized overview of the involvement of mitochondrial oxidative stresses in genetically defined accelerated ageing, progeroid syndromes, physiological ageing, and/or age-related diseases for the innovative therapeutic approaches.
 The gut microbiome and the immune systemOpen AccessReviewThe human body contains trillions of microbes which generally live in symbiosis with the host. The interaction of the gut microbiome with elements of the host immune system has far-reaching effects [...] Read more.
The gut microbiome and the immune systemOpen AccessReviewThe human body contains trillions of microbes which generally live in symbiosis with the host. The interaction of the gut microbiome with elements of the host immune system has far-reaching effects [...] Read more.The human body contains trillions of microbes which generally live in symbiosis with the host. The interaction of the gut microbiome with elements of the host immune system has far-reaching effects in the development of normal gut and systemic immune responses. Disturbances to this intricate relationship may be responsible for a multitude of gastrointestinal and systemic immune mediated diseases. This review describes the development of the gut microbiome and its interaction with host immune cells in both health and disease states.
Tenzin Choden, Nathaniel Aviv CohenPublished: May 31, 2022 Explor Med. 2022;3:219–233
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2022.00087The human body contains trillions of microbes which generally live in symbiosis with the host. The interaction of the gut microbiome with elements of the host immune system has far-reaching effects in the development of normal gut and systemic immune responses. Disturbances to this intricate relationship may be responsible for a multitude of gastrointestinal and systemic immune mediated diseases. This review describes the development of the gut microbiome and its interaction with host immune cells in both health and disease states.
 Reactive oxygen species in cancer progression and its role in therapeuticsOpen AccessReviewThe redox status in pathogenesis is critically regulated by careful balance between the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and their elimination. Increased ROS level above the cellular tole [...] Read more.
Reactive oxygen species in cancer progression and its role in therapeuticsOpen AccessReviewThe redox status in pathogenesis is critically regulated by careful balance between the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and their elimination. Increased ROS level above the cellular tole [...] Read more.The redox status in pathogenesis is critically regulated by careful balance between the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and their elimination. Increased ROS level above the cellular tolerability threshold results in apoptotic or necrotic cell death. ROS belongs to a group of highly reactive compounds that have evolved to play key roles in cellular signaling pathways. It’s widely assumed that a reasonable amount of ROS is essential for a variety of biological processes. Elevated levels of ROS are known to cause various pathologic conditions like neurological disorders, cardiovascular conditions, inflammation, autoimmunity, and cancer. ROS is well known to initiate and assist in progression of tumor by promoting proliferation and survival of cancer cells and thus facilitates pro-tumorigenic signaling in tumor microenvironment. As cancer cells become more resilient to the effects of ROS manipulating drugs, increased antioxidant capacity attenuates their susceptibility to cancer treatment. Excessive environmental stress, on the other hand, can cause cancer cells to die. This review summarizes various molecular mechanisms including the role of checkpoint inhibitors that can be harnessed to develop effective therapeutic strategies for targeting ROS related signaling in cancer.
Ranjeet Singh, Partha Pratim MannaPublished: February 22, 2022 Explor Med. 2022;3:43–57
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2022.00073
This article belongs to the special issue Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in Pathophysiological ConditionsThe redox status in pathogenesis is critically regulated by careful balance between the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and their elimination. Increased ROS level above the cellular tolerability threshold results in apoptotic or necrotic cell death. ROS belongs to a group of highly reactive compounds that have evolved to play key roles in cellular signaling pathways. It’s widely assumed that a reasonable amount of ROS is essential for a variety of biological processes. Elevated levels of ROS are known to cause various pathologic conditions like neurological disorders, cardiovascular conditions, inflammation, autoimmunity, and cancer. ROS is well known to initiate and assist in progression of tumor by promoting proliferation and survival of cancer cells and thus facilitates pro-tumorigenic signaling in tumor microenvironment. As cancer cells become more resilient to the effects of ROS manipulating drugs, increased antioxidant capacity attenuates their susceptibility to cancer treatment. Excessive environmental stress, on the other hand, can cause cancer cells to die. This review summarizes various molecular mechanisms including the role of checkpoint inhibitors that can be harnessed to develop effective therapeutic strategies for targeting ROS related signaling in cancer.
 Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes: pathophysiological mechanisms shared between the two faces of the same coinOpen AccessReviewThe pathophysiological mechanisms underlying the close relationship between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are multiple, complex and only partially known. The purpose of this paper was [...] Read more.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes: pathophysiological mechanisms shared between the two faces of the same coinOpen AccessReviewThe pathophysiological mechanisms underlying the close relationship between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are multiple, complex and only partially known. The purpose of this paper was [...] Read more.The pathophysiological mechanisms underlying the close relationship between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are multiple, complex and only partially known. The purpose of this paper was to review the current knowledge of these mechanisms in a unified manner. Subjects with NAFLD and T2DM have established insulin resistance (IR), which exacerbates the two comorbidities. IR worsens NAFLD by increasing the accumulation of free fatty acids (FFAs) in the liver. This occurs due to an increase in the influx of FFAs from peripheral adipose tissue by the activation of hormone-sensitive lipase. In addition, there is de novo increased lipogenesis, a transcription factor, the sterols regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1c (SREBP-1c), which activates the expression of several genes strongly promotes lipogenesis by the liver and facilitate storage of triglycerides. Lipids accumulation in the liver induces a chronic stress in the endoplasmic reticulum of the hepatocytes. Genome-wide association studies have identified genetic variants associated with NAFLD severity, but unrelated to IR. In particular, the alteration of patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3 contributes to the susceptibility to NAFLD. Furthermore, the lipotoxicity of ceramides and diacylglycerol, well known in T2DM, triggers a chronic inflammatory process favoring the progression from hepatic steatosis to steatohepatitis. Reactive oxygen species produced by mitochondrial dysfunction trigger both liver inflammation and beta-cells damage, promoting the progression of both NAFLD and T2DM. The close association between NAFLD and T2DM is bidirectional, as T2DM may trigger both NAFLD onset and its progression, but NAFLD itself may contribute to the development of IR and T2DM. Future studies on the mechanisms will have to deepen the knowledge of the interaction between the two pathologies and should allow the identification of new therapeutic targets for the treatment of NAFLD, currently substantially absent.
Carlo Acierno ... Ferdinando Carlo SassoPublished: October 30, 2020 Explor Med. 2020;1:287–306
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2020.00019
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring NAFLD/NASHThe pathophysiological mechanisms underlying the close relationship between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are multiple, complex and only partially known. The purpose of this paper was to review the current knowledge of these mechanisms in a unified manner. Subjects with NAFLD and T2DM have established insulin resistance (IR), which exacerbates the two comorbidities. IR worsens NAFLD by increasing the accumulation of free fatty acids (FFAs) in the liver. This occurs due to an increase in the influx of FFAs from peripheral adipose tissue by the activation of hormone-sensitive lipase. In addition, there is de novo increased lipogenesis, a transcription factor, the sterols regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1c (SREBP-1c), which activates the expression of several genes strongly promotes lipogenesis by the liver and facilitate storage of triglycerides. Lipids accumulation in the liver induces a chronic stress in the endoplasmic reticulum of the hepatocytes. Genome-wide association studies have identified genetic variants associated with NAFLD severity, but unrelated to IR. In particular, the alteration of patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3 contributes to the susceptibility to NAFLD. Furthermore, the lipotoxicity of ceramides and diacylglycerol, well known in T2DM, triggers a chronic inflammatory process favoring the progression from hepatic steatosis to steatohepatitis. Reactive oxygen species produced by mitochondrial dysfunction trigger both liver inflammation and beta-cells damage, promoting the progression of both NAFLD and T2DM. The close association between NAFLD and T2DM is bidirectional, as T2DM may trigger both NAFLD onset and its progression, but NAFLD itself may contribute to the development of IR and T2DM. Future studies on the mechanisms will have to deepen the knowledge of the interaction between the two pathologies and should allow the identification of new therapeutic targets for the treatment of NAFLD, currently substantially absent.
 Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes: pathophysiological mechanisms shared between the two faces of the same coinOpen AccessReviewThe pathophysiological mechanisms underlying the close relationship between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are multiple, complex and only partially known. The purpose of this paper was [...] Read more.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes: pathophysiological mechanisms shared between the two faces of the same coinOpen AccessReviewThe pathophysiological mechanisms underlying the close relationship between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are multiple, complex and only partially known. The purpose of this paper was [...] Read more.The pathophysiological mechanisms underlying the close relationship between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are multiple, complex and only partially known. The purpose of this paper was to review the current knowledge of these mechanisms in a unified manner. Subjects with NAFLD and T2DM have established insulin resistance (IR), which exacerbates the two comorbidities. IR worsens NAFLD by increasing the accumulation of free fatty acids (FFAs) in the liver. This occurs due to an increase in the influx of FFAs from peripheral adipose tissue by the activation of hormone-sensitive lipase. In addition, there is de novo increased lipogenesis, a transcription factor, the sterols regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1c (SREBP-1c), which activates the expression of several genes strongly promotes lipogenesis by the liver and facilitate storage of triglycerides. Lipids accumulation in the liver induces a chronic stress in the endoplasmic reticulum of the hepatocytes. Genome-wide association studies have identified genetic variants associated with NAFLD severity, but unrelated to IR. In particular, the alteration of patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3 contributes to the susceptibility to NAFLD. Furthermore, the lipotoxicity of ceramides and diacylglycerol, well known in T2DM, triggers a chronic inflammatory process favoring the progression from hepatic steatosis to steatohepatitis. Reactive oxygen species produced by mitochondrial dysfunction trigger both liver inflammation and beta-cells damage, promoting the progression of both NAFLD and T2DM. The close association between NAFLD and T2DM is bidirectional, as T2DM may trigger both NAFLD onset and its progression, but NAFLD itself may contribute to the development of IR and T2DM. Future studies on the mechanisms will have to deepen the knowledge of the interaction between the two pathologies and should allow the identification of new therapeutic targets for the treatment of NAFLD, currently substantially absent.
Carlo Acierno ... Ferdinando Carlo SassoPublished: October 30, 2020 Explor Med. 2020;1:287–306
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2020.00019
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring NAFLD/NASHThe pathophysiological mechanisms underlying the close relationship between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are multiple, complex and only partially known. The purpose of this paper was to review the current knowledge of these mechanisms in a unified manner. Subjects with NAFLD and T2DM have established insulin resistance (IR), which exacerbates the two comorbidities. IR worsens NAFLD by increasing the accumulation of free fatty acids (FFAs) in the liver. This occurs due to an increase in the influx of FFAs from peripheral adipose tissue by the activation of hormone-sensitive lipase. In addition, there is de novo increased lipogenesis, a transcription factor, the sterols regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1c (SREBP-1c), which activates the expression of several genes strongly promotes lipogenesis by the liver and facilitate storage of triglycerides. Lipids accumulation in the liver induces a chronic stress in the endoplasmic reticulum of the hepatocytes. Genome-wide association studies have identified genetic variants associated with NAFLD severity, but unrelated to IR. In particular, the alteration of patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3 contributes to the susceptibility to NAFLD. Furthermore, the lipotoxicity of ceramides and diacylglycerol, well known in T2DM, triggers a chronic inflammatory process favoring the progression from hepatic steatosis to steatohepatitis. Reactive oxygen species produced by mitochondrial dysfunction trigger both liver inflammation and beta-cells damage, promoting the progression of both NAFLD and T2DM. The close association between NAFLD and T2DM is bidirectional, as T2DM may trigger both NAFLD onset and its progression, but NAFLD itself may contribute to the development of IR and T2DM. Future studies on the mechanisms will have to deepen the knowledge of the interaction between the two pathologies and should allow the identification of new therapeutic targets for the treatment of NAFLD, currently substantially absent.
 Reactive oxygen species in cancer progression and its role in therapeuticsOpen AccessReviewThe redox status in pathogenesis is critically regulated by careful balance between the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and their elimination. Increased ROS level above the cellular tole [...] Read more.
Reactive oxygen species in cancer progression and its role in therapeuticsOpen AccessReviewThe redox status in pathogenesis is critically regulated by careful balance between the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and their elimination. Increased ROS level above the cellular tole [...] Read more.The redox status in pathogenesis is critically regulated by careful balance between the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and their elimination. Increased ROS level above the cellular tolerability threshold results in apoptotic or necrotic cell death. ROS belongs to a group of highly reactive compounds that have evolved to play key roles in cellular signaling pathways. It’s widely assumed that a reasonable amount of ROS is essential for a variety of biological processes. Elevated levels of ROS are known to cause various pathologic conditions like neurological disorders, cardiovascular conditions, inflammation, autoimmunity, and cancer. ROS is well known to initiate and assist in progression of tumor by promoting proliferation and survival of cancer cells and thus facilitates pro-tumorigenic signaling in tumor microenvironment. As cancer cells become more resilient to the effects of ROS manipulating drugs, increased antioxidant capacity attenuates their susceptibility to cancer treatment. Excessive environmental stress, on the other hand, can cause cancer cells to die. This review summarizes various molecular mechanisms including the role of checkpoint inhibitors that can be harnessed to develop effective therapeutic strategies for targeting ROS related signaling in cancer.
Ranjeet Singh, Partha Pratim MannaPublished: February 22, 2022 Explor Med. 2022;3:43–57
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2022.00073
This article belongs to the special issue Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in Pathophysiological ConditionsThe redox status in pathogenesis is critically regulated by careful balance between the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and their elimination. Increased ROS level above the cellular tolerability threshold results in apoptotic or necrotic cell death. ROS belongs to a group of highly reactive compounds that have evolved to play key roles in cellular signaling pathways. It’s widely assumed that a reasonable amount of ROS is essential for a variety of biological processes. Elevated levels of ROS are known to cause various pathologic conditions like neurological disorders, cardiovascular conditions, inflammation, autoimmunity, and cancer. ROS is well known to initiate and assist in progression of tumor by promoting proliferation and survival of cancer cells and thus facilitates pro-tumorigenic signaling in tumor microenvironment. As cancer cells become more resilient to the effects of ROS manipulating drugs, increased antioxidant capacity attenuates their susceptibility to cancer treatment. Excessive environmental stress, on the other hand, can cause cancer cells to die. This review summarizes various molecular mechanisms including the role of checkpoint inhibitors that can be harnessed to develop effective therapeutic strategies for targeting ROS related signaling in cancer.
 PNPLA3 gene and kidney diseaseOpen AccessReviewChronic kidney disease (CKD) is a disease regularly seen in clinical practice. At present, CKD is described as a change of kidney structure and/or function and it is classified in relation to cause, values of glomerular filtration [...] Read more.
PNPLA3 gene and kidney diseaseOpen AccessReviewChronic kidney disease (CKD) is a disease regularly seen in clinical practice. At present, CKD is described as a change of kidney structure and/or function and it is classified in relation to cause, values of glomerular filtration [...] Read more.Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a disease regularly seen in clinical practice. At present, CKD is described as a change of kidney structure and/or function and it is classified in relation to cause, values of glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria category. Seeing that CKD is closely linked to the development of end-stage renal disease and other comorbidities, the determination of additional independent predictors for CKD is clinically necessary. At present, there is evidence associating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) with CKD, thereby suggesting that NAFLD patients may require intensive surveillance to reduce their risk of CKD. In 2008, genome-wide association studies documented an association between the variant rs738409 (C > G p.I148M) in the patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3 (PNPLA3) gene (mainly implicated in the lipid regulation) and the entire spectrum of NAFLD (i.e., liver steatosis, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, fibrosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma). In the last years, accumulating epidemiological evidence suggests the existence of a relationship between PNPLA3 rs738409 and risk of CKD, indicating that rs738409 may also contribute to the kidney injury. This is of particular scientific interest, as such association may explain, at least in part, the epidemiological association between liver and kidney disease. In this narrative review, we will discuss the accumulating evidence regarding the association between PNPLA3 rs738409 and risk of CKD, the putative biological mechanisms underpinning such relationship, and the possible future perspective.
Alessandro Mantovani, Chiara ZusiPublished: February 29, 2020 Explor Med. 2020;1:42–50
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2020.00004Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a disease regularly seen in clinical practice. At present, CKD is described as a change of kidney structure and/or function and it is classified in relation to cause, values of glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria category. Seeing that CKD is closely linked to the development of end-stage renal disease and other comorbidities, the determination of additional independent predictors for CKD is clinically necessary. At present, there is evidence associating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) with CKD, thereby suggesting that NAFLD patients may require intensive surveillance to reduce their risk of CKD. In 2008, genome-wide association studies documented an association between the variant rs738409 (C > G p.I148M) in the patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3 (PNPLA3) gene (mainly implicated in the lipid regulation) and the entire spectrum of NAFLD (i.e., liver steatosis, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, fibrosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma). In the last years, accumulating epidemiological evidence suggests the existence of a relationship between PNPLA3 rs738409 and risk of CKD, indicating that rs738409 may also contribute to the kidney injury. This is of particular scientific interest, as such association may explain, at least in part, the epidemiological association between liver and kidney disease. In this narrative review, we will discuss the accumulating evidence regarding the association between PNPLA3 rs738409 and risk of CKD, the putative biological mechanisms underpinning such relationship, and the possible future perspective.
 Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and portal hypertensionOpen AccessReviewNonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a substantial and growing problem worldwide and has become the second most common indication for liver transplantation as it may progress to cirrhosis and develop complications from port [...] Read more.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and portal hypertensionOpen AccessReviewNonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a substantial and growing problem worldwide and has become the second most common indication for liver transplantation as it may progress to cirrhosis and develop complications from port [...] Read more.Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a substantial and growing problem worldwide and has become the second most common indication for liver transplantation as it may progress to cirrhosis and develop complications from portal hypertension primarily caused by advanced fibrosis and erratic tissue remodeling. However, elevated portal venous pressure has also been detected in experimental models of fatty liver and in human NAFLD when fibrosis is far less advanced and cirrhosis is absent. Early increases in intrahepatic vascular resistance may contribute to the progression of liver disease. Specific pathophenotypes linked to the development of portal hypertension in NAFLD include hepatocellular lipid accumulation and ballooning injury, capillarization of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells, enhanced contractility of hepatic stellate cells, activation of Kupffer cells and pro-inflammatory pathways, adhesion and entrapment of recruited leukocytes, microthrombosis, angiogenesis and perisinusoidal fibrosis. These pathological events are amplified in NAFLD by concomitant visceral obesity, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes and dysbiosis, promoting aberrant interactions with adipose tissue, skeletal muscle and gut microbiota. Measurement of the hepatic venous pressure gradient by retrograde insertion of a balloon-tipped central vein catheter is the current reference method for predicting outcomes of cirrhosis associated with clinically significant portal hypertension and guiding interventions. This invasive technique is rarely considered in the absence of cirrhosis where currently available clinical, imaging and laboratory correlates of portal hypertension may not reflect early changes in liver hemodynamics. Availability of less invasive but sufficiently sensitive methods for the assessment of portal venous pressure in NAFLD remains therefore an unmet need. Recent efforts to develop new biomarkers and endoscopy-based approaches such as endoscopic ultrasound-guided measurement of portal pressure gradient may help achieve this goal. In addition, cellular and molecular targets are being identified to guide emerging therapies in the prevention and management of portal hypertension.
Marvin Ryou ... Gyorgy BaffyPublished: June 29, 2020 Explor Med. 2020;1:149–169
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2020.00011
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring NAFLD/NASHNonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a substantial and growing problem worldwide and has become the second most common indication for liver transplantation as it may progress to cirrhosis and develop complications from portal hypertension primarily caused by advanced fibrosis and erratic tissue remodeling. However, elevated portal venous pressure has also been detected in experimental models of fatty liver and in human NAFLD when fibrosis is far less advanced and cirrhosis is absent. Early increases in intrahepatic vascular resistance may contribute to the progression of liver disease. Specific pathophenotypes linked to the development of portal hypertension in NAFLD include hepatocellular lipid accumulation and ballooning injury, capillarization of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells, enhanced contractility of hepatic stellate cells, activation of Kupffer cells and pro-inflammatory pathways, adhesion and entrapment of recruited leukocytes, microthrombosis, angiogenesis and perisinusoidal fibrosis. These pathological events are amplified in NAFLD by concomitant visceral obesity, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes and dysbiosis, promoting aberrant interactions with adipose tissue, skeletal muscle and gut microbiota. Measurement of the hepatic venous pressure gradient by retrograde insertion of a balloon-tipped central vein catheter is the current reference method for predicting outcomes of cirrhosis associated with clinically significant portal hypertension and guiding interventions. This invasive technique is rarely considered in the absence of cirrhosis where currently available clinical, imaging and laboratory correlates of portal hypertension may not reflect early changes in liver hemodynamics. Availability of less invasive but sufficiently sensitive methods for the assessment of portal venous pressure in NAFLD remains therefore an unmet need. Recent efforts to develop new biomarkers and endoscopy-based approaches such as endoscopic ultrasound-guided measurement of portal pressure gradient may help achieve this goal. In addition, cellular and molecular targets are being identified to guide emerging therapies in the prevention and management of portal hypertension.
 3D printing in biomedicine: advancing personalized care through additive manufacturingOpen AccessReviewThe integration of three-dimensional (3D) printing techniques into the domains of biomedical research and personalized medicine highlights the evolving paradigm shifts within contemporary healthcare [...] Read more.
3D printing in biomedicine: advancing personalized care through additive manufacturingOpen AccessReviewThe integration of three-dimensional (3D) printing techniques into the domains of biomedical research and personalized medicine highlights the evolving paradigm shifts within contemporary healthcare [...] Read more.The integration of three-dimensional (3D) printing techniques into the domains of biomedical research and personalized medicine highlights the evolving paradigm shifts within contemporary healthcare. This technological advancement signifies potential breakthroughs in patient-specific therapeutic interventions and innovations. This systematic review offers a critical assessment of the existing literature, elucidating the present status, inherent challenges, and prospective avenues of 3D printing in augmenting biomedical applications and formulating tailored medical strategies. Based on an exhaustive literature analysis comprising empirical studies, case studies, and extensive reviews from the past decade, pivotal sectors including tissue engineering, prosthetic development, drug delivery systems, and customized medical apparatuses are delineated. The advent of 3D printing provides precision in the fabrication of patient-centric implants, bio-structures, and devices, thereby mitigating associated risks. Concurrently, it facilitates the ideation of individualized drug delivery paradigms to optimize therapeutic outcomes. Notwithstanding these advancements, issues concerning material biocompatibility, regulatory compliance, and the economic implications of avant-garde printing techniques persist. To fully harness the transformative potential of 3D printing in healthcare, collaborative endeavors amongst academicians, clinicians, industrial entities, and regulatory bodies are paramount. With continued research and innovation, 3D printing is poised to redefine the trajectories of biomedical science and patient-centric care. The paper aims to justify the research objective of whether to what extent the integration of 3D printing technology in biomedicine enhances patient-specific treatment and contributes to improved healthcare outcomes.
Kalyani Pathak ... Barbie BorthakurPublished: December 29, 2023 Explor Med. 2023;4:1135–1167
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2023.00200
This article belongs to the special issue Exploration of 3D and 4D Printing in the Biomedical and Personalized Medicine Fields: Merits and ChallengesThe integration of three-dimensional (3D) printing techniques into the domains of biomedical research and personalized medicine highlights the evolving paradigm shifts within contemporary healthcare. This technological advancement signifies potential breakthroughs in patient-specific therapeutic interventions and innovations. This systematic review offers a critical assessment of the existing literature, elucidating the present status, inherent challenges, and prospective avenues of 3D printing in augmenting biomedical applications and formulating tailored medical strategies. Based on an exhaustive literature analysis comprising empirical studies, case studies, and extensive reviews from the past decade, pivotal sectors including tissue engineering, prosthetic development, drug delivery systems, and customized medical apparatuses are delineated. The advent of 3D printing provides precision in the fabrication of patient-centric implants, bio-structures, and devices, thereby mitigating associated risks. Concurrently, it facilitates the ideation of individualized drug delivery paradigms to optimize therapeutic outcomes. Notwithstanding these advancements, issues concerning material biocompatibility, regulatory compliance, and the economic implications of avant-garde printing techniques persist. To fully harness the transformative potential of 3D printing in healthcare, collaborative endeavors amongst academicians, clinicians, industrial entities, and regulatory bodies are paramount. With continued research and innovation, 3D printing is poised to redefine the trajectories of biomedical science and patient-centric care. The paper aims to justify the research objective of whether to what extent the integration of 3D printing technology in biomedicine enhances patient-specific treatment and contributes to improved healthcare outcomes.
 Identification of digital voice biomarkers for cognitive healthOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Human voice contains rich information. Few longitudinal studies have been conducted to investigate the potential of voice to monitor cognitive health. The objective of this study is to identify voice biomarkers that are pr [...] Read more.
Identification of digital voice biomarkers for cognitive healthOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Human voice contains rich information. Few longitudinal studies have been conducted to investigate the potential of voice to monitor cognitive health. The objective of this study is to identify voice biomarkers that are pr [...] Read more.Aim:
Human voice contains rich information. Few longitudinal studies have been conducted to investigate the potential of voice to monitor cognitive health. The objective of this study is to identify voice biomarkers that are predictive of future dementia.
Methods:
Participants were recruited from the Framingham Heart Study. The vocal responses to neuropsychological tests were recorded, which were then diarized to identify participant voice segments. Acoustic features were extracted with the OpenSMILE toolkit (v2.1). The association of each acoustic feature with incident dementia was assessed by Cox proportional hazards models.
Results:
Our study included 6, 528 voice recordings from 4, 849 participants (mean age 63 ± 15 years old, 54.6% women). The majority of participants (71.2%) had one voice recording, 23.9% had two voice recordings, and the remaining participants (4.9%) had three or more voice recordings. Although all asymptomatic at the time of examination, participants who developed dementia tended to have shorter segments than those who were dementia free (P < 0.001). Additionally, 14 acoustic features were significantly associated with dementia after adjusting for multiple testing (P < 0.05 / 48 = 1 × 10–3). The most significant acoustic feature was jitterDDP_sma_de (P = 7.9 × 10–7), which represents the differential frame-to-frame Jitter. A voice based linear classifier was also built that was capable of predicting incident dementia with area under curve of 0.812.
Conclusions:
Multiple acoustic and linguistic features are identified that are associated with incident dementia among asymptomatic participants, which could be used to build better prediction models for passive cognitive health monitoring.
Honghuang Lin ... Rhoda AuPublished: December 31, 2020 Explor Med. 2020;1:406–417
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2020.00028
This article belongs to the special issue Digital Biomarkers: The New Frontier for Medicine and ResearchAim:
Human voice contains rich information. Few longitudinal studies have been conducted to investigate the potential of voice to monitor cognitive health. The objective of this study is to identify voice biomarkers that are predictive of future dementia.
Methods:
Participants were recruited from the Framingham Heart Study. The vocal responses to neuropsychological tests were recorded, which were then diarized to identify participant voice segments. Acoustic features were extracted with the OpenSMILE toolkit (v2.1). The association of each acoustic feature with incident dementia was assessed by Cox proportional hazards models.
Results:
Our study included 6, 528 voice recordings from 4, 849 participants (mean age 63 ± 15 years old, 54.6% women). The majority of participants (71.2%) had one voice recording, 23.9% had two voice recordings, and the remaining participants (4.9%) had three or more voice recordings. Although all asymptomatic at the time of examination, participants who developed dementia tended to have shorter segments than those who were dementia free (P < 0.001). Additionally, 14 acoustic features were significantly associated with dementia after adjusting for multiple testing (P < 0.05 / 48 = 1 × 10–3). The most significant acoustic feature was jitterDDP_sma_de (P = 7.9 × 10–7), which represents the differential frame-to-frame Jitter. A voice based linear classifier was also built that was capable of predicting incident dementia with area under curve of 0.812.
Conclusions:
Multiple acoustic and linguistic features are identified that are associated with incident dementia among asymptomatic participants, which could be used to build better prediction models for passive cognitive health monitoring.
Special Issues Practical Tips for Cancer Care: Guidance for Patients, Caregivers, and Healthcare Professionals
Practical Tips for Cancer Care: Guidance for Patients, Caregivers, and Healthcare ProfessionalsProf. Patricia Tai
Submission Deadline: September 30, 2025
Published Articles: 0
 Assessment of Atrial and Ventricular Volumes and Functional Properties: Novel Insights
Assessment of Atrial and Ventricular Volumes and Functional Properties: Novel InsightsProf. Attila Nemes
Submission Deadline: August 31, 2025
Published Articles: 0
 Lipid Peroxidation and Cancer
Lipid Peroxidation and CancerProf. Neven Zarkovic
Submission Deadline: July 31, 2025
Published Articles: 0
 Innovative Approaches to Chronic Pain Management: from Multidisciplinary Strategies to Artificial Intelligence Perspectives
Innovative Approaches to Chronic Pain Management: from Multidisciplinary Strategies to Artificial Intelligence PerspectivesProf. Marco Cascella
Submission Deadline: April 30, 2025
Published Articles: 2
 Global Perspectives on the Clinical Diagnosis, Treatment, and Functional Cure of HIV Infection in the Post-ART Era
Global Perspectives on the Clinical Diagnosis, Treatment, and Functional Cure of HIV Infection in the Post-ART EraProf. Hongzhou Lu
Submission Deadline: March 31, 2025
Published Articles: 0
 Disrupted Cytokine Signaling Pathways in Autoimmunity
Disrupted Cytokine Signaling Pathways in AutoimmunityProf. Alister C. Ward
Submission Deadline: May 31, 2025
Published Articles: 0
 Molecular Diagnostics in Oncology
Molecular Diagnostics in OncologyProf. Evgeny Imyanitov
Submission Deadline: December 31, 2024
Published Articles: 1
 Advances in Oral Cancer: Prevention, Diagnosis, and Therapeutics
Advances in Oral Cancer: Prevention, Diagnosis, and TherapeuticsDr. Luca Fiorillo
Submission Deadline: December 31, 2024
Published Articles: 3
 Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Cardiovascular Medicine
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Cardiovascular MedicineProf. Zhong Wang Dr. Ienglam Lei Dr. Liu Liu
Submission Deadline: August 31, 2025
Published Articles: 0
 Oral Health Interconnections and Multidisciplinary Approaches
Oral Health Interconnections and Multidisciplinary ApproachesDr. Giuseppe Minervini
Submission Deadline: December 31, 2024
Published Articles: 10
 Prostate Specific Membrane Antigen (PSMA) in Prostate Cancer
Prostate Specific Membrane Antigen (PSMA) in Prostate CancerDr. Finn Edler von Eyben
Submission Deadline: June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 0
 Neurophysiological Mechanisms of Aging and Dementia
Neurophysiological Mechanisms of Aging and DementiaProf. Fabrizio Vecchio
Submission Deadline: June 30, 2024
Published Articles: 4
 Personalized Medicine in Cancer Therapy
Personalized Medicine in Cancer TherapyProf. Haim Werner Prof. Ilan Bruchim
Submission Deadline: June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 0
 Spotlight on Cervical Cancer: Prevention, Early-Diagnosis, and Treatments
Spotlight on Cervical Cancer: Prevention, Early-Diagnosis, and TreatmentsDr. Andrea Giannini Dr. Giorgio Bogani
Submission Deadline: February 29, 2024
Published Articles: 4
 Advances in the Identification and Mechanisms of Action of Luminal Compounds Involved in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Advances in the Identification and Mechanisms of Action of Luminal Compounds Involved in Inflammatory Bowel DiseasesDr. Francois Blachier
Submission Deadline: September 30, 2024
Published Articles: 1
 Drug Adherence in Hypertension
Drug Adherence in HypertensionProf. Sverre E. Kjeldsen
Submission Deadline: December 31, 2024
Published Articles: 6
 Emerging Infectious Diseases
Emerging Infectious DiseasesProf. Marcos Roberto Tovani-Palone
Submission Deadline: June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 3
 Gut Microbiota Derived Metabolites and Chronic Inflammatory Diseases
Gut Microbiota Derived Metabolites and Chronic Inflammatory DiseasesDr. Zeneng Wang
Submission Deadline: September 30, 2024
Published Articles: 4
 Lung Fibrosis—Models and Mechanisms
Lung Fibrosis—Models and MechanismsProf. Bernhard Ryffel
Submission Deadline: June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 4
 Breast Cancer: Basic and Clinical Advances
Breast Cancer: Basic and Clinical AdvancesDr. Andrea Nicolini
Submission Deadline: December 31, 2023
Published Articles: 8
 Biomaterials and Biomarkers in Dentistry: Up to Date
Biomaterials and Biomarkers in Dentistry: Up to DateProf. Gaetano Isola
Submission Deadline: August 31, 2024
Published Articles: 6
 RNA World in Health and Disease
RNA World in Health and DiseaseDr. Marco Ragusa Dr. Cristina Barbagallo
Submission Deadline: June 30, 2024
Published Articles: 5
 Exploration of 3D and 4D Printing in the Biomedical and Personalized Medicine Fields: Merits and Challenges
Exploration of 3D and 4D Printing in the Biomedical and Personalized Medicine Fields: Merits and ChallengesDr. Nermeen A. Elkasabgy
Submission Deadline: December 31, 2023
Published Articles: 5
 Determinants of Exceptional Longevity
Determinants of Exceptional LongevityDr. Calogero Caruso
Submission Deadline: December 31, 2023
Published Articles: 6
 Techniques in Repurposing and Targeted Delivery: Bringing a New Life to Shelved Drugs
Techniques in Repurposing and Targeted Delivery: Bringing a New Life to Shelved DrugsDr. Md Noushad Javed
Submission Deadline: October 31, 2022
Published Articles: 9
 Beyond Weed: Clinical Applications of Cannabis and Cannabinoids
Beyond Weed: Clinical Applications of Cannabis and CannabinoidsDr. Staci Gruber Dr. M. Kathryn Dahlgren Dr. Kelly Sagar
Submission Deadline: October 15, 2022
Published Articles: 8
 Disease Diagnosis, Molecular Mechanism and Therapeutic Strategies in Kidney Injury and Fibrosis
Disease Diagnosis, Molecular Mechanism and Therapeutic Strategies in Kidney Injury and FibrosisProf. Yingyong Zhao
Submission Deadline: June 30, 2022
Published Articles: 6
 The Role of Gut Microbiota and its Metabolites in Gastrointestinal Diseases
The Role of Gut Microbiota and its Metabolites in Gastrointestinal DiseasesDr. Feng Tian Dr. Changqing Jing
Submission Deadline: May 20, 2022
Published Articles: 7
 Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in Pathophysiological Conditions
Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in Pathophysiological ConditionsProf. Dr. Esma R. Isenovic Dr. Milan Obradovic
Submission Deadline: December 31, 2021
Published Articles: 8
 Exploring Chronic Liver Disease
Exploring Chronic Liver DiseaseDr. Amedeo Lonardo
Submission Deadline: December 31, 2021
Published Articles: 11
 Exploring Aortic Disease
Exploring Aortic DiseaseDr. Kathleen G. Morgan
Submission Deadline: January 01, 2023
Published Articles: 7
 Angiotensins—A Century of Progress
Angiotensins—A Century of ProgressDr. Carlos M. Ferrario Dr. Leanne Groban
Submission Deadline: December 31, 2020
Published Articles: 10
 Nanomedicine and Cancer Immunotherapy
Nanomedicine and Cancer ImmunotherapyDr. Haijun Yu Dr. Yang Shi
Submission Deadline: January 01, 2023
Published Articles: 5
 Exploring Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Exploring Type 2 Diabetes MellitusDr. Alessandro Mantovani Dr. Giovanni Targher
Submission Deadline: July 31, 2020
Published Articles: 6
 Exploring NAFLD/NASH
Exploring NAFLD/NASHDr. Amedeo Lonardo Dr. Giovanni Targher
Submission Deadline: June 01, 2020
Published Articles: 12
 Digital Biomarkers: The New Frontier for Medicine and Research
Digital Biomarkers: The New Frontier for Medicine and ResearchDr. Rhoda Au
Submission Deadline: June 20, 2020
Published Articles: 10
 The Biological Basis of Substance Use Disorders
The Biological Basis of Substance Use DisordersDr. Richard M. Sherva
Submission Deadline: January 01, 2023
Published Articles: 7
-
-
NewsletterWinners of Highly Cited Paper Award 2024
 Jan. 22, 2025Prof. Prabir Patra of EM Editorial Board Promotes Journal at 2024 BMES Annual Meeting
Jan. 22, 2025Prof. Prabir Patra of EM Editorial Board Promotes Journal at 2024 BMES Annual Meeting Oct. 31, 2024MoreEM Proudly Sponsored the 30th Congress of the International Society of Hypertension - ISH 2024
Oct. 31, 2024MoreEM Proudly Sponsored the 30th Congress of the International Society of Hypertension - ISH 2024 Sep. 23, 2024
Sep. 23, 2024 -
Selected Special Issues
-
Articles Available in PMCPapers supported by NIH (or other funding bodies) are encouraged to be deposited in PMC.Neuropsychological test validation of speech markers of cognitive impairment in the Framingham Cognitive Aging Cohort View in PMCProof of concept: digital clock drawing behaviors prior to transcatheter aortic valve replacement may predict length of hospital stay and cost of care View in PMCGenome-wide association study of phenotypes measuring progression from first cocaine or opioid use to dependence reveals novel risk genes View in PMCPlacental OPRM1 DNA methylation and associations with neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome, a pilot study View in PMC