-
Exploration of Targeted Anti-tumor Therapy
eISSN: 2692-3114EiC: Nicola Normanno, ItalyFrequency: Continuous PublicationAPC: $2,000 per article (See APC Waivers and Discounts)Publishing Model: Open AccessPeer Review Model: Single BlindIndexing & Archiving: PubMed/PMC, Scopus, Google Scholar, DOAJ, CAS, Dimensions, Portico, etc. The journal is also the member of COPE.Articles Nanoimmunotherapy: the smart trooper for cancer therapyOpen AccessReviewImmunotherapy has gathered significant attention and is now a widely used cancer treatment that uses the body’s immune system to fight cancer. Despite initial successes, its broader clinical appli [...] Read more.Suphiya Parveen ... Fahima DilnawazPublished: April 10, 2025 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2025;6:1002308
Nanoimmunotherapy: the smart trooper for cancer therapyOpen AccessReviewImmunotherapy has gathered significant attention and is now a widely used cancer treatment that uses the body’s immune system to fight cancer. Despite initial successes, its broader clinical appli [...] Read more.Suphiya Parveen ... Fahima DilnawazPublished: April 10, 2025 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2025;6:1002308
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2025.1002308
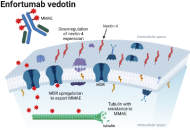
This article belongs to the special issue Comprehensive Immunotherapy of Solid Tumors Strategies to overcome resistance to enfortumab vedotin and pembrolizumab for patients with urothelial carcinoma: harnessing present knowledge for future advancesOpen AccessReviewThe combination of enfortumab vedotin and pembrolizumab (EVP) has been recently approved for patients with locally advanced and metastatic urothelial carcinoma. This combination showed a higher obje [...] Read more.Albert Jang, Jason R. BrownPublished: April 07, 2025 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2025;6:1002307
Strategies to overcome resistance to enfortumab vedotin and pembrolizumab for patients with urothelial carcinoma: harnessing present knowledge for future advancesOpen AccessReviewThe combination of enfortumab vedotin and pembrolizumab (EVP) has been recently approved for patients with locally advanced and metastatic urothelial carcinoma. This combination showed a higher obje [...] Read more.Albert Jang, Jason R. BrownPublished: April 07, 2025 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2025;6:1002307
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2025.1002307
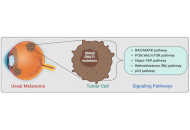
This article belongs to the special issue Emerging Molecular Targets and Therapies of Genitourinary Tumors Exploring recent advances in signaling pathways and hallmarks of uveal melanoma: a comprehensive reviewOpen AccessReviewThe purpose of this review was to provide a comprehensive review of the latest insights on the pathogenesis of uveal melanoma (UM) and its intracellular pathways. This article covers the epidemiolog [...] Read more.Majid Banimohammad ... Hamidreza Pazoki-ToroudiPublished: April 02, 2025 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2025;6:1002306
Exploring recent advances in signaling pathways and hallmarks of uveal melanoma: a comprehensive reviewOpen AccessReviewThe purpose of this review was to provide a comprehensive review of the latest insights on the pathogenesis of uveal melanoma (UM) and its intracellular pathways. This article covers the epidemiolog [...] Read more.Majid Banimohammad ... Hamidreza Pazoki-ToroudiPublished: April 02, 2025 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2025;6:1002306
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2025.1002306
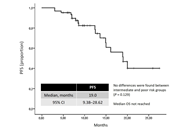
This article belongs to the special issue Predictive and Prognostic Biomarkers in Cancer: Towards the Precision Medicine Era Real-world outcomes of lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab in intermediate- and poor-risk metastatic renal cell carcinomaOpen AccessShort CommunicationThe combination of lenvatinib and pembrolizumab (Len + Pembro) demonstrated significant efficacy in the phase 3 CLEAR study for metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC). However, poor-risk patients rep [...] Read more.Ilya Tsimafeyeu ... Mark GluzmanPublished: April 01, 2025 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2025;6:1002305
Real-world outcomes of lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab in intermediate- and poor-risk metastatic renal cell carcinomaOpen AccessShort CommunicationThe combination of lenvatinib and pembrolizumab (Len + Pembro) demonstrated significant efficacy in the phase 3 CLEAR study for metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC). However, poor-risk patients rep [...] Read more.Ilya Tsimafeyeu ... Mark GluzmanPublished: April 01, 2025 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2025;6:1002305
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2025.1002305
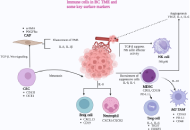
This article belongs to the special issue Emerging Molecular Targets and Therapies of Genitourinary Tumors Key immune cells and their crosstalk in the tumor microenvironment of bladder cancer: insights for innovative therapiesOpen AccessReviewBladder cancer (BC) is a heterogeneous disease associated with high mortality if not diagnosed early. BC is classified into non-muscle-invasive BC (NMIBC) and muscle-invasive BC (MIBC), with MIBC li [...] Read more.Anna Di Spirito ... Lorenzo MortaraPublished: March 31, 2025 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2025;6:1002304
Key immune cells and their crosstalk in the tumor microenvironment of bladder cancer: insights for innovative therapiesOpen AccessReviewBladder cancer (BC) is a heterogeneous disease associated with high mortality if not diagnosed early. BC is classified into non-muscle-invasive BC (NMIBC) and muscle-invasive BC (MIBC), with MIBC li [...] Read more.Anna Di Spirito ... Lorenzo MortaraPublished: March 31, 2025 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2025;6:1002304
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2025.1002304
This article belongs to the special issue Novel Insights into Immunotherapy Targeting Tumor Microenvironment in Cancer State-of-the-art photodynamic therapy for malignant gliomas: innovations in photosensitizers and combined therapeutic approachesOpen AccessReviewGlioblastoma (GBM), the most aggressive and lethal primary brain tumor, poses a significant therapeutic challenge due to its highly invasive nature and resistance to conventional therapies, includin [...] Read more.Bruno A. Cesca ... Luis E. IbarraPublished: March 28, 2025 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2025;6:1002303
State-of-the-art photodynamic therapy for malignant gliomas: innovations in photosensitizers and combined therapeutic approachesOpen AccessReviewGlioblastoma (GBM), the most aggressive and lethal primary brain tumor, poses a significant therapeutic challenge due to its highly invasive nature and resistance to conventional therapies, includin [...] Read more.Bruno A. Cesca ... Luis E. IbarraPublished: March 28, 2025 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2025;6:1002303
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2025.1002303Special Issues Artificial Intelligence Technology in Tumor Radiotherapy
Artificial Intelligence Technology in Tumor RadiotherapyProf. Tuan D. Pham
Submission Deadline: September 30, 2025
Published Articles: 0
 Liquid Biopsy: has already changed the clinical decision making in solid tumors treatment?
Liquid Biopsy: has already changed the clinical decision making in solid tumors treatment?Dr. Giulia Martini
Submission Deadline: June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 0
 Predictive and Prognostic Biomarkers in Cancer: Towards the Precision Medicine Era
Predictive and Prognostic Biomarkers in Cancer: Towards the Precision Medicine EraProf. Luca Falzone Dr. Antonio Rizzo Dr. Stefano Marletta Dr. Graziana Spoto
Submission Deadline: February 28, 2025
Published Articles: 2
 Potential Clinical Applications of Inorganic Nanomaterials in Cancer
Potential Clinical Applications of Inorganic Nanomaterials in CancerProf. Javier Reguera
Submission Deadline: April 30, 2025
Published Articles: 1
 Potential of Non-Coding RNAs in Cancer Research and Treatment
Potential of Non-Coding RNAs in Cancer Research and TreatmentProf. Francesco Bertoni Dr. Luciano Cascione
Submission Deadline: June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 0
 Novel Biomarkers in the Immunotherapy Era
Novel Biomarkers in the Immunotherapy EraDr. Carminia Maria Della Corte Dr. Floriana Morgillo Dr. Caterina De Rosa
Submission Deadline: December 31, 2024
Published Articles: 1
 Comprehensive Immunotherapy of Solid Tumors
Comprehensive Immunotherapy of Solid TumorsDr. Michela Valeria Rita Starace
Submission Deadline: October 31, 2024
Published Articles: 3
 Advances in Cancer Genomics and Therapeutic Targets
Advances in Cancer Genomics and Therapeutic TargetsProf. Apostolos Zaravinos
Submission Deadline: October 31, 2024
Published Articles: 2
 Molecular Mechanisms and Intervention Options in Metastatic Spread of Cancer
Molecular Mechanisms and Intervention Options in Metastatic Spread of CancerDr. Katrin Sak
Submission Deadline: June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 2
 Immunotherapy Strategies for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
Immunotherapy Strategies for Non-small Cell Lung CancerProf. Stergios Boussios Prof. Matin Sheriff
Submission Deadline: July 31, 2024
Published Articles: 5
 Use of Different Radiation Treatment Modalities in Cancer Therapy: The Role of Inflammation and Immune Response
Use of Different Radiation Treatment Modalities in Cancer Therapy: The Role of Inflammation and Immune ResponseProf. Alexandros Georgakilas
Submission Deadline: May 31, 2025
Published Articles: 1
 Immune Checkpoint Therapy and Biomarkers in Cancer
Immune Checkpoint Therapy and Biomarkers in CancerProf. Eyad Elkord
Submission Deadline: December 31, 2024
Published Articles: 6
 Emerging Molecular Targets and Therapies of Genitourinary Tumors
Emerging Molecular Targets and Therapies of Genitourinary TumorsAlcides Chaux
Submission Deadline: September 30, 2024
Published Articles: 8
 Mechanisms of Targeted Therapy Resistance and Reversal Strategies
Mechanisms of Targeted Therapy Resistance and Reversal StrategiesProf. Pier Paolo Piccaluga
Submission Deadline: December 31, 2024
Published Articles: 3
 Current Innovative Cancer Treatment
Current Innovative Cancer TreatmentProf. Salem Chouaib Dr. Ghazi Jerbi
Submission Deadline: February 29, 2024
Published Articles: 0
 Cancer Epigenetics: Implications for Novel Therapeutic Strategies
Cancer Epigenetics: Implications for Novel Therapeutic StrategiesProf. Mingzhou Guo
Submission Deadline: February 01, 2025
Published Articles: 2
 Novel Insights into Immunotherapy Targeting Tumor Microenvironment in Cancer
Novel Insights into Immunotherapy Targeting Tumor Microenvironment in CancerProf. Hailin Tang
Submission Deadline: October 31, 2023
Published Articles: 4
 Molecular Diagnosis and Personalized Therapy of Cancer
Molecular Diagnosis and Personalized Therapy of CancerProf. Monica Fedele Prof. Andrea Vecchione
Submission Deadline: May 31, 2024
Published Articles: 4
 Innovative Strategies to Target Triple-negative Breast Cancer
Innovative Strategies to Target Triple-negative Breast CancerDr. Laura Cerchia Dr. Simona Camorani
Submission Deadline: May 31, 2023
Published Articles: 8
 Posttranslational Modifications in Health and Disease
Posttranslational Modifications in Health and DiseaseProf. Oliver Krämer
Submission Deadline: December 31, 2024
Published Articles: 4
 The Role of Bcl-2 Family Proteins in Cancer Progression and Their Relevance to Cancer Therapy
The Role of Bcl-2 Family Proteins in Cancer Progression and Their Relevance to Cancer TherapyDr. Donatella Del Bufalo Dr. Germain Gillet
Submission Deadline: November 30, 2021
Published Articles: 5
-
-
FocusMorePage View 2469May. 18, 2023
-
NewsletterWinners of Highly Cited Paper Award 2024
 Feb. 5, 2025ETAT at the "Frontier Interdisciplinary and High-Level Academic Journal Seminar"
Feb. 5, 2025ETAT at the "Frontier Interdisciplinary and High-Level Academic Journal Seminar" Dec. 30, 2024ETAT Journal’s Recent Exposure at Conferences
Dec. 30, 2024ETAT Journal’s Recent Exposure at Conferences Dec. 24, 2024MoreWinners of Highly Cited Paper Award 2023
Dec. 24, 2024MoreWinners of Highly Cited Paper Award 2023 Mar. 28, 2024
Mar. 28, 2024