-
 Special Issue Topic
Special Issue TopicGut Microbiota Derived Metabolites and Chronic Inflammatory Diseases
Submission Deadline: September 30, 2024Guest Editor
Dr. Zeneng Wang E-Mail
Staff Scientist, Department of Cardiovascular & Metabolic Sciences, Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland Clinic, USA
Research Keywords: gut microbiome; cardiovascular disease; atherosclerosis; metabolomics; mass spectrometry
About the Special Issue
Microbes inhabit human gut with a number reaching trillions, higher than the cell number composing human body and total genome size 150 times as long as human genome. Gut microbiota plays important roles in human health, which include maintaining gut barrier, helping digesting food, producing vitamins, preventing pathogen overgrowth and modulating human immunity as well. Gut microbiota is involved in synthesis of some bioactive metabolites, which circulate in human blood and are delivered to different target tissues, mediating the effects of gut microbiota. So gut microbiota is regarded as the largest endocrine organ. There are hundreds of gut microbiota derived metabolites reported. Some of them, such as short chain fatty acids, which are the fermented metabolites of dietary fiber, can maintain gut barrier, induce release of gut hormones, peptide YY (PYY) and glucagon like peptide 1 (GLP-1), to modulate satiety, energy harvest and fat storage and inhibit inflammation. Some of them, such as trimethylamine N-oxide, p-cresyl sulfate and indoxyl sulfate, show pro-inflammatory effects, leading to enhanced chronic inflammatory diseases. Recently gut microbiota metabolites of tryptophan, indole acetic acid and indole-3-propionic acid, have been reported to enhance sensitivity of chemotherapy against cancer. Targeting gut microbiota derived metabolites will become a strategy to treat chronic diseases. In this special issue, we will discuss the roles of gut microbiota derived metabolites in inflammatory chronic diseases, which will provide important clues to prevent and treat the diseases.
Call for Papers
Published Articles
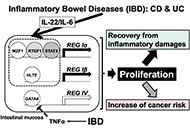 The regenerating gene (Reg) family genes in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)Open AccessReviewRegenerating gene (Reg) was first isolated in 1988 and proposed to be specifically expressed in rat regenerating pancreatic islets. Since then, many genes homologous to Reg have been discovered in o [...] Read more.Shin Takasawa ... Maiko TakedaPublished: February 05, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001278
The regenerating gene (Reg) family genes in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)Open AccessReviewRegenerating gene (Reg) was first isolated in 1988 and proposed to be specifically expressed in rat regenerating pancreatic islets. Since then, many genes homologous to Reg have been discovered in o [...] Read more.Shin Takasawa ... Maiko TakedaPublished: February 05, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001278
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001278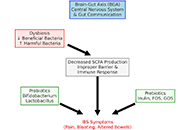 Gut microbiota-derived metabolites and chronic inflammatory diseasesOpen AccessReviewThe gut microbiota, a complex ecosystem of microorganisms, plays an essential role in maintaining immune and metabolic homeostasis. Disruption of this microbial balance, known as dysbiosis, has been [...] Read more.Alejandra Vargas ... David A. JohnsonPublished: January 19, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001275
Gut microbiota-derived metabolites and chronic inflammatory diseasesOpen AccessReviewThe gut microbiota, a complex ecosystem of microorganisms, plays an essential role in maintaining immune and metabolic homeostasis. Disruption of this microbial balance, known as dysbiosis, has been [...] Read more.Alejandra Vargas ... David A. JohnsonPublished: January 19, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001275
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001275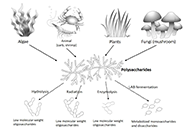 Natural polysaccharides-based postbiotics and their potential applicationsOpen AccessReviewPostbiotics, representing the newest member of the family of biotics, are metabolites produced as a result of fermentation of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) in the De Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe (MRS) mediu [...] Read more.Weinan Du ... Juxiu LiPublished: June 28, 2024 Explor Med. 2024;5:444–458
Natural polysaccharides-based postbiotics and their potential applicationsOpen AccessReviewPostbiotics, representing the newest member of the family of biotics, are metabolites produced as a result of fermentation of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) in the De Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe (MRS) mediu [...] Read more.Weinan Du ... Juxiu LiPublished: June 28, 2024 Explor Med. 2024;5:444–458
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2024.00230 Analysis of microbiocenosis of a gingival sulcus and periodontal pockets of patients with periodontal diseases associated with systemic pathologyOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The aim is to analyze the microbiome of gingival sulcus and periodontal pockets of patients with periodontal disease associated with systemic diseases. Methods: A microbiological study [...] Read more.Olha Denefil ... Khrystyna LozaPublished: December 11, 2023 Explor Med. 2023;4:942–955
Analysis of microbiocenosis of a gingival sulcus and periodontal pockets of patients with periodontal diseases associated with systemic pathologyOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The aim is to analyze the microbiome of gingival sulcus and periodontal pockets of patients with periodontal disease associated with systemic diseases. Methods: A microbiological study [...] Read more.Olha Denefil ... Khrystyna LozaPublished: December 11, 2023 Explor Med. 2023;4:942–955
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2023.00186 -
-
Ongoing Special Issues
-
Completed Special Issues