Abstract
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a severe neurodegenerative disease that is associated with selective and progressive loss of motor neurons. As a consequence, the symptoms of ALS are muscle cramps and weakness, and it eventually leads to death. The general markers for early diagnosis can assist ALS patients in receiving early intervention and prolonging their survival. Recently, some novel approaches or previously suggested methods have validated the potential for early diagnosis of ALS. The purpose of this review is to summarize the status of current general markers discovery and development for early diagnosis of ALS, including genes, proteins neuroimaging, neurophysiology, neuroultrasound, and machine learning models. The main genetic markers evaluated are superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1), chromosome 9 open reading frame 72 (C9orf72), transactivation-responsive DNA binding protein 43 (TARDBP), and fused in sarcoma (FUS) genes. Among proteins, neurofilament light chain is still the most established disease-specific adaptive change in ALS. The expression of chitinases, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), and inflammatory factors are changed in the early stage of ALS. Besides, more patient-friendly and accessible feature assays are explored by the development of neuroimaging, neurophysiology, and neuroultrasound techniques. The novel disease-specific changes exhibited the promising potential for early diagnosis of ALS. All of these general markers still have limitations in the early diagnosis, therefore there is an urgent need for the validation and development of new disease-specific features for ALS.
Keywords
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, marker, genes, neurofilament, magnetic resonance imaging, positron emission tomography, neurophysiology, neuroultrasoundIntroduction
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a highly lethal disease characterized by selective and progressive loss of cortical, spinal, and bulbar motor neurons [1]. Initially presenting from focal muscle weakness involving upper or lower limbs, bulbar, or respiratory regions, ALS gradually spreads to global muscles, ultimately resulting in respiratory dysfunction [2]. Epidemiological studies in Europe have shown the global incidence of ALS is approximately 1–2.6 cases per 100,000 individuals annually, with a prevalence of around 6 cases per 100,000 [3, 4]. ALS most commonly occurs around the age of 60, affecting more males than females [4]. The median time from symptom onset to diagnosis is typically 14 months due to the complex heterogenicity. Fatality of ALS patients usually occurs within 3–5 years after diagnosis due to respiratory paralysis [3]. The etiology of ALS remains an unsolved mystery. However, it is currently believed that genetic, environmental, and pathological factors are all implicated.
Interestingly, there is an increasing body of epidemiological evidence linking environmental toxins with neurodegenerative diseases, including ALS, Alzheimer’s disease (AD), and Parkinson’s disease (PD) [5, 6]. Numerous environmental factors play roles in the pathogenesis of ALS, such as pesticides, electromagnetic fields, smoking, physical activity, body mass index, microbiota structure, cyanobacteria, and cyanotoxins. Recent studies have revealed the presence of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine (L-BMAA) in the brain and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples of AD and ALS patients [7]. L-BMAA was produced by cyanobacteria and algal species, indicating that exposure to cyanotoxins may contribute to the development of human neurodegenerative diseases [8]. Spencer et al. [9] first proposed a connection between the pathogenesis of ALS/parkinsonism-dementia complex (PDC) and the neurotoxin L-BMAA, which was produced by cyanobacteria of the genus Nostoc [9]. However, Montine et al. [10] assayed free L-BMAA in the brains of five control subjects and five patients with AD, who were from the US Pacific Northwest as well as Chamorros with and without PDC, but they detected no free L-BMAA in any of these samples. Cruz-Aguado et al. [11] also supported neither the causal role of L-BMAA in neurodegeneration nor the specific involvement of this amino acid in ALS/PDC. Hence, the involvement of L-BMAA in neurotoxicity and neurodegeneration remains controversial. Transactivation-responsive DNA binding protein 43 (TDP-43), a protein encoded by the TDP-43 gene (TARDBP), has been found to overexpress and aggregate both in vitro and vivo models, such as SH-SY5Y cell lines [12] and primary neurons in rats [13], mice [14], and zebrafish [15], when exposed to L-BMAA. These aberrant forms of TDP-43 are also present in patients with neurodegenerative diseases such as ALS and frontotemporal dementia (FTD) [16], suggesting their potential involvement in the pathogenesis of these neurodegenerative diseases. Recently, a proteomic study of murine neuroblastoma Neuro-2A (N2A) cells following low-dose exposure to saxitoxin revealed alterations in various proteins, which play key roles in the regulation of skeleton maintenance for cells, membrane potentials, mitochondrial functions, and cell apoptotic pathways [17]. It is also noteworthy that low doses of saxitoxins induce a decrease in voltage-dependent anion-selective channel 1 (VDAC1), a multifunctional protein expressed in the mitochondria and other cell compartments. VDAC1 regulates the main metabolic and energetic functions of the cell, such as Ca2+ homeostasis, oxidative stress, and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis [8]. VDAC1 serves as the main mitochondrial docking site of many misfolded proteins, such as amyloid β and Tau in AD, as well as several superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) mutants in ALS [18].
Although there is an absence of effective therapies for neurodegenerative diseases, early diagnosis, and intervention can improve the life quality of ALS patients [19]. However, most clinical trials for ALS treatment have strict inclusion criteria that require a short disease duration. This means that a diagnosis of ALS at an early stage would allow more patients to be enrolled in these trials. Unfortunately, the median time from symptom onset to diagnosis is typically 14 months, as neurologists often struggle with the uncertainty of the diagnosis and repeat investigations for confirmation. ALS is a highly complicated and heterogeneous disease, causing difficulty in early diagnosis. Currently, ALS diagnosis depends on the regional extent of clinical and electrophysiological signs, and many other diseases can mimic ALS in the early stages. No clear evidence indicates the involvement of upper motor neuron (UMN) and lower motor neuron (LMN) across multi-levels at an early stage. In particular, there are no sensitive UMN injury identification techniques with atypical clinical signs. Thus, it is very challenging to diagnose ALS at an early stage.
A series of criteria have been designed over the years in consensus meetings, regarding the patterns of UMN and LMN signs required for diagnostic certainty, together with the absence of features suggestive of other neurological disorders. These clinical criteria were revised to define more precisely the neurophysiological criteria for LMN signs [20–22]. At all these consensus meetings it was recognized that early features of UMN disorder in ALS were difficult to elicit. To facilitate the early diagnosis of ALS, an international consensus group proposed the Gold Coast criteria, which established an increased diagnostic sensitivity when compared with the previous criteria [23]. However, effective markers can further facilitate the diagnosis, monitor the disease progression, and evaluate the therapeutic effects. In particular, the disease-specific features for early diagnosis assist ALS patients in receiving early intervention and prolonging their survival.
Nevertheless, there are no widely accepted characteristic changes in ALS diagnosis. With the advancement of diagnostic techniques, novel approaches demonstrate the potential for early ALS diagnosis. The purpose of this review is to summarize the current status of features discovery and development for the early diagnosis of ALS, including genes, proteins, neuroimaging, neurophysiology, neuroultrasound, and machine learning models (Figure 1). The main genetic markers evaluated for ALS diagnosis are SOD1, chromosome 9 open reading frame 72 (C9orf72), TARDBP, and fused in sarcoma (FUS) genes. Although neurofilament is the most established disease-specific protein, other proteins, such as chitinases, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), and inflammation cytokines, can play crucial roles in early diagnosis. Besides, the development of more patient-friendly and accessible feature assays has been facilitated by the advancement in neuroimaging techniques, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), positron emission tomography (PET), and ultrasound. Furthermore, the use of machine learning models as an emerging tool to identify new characteristic changes in ALS will be discussed.
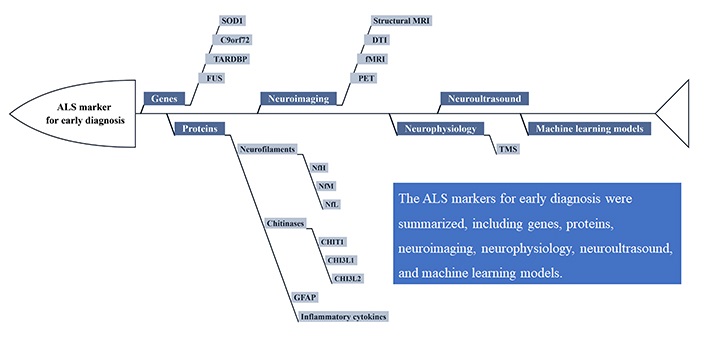
The promising markers for early diagnosis of ALS. DTI: diffusion tension imaging; fMRI: functional MRI; TMS: transcranial magnetic stimulation; NfH: neurofilament heavy chain; NfM: neurofilament medium chain; NfL: neurofilament light chain; CHIT1: chitotriosidase; CHI3L1: chitinase-3-like protein 1
Genes
About 10% of ALS cases are familial ALS (fALS), with frequent dominant traits and high penetrance [24]. The genetic cause has been elucidated in approximately 60–70% of fALS patients [25]. About 90% of individuals with ALS were classified as sporadic ALS (sALS) without a family history, but genetic factors have also been considered necessary. The estimated heritability of sALS is up to 50% [26]. The first ALS gene, cytosolic SOD1 was reported in 1993 [27, 28]. Since then, more than 50 potential ALS genes have been reported. However, validating the pathogenicity of a specific variant remains challenging. Among European populations, four genes account for nearly 70% of fALS, namely, SOD1, C9orf72, TARDBP, and FUS [29]. Typical mutants can become diagnostic features and therapeutic targets for ALS. Some loci are also associated with prognosis and can even reflect treatment efficacy. Early genetic screening will assist rapid diagnosis of asymptomatic and pre-symptomatic family members of fALS patients. Moreover, early genetic screening will provide crucial diagnostic evidence in suspected sALS patients. Since some genetic target therapies have been developed, they could control the disease early in patients with gene mutations.
SOD1
SOD1, the first ALS gene identified in 1993, causes autosomal dominant fALS [27, 28]. SOD1 is a potent antioxidative enzyme that protects cells from oxidative stress damage. More than 170 mutations in SOD1 have been found to cause ALS, with most occurring in fALS. Approximately 3% of mutations are in sALS [28]. The frequency of the SOD1 gene mutations is about 12–23% in fALS and 0–7% in sALS [30]. The most common mutations of SOD1 in ALS patients include D90A, A4V, H46R, and G93A. While G93A is relatively rare, it has been extensively studied [30]. SOD1 mutations can cause ALS through toxic gain of function generated by aggregating misfolded SOD1 proteins. High expression levels of human ALS-associated SOD1 mutants (e.g., SOD1G93A, SOD1G37R, or SOD1G85R) could exhibit overt adult-onset motor neuron disease phenotypes mimicking the clinical ALS symptoms [28, 31, 32]. Thus, SOD1 could be the features for early diagnosis and a potential therapeutic target. Therapeutic SOD1 silencing using antisense oligonucleotides or microRNAs has been tested in the SOD1G93A mouse model and non-human primates [33, 34].
The first clinical study of intrathecal delivery of an antisense oligonucleotide, tofersen, was conducted in 2013 to assess its safety and tolerability. Tofersen is an antisense oligonucleotide that mediates the degradation of SOD1 mRNA to reduce SOD1 protein synthesis. Seven of eight patients in the placebo group had adverse events, compared to 20 of 24 in the ISIS 333611 (tofersen) group. No serious adverse events occurred in patients given ISIS 333611. Re-enrolment and re-treatment were also well tolerated, showing promising therapeutic potential and no significant safety concerns [35]. A phase 1–2 ascending-dose trial was conducted to evaluate tofersen in adults with ALS due to SOD1 mutations [36]. In each dose cohort, participants were randomly assigned to receive five doses of tofersen or placebo, administered intrathecally for 12 weeks. Lumbar puncture—related adverse events were most common in participants. Some participants receiving tofersen experienced elevations in CSF white-cell count and protein levels. The change from the baseline CSF SOD1 concentration to that at day 85 was also recorded. The difference between the tofersen groups and the placebo group was 2 percentage points [95% confidence interval (CI), –18 to 27] for the 20 mg dose, –25 percentage points (95% CI, −40 to −5) for the 40 mg dose, −19 percentage points (95% CI, −35 to 2) for the 60 mg dose, and −33 percentage points (95% CI, −47 to −16) for the 100 mg dose [36]. Recently, the result of trial III of tofersen has been revealed. Neurologic serious adverse events occurred in 7% of tofersen recipients. In persons with SOD1 ALS, tofersen reduced concentrations of SOD1 in CSF and of NfLs in plasma over 28 weeks [37].
C9orf72
C9orf72 gene mutation is the most common cause of ALS accounting for 20–50% of fALS cases and 5–20% of sALS cases [38]. Meanwhile, this mutation is also the leading genetic cause of FTD, causing approximately 10–30% of FTD cases [38]. The disease mechanism of mutant C9orf72 has been proposed to include gain-of-function of protein, loss-of-function of protein [39], gain-of-function of toxic RNA [40, 41], and generating repeat-associated non-AUG initiation (RAN) translation products [42, 43]. RNA fluorescence in-situ hybridization (FISH) techniques have been used to detect C9orf72 mutant foci by examining intranuclear GGGGCC repeat RNA. These foci can be detected in brain and peripheral cells, such as fibroblasts derived from a skin biopsy [40, 44] and blood leukocytes [45]. Thus, these foci can serve as a potential molecular change for diagnosis and evaluating treatment effects in clinical trials, eliminating the repeat expansion through therapeutic intervention.
A pathological mechanism of C9orf72 gene expansion entails the translation of the expansion into dipeptide repeat proteins [46, 47]. This occurs through RAN translation of the hexanucleotide repeat, resulting in the formation of five dipeptide repeat proteins: glycine-alanine (GA), glycine-arginine (GR), proline-alanine (PA), proline-arginine (PR), and glycine-proline (GP) [47]. Production of poly-PR and poly-GR leads to neurotoxicity via impaired protein translation [48]. Poly-GP has attracted attention as a potential marker in C9orf72 gene expansion carriers in ALS [49]. While asymptomatic mutation carriers have elevated levels of poly-GP in CSF and peripheral blood mononuclear cells, these levels are further increased in individuals with the disease [50].
TARDBP
TDP-43 encoded by TARDBP is a DNA/RNA-binding protein primarily located in the nucleus [51]. TDP-43 plays a crucial regulatory role in RNA metabolism, including mRNA splicing, translation, RNA transportation, and microRNA biogenesis [52–54]. The pathological findings of cytoplasmic aggregation and nucleus depletion of TDP-43 are present in over 97% of ALS and 45% of FTD patients [55]. TARDBP mutation occurs in approximately 3% of fALS cases and 1.2% of sALS cases [56]. The c.1144GA (p.A382T) is a founder mutation, highly prevalent in ALS cases from Sardinia, a genetically isolated island [57]. There are more frequent TARDBP mutations in European populations in sALS [56]. The causal mutations in TARDBP are relatively rare. However, the ubiquitous TDP-43 cytoplasmic inclusions and nucleus depletion described the causal role of the TDP-43 pathological axis in ALS.
FUS
Like TARDBP, DNA/RNA binding protein FUS mutations can cause ALS and a rare FTD. More than 50 FUS mutations have been reported in ALS. The FUS mutation frequency is about 3% in fALS and 0.4% in sALS [56], typically showing an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. Similar to TDP-43 pathology, the FUS pathogenesis in ALS arises from the toxic FUS aggregation in the cytoplasm, and FUS deletion in the nucleus induces nuclear function loss. Expressing the mutations associated with rapidly progressive and juvenile-onset ALS in vivo at physiological levels can cause progressive and age-dependent motor neuron degeneration in mice [58].
Recently, Eleanor and Lou Gehrig ALS centers at Columbia University’s Irving Medical Center initiated the first clinical trial targeting FUS, which is called Jacifusen. It is a multicenter phase 1–3 study, double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled of antisense oligonucleotides targeting the FUS mRNA and supported by ALS association and Project ALS. The primary outcome is to measure the change in ALS Functional Rating Scale (ALSFRS)-Revised (ALSFRS-R) and Ventilation Assistance-free survival (VAFS) at 505 days while the outcome is unknown yet [59].
Besides, other studies using genome editing with clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats-associated protein 9 (CRISPR/Cas9) have been reported. Researchers use induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) derived from ALS patients with FUS mutations to study FUS pathogenesis. Wang et al. [60] first revealed the CRISPR/Cas-9-mediated FUS (G1566A) correction. After that, Bhinge et al. [61] reported the CRISPR/Cas-9-mediated correction of FUS (H517Q) mutation, which showed that the abnormal activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling is related to the pathogenesis process in ALS patients [61]. Furthermore, another study with CRISPR/Cas9-mediated FUS (R521H) correction proved that pathological axonal transport defects in motor neurons with FUS mutation could be rescued by gene correction [62]. CRISPR/Cas9 mediated gene editing may facilitate the development of new therapies in ALS even though more clinical studies are required.
Other genes
Other ALS-related genes include RNA binding proteins, such as TATA-box binding protein associated factor 15 (TAF15), Ewing sarcoma breakpoint region 1 (EWS) RNA binding protein 1 (EWSR1), ataxin-2 (ATXN2), and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs). Moreover, other genes also include mitochondria proteins, such as coiled-coil-helix-coiled-coil-helix domain containing 10 (CHCHD10), cytoskeleton-related proteins, including tubulin alpha-4A (TUBA4A), and kinesin family member 5A (KIF5A), and several other newly-defined genes. However, mutation prevalence in these genes is relatively rare in ALS cases. Therefore, the most common genes (SOD1, C9orf72, TARDBP, and FUS) should be screened at the beginning.
Proteins
Neurofilaments
Neurofilaments are neuronal cytoskeletal proteins that are highly expressed in large caliber myelinated axons, functioning in axonal growth and maintenance. These consist of NfH, NfM, and NfL and α-internecine. A few studies have shown elevated levels of neurofilaments in CSF, plasma, and serum of ALS patients.
Currently, NfL is the most established disease-specific feature in ALS. The CSF NfL levels in ALS patients are significantly higher than in healthy controls and patients with FTD [63]. The CSF and blood NfL correlated with disease progression and survival time, indicating it could be a prognostic disease-specific marker [64, 65]. Additionally, CSF and blood NfL are altered in the early stage of the disease, transitioning from pre-symptomatic to symptomatic [66]. Benatar et al. [67] detected the serum and CSF NfL levels in ALS patients through the ALS-associated gene mutations [SOD1, C9orf72, TARDBP, FUS, valosin-containing protein (VCP), etc.]. The pre-symptomatic ALS patients were named the individual carriers of the ALS-associated gene mutations without clinical symptoms at the time of enrollment. In the longitudinal study, some pre-symptomatic patients converted to ALS patients with clinical symptoms. Both serum and CSF NfL levels were significantly higher in ALS patients than in healthy controls and pre-symptomatic ALS patients. In clinically converted ALS patients, NfL levels were found to be elevated 12 months before the onset of the earliest clinical symptoms. Moreover, different subtypes of ALS showed varying NfL levels, with bulbar-onset ALS patients having significantly higher plasma NfL levels than the spinal-onset ones [68].
In addition to NfL, NfH also showed diagnostic potential in ALS. Most studies have focused on phosphorylated NfH (pNfH) due to its phosphorylation. Previous studies have revealed elevated pNfH levels in serum, plasma, and CSF in ALS patients, increasing along with the disease progression [69]. Simultaneously, there were significantly increased NfH levels prior to symptom onset. However, serum and CSF pNfH were found to be less sensitive to pre-symptomatic ALS compared to NfL [70].
The increasing levels of neurofilament are observed in various neurological disorders due to axonal damage. This includes inflammatory, neurodegenerative, traumatic, and cerebrovascular diseases, which limits the diagnostic specificity of neurofilaments in ALS. However, neurofilaments remain the most promising and characteristic changes in ALS. They can be measured by easily acquiring serum/plasma, and the detecting techniques have favorable maturity, sensitivity, and reproducibility in assessing neurofilament levels.
Chitinases
The chitinases belong to the family 18 of glycosyl hydrolases (GH18), which can cleave chitin. The GH18 family is widely expressed across various organisms. Mammalian chitinases include the enzymatically active chitinases: CHIT1, acidic mammalian chitinase (AMCase), CHI3L1, CHI3L2 [71].
Several studies have revealed that ALS patients have significantly elevated CSF levels of CHIT1, CHI3L1, and CHI3L2 than healthy controls, mimics, and asymptomatic mutation carriers [72–74]. Among human chitinases, CHIT1 is the most abundant in monocytes and macrophages. Increased CHIT1 is a disease-specific change of microglia activation in the CSF of ALS patients. Some studies have indicated that CHIT1 levels in the CSF were elevated, distinguishing ALS from healthy controls, other neurodegenerative disease patients, and diseases mimicking ALS [73–76]. CHIT1 levels have been associated with disease progression and survival time in ALS patients, suggesting its potential as an early marker for the disease [74]. Based on these findings, Steinacker et al. [77] conducted a study investigating the diagnostic and prognostic potential of CHIT1 in 275 early symptomatic ALS patients from 8 European neurological centers. However, they observed that CHIT1 levels were elevated in both early and symptomatic ALS and did not correlate with the rate of disease progression. CHIT1 could only predict disease progression in ALS patients with a short history and classified within low clinical certainty diagnostic categories. However, Steinacker et al. [77] revealed that the levels of three chitinases (CHIT1, CHI3L1, and CHI3L2) were also increased in other neurodegenerative conditions, with their discriminatory power outperformed by NfH and NfL [77]. Therefore, CSF chitinase proteins may have limited value as independent diagnostic and stratification index in ALS. However, they offer a window into non-autonomous mechanisms of motor neuron loss in ALS, particularly during the evaluation of responses to therapies targeting neuroinflammatory pathways [74].
GFAP
GFAP is released by astrocytes and acts as an intermediate filament protein during astrogliosis [78]. GFAP has been considered to be a potential feature for FTD based on the elevated GFAP levels in the CSF [79] and plasma in FTD patients [80]. In ALS patients and controls, serum GFAP similarly moderately correlated with age. Nevertheless, ALS patients were found to carry higher serum GFAP levels compared to controls [81]. GFAP is also elevated in CSF samples in the previous report [79]. However, as a measure of astrogliosis, GFAP is common in other neurodegenerative diseases, such as AD and dementia with Lewy bodies, making it impossible to be used as a specific index for ALS.
Inflammatory cytokines
The role of neuroinflammation in the pathogenesis of ALS patients has already been identified. A systematic review was conducted to study the status of proteins and anti-inflammatory cytokines in neurodegeneration diseases, including ALS [82]. Interleukin-2 (IL-2), IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, IL-17, and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) remained unchanged, but tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), TNF receptor 1, IL-6, IL-1β, IL-8, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) levels were significantly elevated in the peripheral blood of ALS patients [83]. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, IL-2, IL-15, IL-17, monocyte chemotactic protein-1, macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-1α, TNF-α, and VEGF levels were significantly increased in the CSF of ALS patients, but granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-7, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12p70, IL-13, MIP-1β, and regulated upon activation, normal T cell expressed, and presumably secreted (RANTES) levels were not significantly different in the CSF samples of ALS patients [84]. These results confirm the presence of inflammatory response in ALS, but these inflammatory cytokines currently cannot act as disease-specific changes due to the lack of specificity.
Neuroimaging
Structural MRI
Focal brain atrophy is a crucial feature in ALS patients and can be analyzed using structural MRI. An extended follow-up study was conducted in asymptomatic C9orf72 carriers, which showed that cortical changes could be detected up to 20 years before the estimated symptom onset [85]. A large multi-center study in FTD patients carrying C9orf72 mutation revealed that the insula and temporal lobe volume decreased 10 years before expected symptom onset [85]. In addition, another study demonstrated that pre-symptomatic C9orf72 carriers had experienced a loss of white matter integrity in tracts connecting the frontal lobe, thalamic radiation, and tracts related to motor functioning compared to healthy controls [86]. However, previous studies did not have consistent results regarding brain atrophy in ALS patients, disputing the early diagnostic value of structural MRI in ALS.
DTI
An essential feature of ALS is the degenerating white matter fibers, particularly the corticospinal tracts and corpus callosum. DTI, a mathematical model depending on diffusion MRI, is used to evaluate the degeneration of the white matter bundle. Several studies have reported a decrease in fractional anisotropy and an increase in mean diffusivity in the corticospinal tracts [87]. Additionally, some studies have observed changes in white matter tracts using DTI in pre-symptomatic individuals carrying the C9orf72 mutation, especially in those under the age of 40 [88, 89].
fMRI
Task-based and resting state fMRI is performed to understand the functional brain network. The pre-symptomatic C9orf72 carriers had prominent intrinsic connectivity deficits within salience and medial pulvinar thalamus-seeded networks [90]. Another study revealed that pre-symptomatic C9orf72 carriers possessed abnormal longitudinal trajectories of intra-network homogeneity in the somatomotor, dorsal attention, and default mode networks compared to healthy controls and symptomatic carriers [91].
PET
18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)-PET for assessing brain glucose metabolism indicated the diagnostic potential in early-stage ALS. Popuri et al. [92] observed that pre-symptomatic C9orf72 carriers demonstrated changes in brain glucose metabolism up to 10 years before symptom onset and significant gray matter volume changes. Some studies generated diagnostic algorithms that discriminated ALS from controls [93–95]. The algorithms had favorable sensitivity, but low specificity in the multicenter validation. PET can analyze disease mechanisms using specific molecular tracers sensitive to early pathological changes, and detect UMN degeneration in suspected ALS patients. However, consistent diagnostic criteria for PET have not been reached. Large longitudinal studies are required to determine the application value of PET in distinguishing UMN dysfunction before clinical signs emerge.
Neurophysiology
Currently, cortical hyperexcitability could be an early and specific feature of ALS related to excitotoxicity from excessive glutamate receptor activity at the synaptic cleft [96]. Cortical hyperexcitability is potentially useful as an objective diagnostic marker in ALS, which can be captured using TMS. The involvement of UMN dysfunction is difficult to measure traditionally. The pathological spread could be measured using hyperexcitability as a surrogate by recording the response at the abductor pollicis brevis. Thus, TMS offered some diagnostic utility at an early stage. TMS detection revealed that the pre-symptomatic ALS patients had reduced short-interval intracortical inhibition and increased intracortical facilitation [97]. TMS showed a high sensitivity (73.21%) and specificity (80.88%) at early disease stages [98]. TMS could differentiate ALS from neuromuscular mimicking disorders [99, 100] and advance ALS diagnosis by eight months [98].
Neuroultrasound
Fasciculations are acute denervation of motor neurons equivalent to fibrillations and positive sharp waves, essential for ALS diagnosis. Misawa et al. [101] observed that fasciculations were detected using ultrasound in the tongue (60%), biceps brachii (88%), and tibialis anterior muscles (83%). They were more frequently detected than by electromyogram (EMG) [101]. Combining ultrasound and EMG could be a quicker, more sensitive, and less invasive approach for diagnosing ALS. However, no accepted algorithm for combining ultrasound and EMG exists to investigate patients with suspected ALS.
Machine learning models
ALS is a complex syndrome with significant heterogeneity and diverse clinical presentations. One feature or technique cannot depict the complicated disease status. Recently some researchers fed a large amount of disease data into the artificial intelligence system to establish a machine-learning model for ALS diagnosis. Geevasinga et al. [102] developed a novel diagnostic score called the ALS diagnostic index (ALSDI). ALSDI exhibited more than 80% sensitivity, specificity, and diagnostic accuracy involving clinical, conventional neurophysiologic, and TMS measures. It reliably differentiated ALS from mimicking disorders early in the disease process. Tang et al. [103] employed model-based and model-free machine-learning methods to predict the ALS disease progression (changes within the ALSFRS) using an extensive ALS data archive of 8,000 patients with 3 million records and 200 clinical features tracked over 12 months. Their models showed 70% accuracy in predicting univariate clinical outcomes. Fukushima et al. [104] observed 15 muscles and recorded fasciculations using muscle ultrasonography in 100 ALS patients, with 50 early-stage ALS patients within nine months. Then a machine learning-based model was established with eight muscles in the four body regions. The model showed a high sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value for early-stage ALS patients [104]. Therefore, machine learning models describe the usefulness of evaluating a combination of multiple pathways rather than having a single target.
Conclusions
It is still difficult to diagnose and manage ALS early due to the heterogeneous presentation, and the overlap of symptoms and signs with other illnesses. Several characteristic changes and techniques have been developed recently to aid early ALS diagnosis. The updated diagnostic criteria shortened the time from disease onset to diagnosis. Genetic markers provide a relatively definitive diagnosis of ALS but are limited to a small subgroup. NfL is still the most promising fluid disease-specific change but cannot discriminate ALS from other mimic diseases due to limited specificity. Similarly, chitinases had limited value in early diagnosis. Some novel neuroimaging, neurophysiological, and ultrasonic techniques have also been applied to early ALS diagnosis. In particular, TMS capturing cortical hyperexcitability can be complementary to traditional electromyography. Thus, the algorithm or models including multiple diagnostic factors may be a favorable choice due to the high heterogeneity of ALS. To expedite the early diagnosis of ALS, the simpler diagnostic criteria, genetic testing, and NfL measurement could be applied in the future. In addition, the novel techniques should be validated in a larger ALS population. The research efforts will improve the clinical outcomes of ALS patients.
Abbreviations
| AD: | Alzheimer’s disease |
| ALS: | amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| C9orf72: | chromosome 9 open reading frame 72 |
| CHI3L1: | chitinase-3-like protein 1 |
| CHIT1: | chitotriosidase |
| CI: | confidence interval |
| CRISPR/Cas9: | clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats-associated protein 9 |
| CSF: | cerebrospinal fluid |
| DTI: | diffusion tension imaging |
| EMG: | electromyogram |
| fALS: | familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| fMRI: | functional magnetic resonance imaging |
| FTD: | frontotemporal dementia |
| FUS: | fused in sarcoma |
| GFAP: | glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| GP: | glycine-proline |
| IL-2: | interleukin-2 |
| L-BMAA: | β-N-methylamino-L-alanine |
| LMN: | lower motor neuron |
| MRI: | magnetic resonance imaging |
| NfH: | neurofilament heavy chain |
| NfL: | neurofilament light chain |
| PDC: | parkinsonism-dementia complex |
| PET: | positron emission tomography |
| pNfH: | phosphorylated neurofilament heavy chain |
| sALS: | sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| SOD1: | superoxide dismutase 1 |
| TARDBP: | transactivation-responsive DNA binding protein 43 gene |
| TDP-43: | transactivation-responsive DNA binding protein 43 |
| TMS: | transcranial magnetic stimulation |
| TNF: | tumor necrosis factor |
| UMN: | upper motor neuron |
| VDAC1: | voltage-dependent anion-selective channel 1 |
Declarations
Author contributions
YL, LH, and HM: Writing—original draft. SC: Conceptualization. QZ: Conceptualization, Writing—original draft. All authors read and approved the submitted version.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publication
Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Funding
The authors are funded by the grants from
Copyright
© The Author(s) 2023.