-
Guest Editor
Prof. Noureddin Nakhostin Ansari E-Mail
Department of Physiotherapy, School of Rehabilitation, Research Center for War-affected People, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
Research Keywords: neurorehabilitation; physiotherapy; spasticity; stroke
About the Special Issue
Dry needling (DN) is a modality used commonly by physiotherapists for the management of pain and dysfunction associated with the trigger points. In recent years, DN has been introduced as a novel strategy for the management of muscle spasticity after stroke. There are increasingly publications reporting the positive effects of DN on muscle spasticity. DN has been shown effective in reducing spasticity, increasing range of motion, improving active voluntary movements and function after stroke. The positive effects of DN on muscle spasticity after stroke has been placed the DN an emerging key treatment option in the field of neurorehabilitation.
The application of DN has been recently expanded to other neurological diseases with muscle spasticity such as multiple sclerosis. Although increasing evidence emerges on the DN supporting it for the treatment of muscle spasticity, there are still numerous questions around the DN in neurorehabilitation, from the effective dose and protocol to mechanisms behind its effects in muscle spasticity. Current strategies have included the use of DN in combination with exercise therapy to enhance the effects on spasticity and movement dysfunction.
This Special Issue is devoted to the use of DN in the field of neurorehabilitation particularly to the above themes and neurological problems in upper motor neuron syndrome. Studies with human using randomized controlled trials, original research, case series, as well as experiments in animal models, are all encouraged and welcome.
Keywords: dry needling; neurology; neurorehabilitation; spasticity; stroke; multiple sclerosis; movement dysfunction
Published Articles
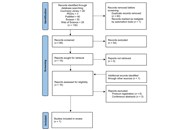 Effectiveness of dry needling on the treatment of patients with multiple sclerosis: systematic reviewOpen AccessSystematic ReviewAim: The aim of this study is to review the effectiveness of dry needling in patients with multiple sclerosis (MS). Methods: PubMed, Physiotherapy Evidence Database (PEDro), Web of Science, [...] Read more.Ali Mutlu ... Buket BüyükturanPublished: December 26, 2023 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2023;3:470–480
Effectiveness of dry needling on the treatment of patients with multiple sclerosis: systematic reviewOpen AccessSystematic ReviewAim: The aim of this study is to review the effectiveness of dry needling in patients with multiple sclerosis (MS). Methods: PubMed, Physiotherapy Evidence Database (PEDro), Web of Science, [...] Read more.Ali Mutlu ... Buket BüyükturanPublished: December 26, 2023 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2023;3:470–480
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ent.2023.00063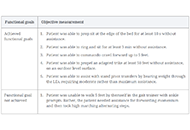 Dry needling with electrical stimulation for the treatment of a pediatric patient with spastic cerebral palsy: a case reportOpen AccessCase ReportThe patient was a 6-year-old child with spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy (CP) categorized with the gross motor function classification system (GMFCS) as a level IV and a Modified Modified Ashwort [...] Read more.Temrah Okonski, Jan DommerholtPublished: November 16, 2022 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2022;2:242–255
Dry needling with electrical stimulation for the treatment of a pediatric patient with spastic cerebral palsy: a case reportOpen AccessCase ReportThe patient was a 6-year-old child with spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy (CP) categorized with the gross motor function classification system (GMFCS) as a level IV and a Modified Modified Ashwort [...] Read more.Temrah Okonski, Jan DommerholtPublished: November 16, 2022 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2022;2:242–255
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ent.2022.00031 Economics of dry needling and botulinum toxin type A for treatment of post-stroke spasticity: a reviewOpen AccessReviewStroke is one of the most common causes of disability and exerts a high burden of direct and indirect costs. Stroke may cause spasticity, which limits patients’ abilities and affects the [...] Read more.Daniel Fernández ... Eva María Gómez-TrullénPublished: June 30, 2022 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2022;2:131–140
Economics of dry needling and botulinum toxin type A for treatment of post-stroke spasticity: a reviewOpen AccessReviewStroke is one of the most common causes of disability and exerts a high burden of direct and indirect costs. Stroke may cause spasticity, which limits patients’ abilities and affects the [...] Read more.Daniel Fernández ... Eva María Gómez-TrullénPublished: June 30, 2022 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2022;2:131–140
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ent.2022.00024 Combined effects of dry needling and exercises therapy on muscle spasticity and motor function in chronic stroke: a pretest-posttest pilot studyOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Spasticity is one of the most common symptoms in post-stroke patients. Dry needling (DN) is a relatively new method for the management of muscle spasticity. A multimodal treatment may be mor [...] Read more.Seyedeh Saeideh Babazadeh-Zavieh ... Korosh MansooriPublished: June 20, 2022 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2022;2:100–109
Combined effects of dry needling and exercises therapy on muscle spasticity and motor function in chronic stroke: a pretest-posttest pilot studyOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Spasticity is one of the most common symptoms in post-stroke patients. Dry needling (DN) is a relatively new method for the management of muscle spasticity. A multimodal treatment may be mor [...] Read more.Seyedeh Saeideh Babazadeh-Zavieh ... Korosh MansooriPublished: June 20, 2022 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2022;2:100–109
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ent.2022.00021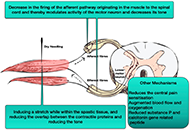 Dry needling in strokeOpen AccessReviewStroke causes acute neurological deficit which is an important cause of morbidity and mortality. Neurorehabilitation is an important dimension in the management of post-stroke deficits. Spasticity, [...] Read more.Nirmal Surya, Guhan RamamurthyPublished: February 17, 2022 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2022;2:28–35
Dry needling in strokeOpen AccessReviewStroke causes acute neurological deficit which is an important cause of morbidity and mortality. Neurorehabilitation is an important dimension in the management of post-stroke deficits. Spasticity, [...] Read more.Nirmal Surya, Guhan RamamurthyPublished: February 17, 2022 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2022;2:28–35
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ent.2022.00016 -
-
Ongoing Special Issues
-
Completed Special Issues
