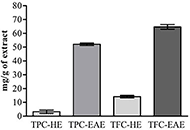
-
Exploration of Foods and Foodomics
eISSN: 2837-9020Editors-in-Chief: Alejandro Cifuentes, Spain; Elena Ibáñez, SpainFrequency: Continuous PublicationAPC: No Article Processing Charge before Mar 31, 2028Publishing Model: Open AccessPeer Review Model: Single BlindPermanent Archive: PorticoIndexing & Archiving: DOAJ, Google Scholar, Dimensions, MyScienceWork, Portico, etc.Articles Sustainable insect proteins vs. conventional proteins as fillings in gluten-free oat-based breakfast wraps: nutritional, microbial, and sensory qualityOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Livestock production plays a significant role in meeting global protein demands but is a major contributor to climate change. With the world population projected to reach 9 billion by 2050, [...] Read more.
Sustainable insect proteins vs. conventional proteins as fillings in gluten-free oat-based breakfast wraps: nutritional, microbial, and sensory qualityOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Livestock production plays a significant role in meeting global protein demands but is a major contributor to climate change. With the world population projected to reach 9 billion by 2050, [...] Read more.Aim:
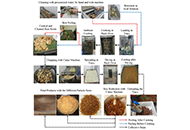
Livestock production plays a significant role in meeting global protein demands but is a major contributor to climate change. With the world population projected to reach 9 billion by 2050, identifying sustainable alternative protein sources has become more critical than ever. Edible insects offer an affordable protein option compared to beef, chicken, and fish, especially in many African and Asian cultures, where these conventional protein sources are considered relatively expensive. This study aimed to investigate the potential of mulberry silkworm pupae and African palm weevil larvae as alternative proteins to conventional protein sources for use in gluten-free wraps.
Methods:
Five gluten-free breakfast wraps were developed using oat flour and fillings made from beef, chicken, mackerel fish, palm weevil larvae, and silkworm pupae. The nutritional composition (amino acid and fatty acid profiles, micronutrient contents) and chemical, microbial, and sensory properties were determined using standard methods.
Results:
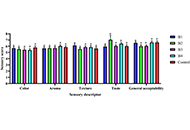
The wraps had protein contents ranging from 23.78% to 35.60%. Breakfast wrap with palm weevil larvae had slightly more fiber (4.01%) and carbohydrate (36.11%) contents and lower fat (10.22%) compared to the other wraps. It also had an impressive vitamin A content (528.96 μg RAE/100 g) and an exceptional amino acid profile. The insect wraps had more vitamin B12 (0.02 mg/g) contents than the conventional wraps. The fish-based version was the most preferred of all the wraps, with an overall acceptability score of 7.80. All developed products were within permissible limits for microbial quality.
Conclusions:
Edible insects, such as palm weevil larvae and silkworm pupae, could serve as an alternative source of protein in the production of gluten-free foods.
Olamide Akande ... Daniel AjewolePublished: March 18, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101078
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2025.101078
This article belongs to the special issue The food (r)evolution towards food quality/security and human nutritionAim:
Livestock production plays a significant role in meeting global protein demands but is a major contributor to climate change. With the world population projected to reach 9 billion by 2050, identifying sustainable alternative protein sources has become more critical than ever. Edible insects offer an affordable protein option compared to beef, chicken, and fish, especially in many African and Asian cultures, where these conventional protein sources are considered relatively expensive. This study aimed to investigate the potential of mulberry silkworm pupae and African palm weevil larvae as alternative proteins to conventional protein sources for use in gluten-free wraps.
Methods:
Five gluten-free breakfast wraps were developed using oat flour and fillings made from beef, chicken, mackerel fish, palm weevil larvae, and silkworm pupae. The nutritional composition (amino acid and fatty acid profiles, micronutrient contents) and chemical, microbial, and sensory properties were determined using standard methods.
Results:
The wraps had protein contents ranging from 23.78% to 35.60%. Breakfast wrap with palm weevil larvae had slightly more fiber (4.01%) and carbohydrate (36.11%) contents and lower fat (10.22%) compared to the other wraps. It also had an impressive vitamin A content (528.96 μg RAE/100 g) and an exceptional amino acid profile. The insect wraps had more vitamin B12 (0.02 mg/g) contents than the conventional wraps. The fish-based version was the most preferred of all the wraps, with an overall acceptability score of 7.80. All developed products were within permissible limits for microbial quality.
Conclusions:
Edible insects, such as palm weevil larvae and silkworm pupae, could serve as an alternative source of protein in the production of gluten-free foods.
 Effect of the production of dried fruit and fruit chips on chemical, sensory and bioactive propertiesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Dried fruits are consumed by many people around the world as a convenient alternative to fresh fruits with a long shelf life. As well as dried fruits, the manufacturing of baked chips based [...] Read more.
Effect of the production of dried fruit and fruit chips on chemical, sensory and bioactive propertiesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Dried fruits are consumed by many people around the world as a convenient alternative to fresh fruits with a long shelf life. As well as dried fruits, the manufacturing of baked chips based [...] Read more.Aim:
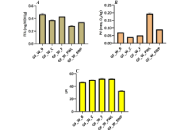
Dried fruits are consumed by many people around the world as a convenient alternative to fresh fruits with a long shelf life. As well as dried fruits, the manufacturing of baked chips based on fruits having good nutrition and sensory properties represents an alternative to healthier food. The aim of this study is to determine the different chemical properties of dried fruits and fruit chips when they are being fried in ovens. Another aim was to evaluate the changes in total phenolic content (TPC), antioxidant activity, ascorbic acid and hydroxy methyl furfural (HMF) content of chips and dried forms.
Methods:
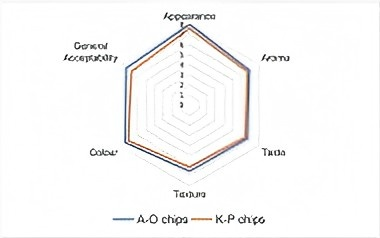
In this study, apple, pear, orange, and kiwi were dried in a convection oven at 100°–120°C. Moreover, apple-orange (A-O) and kiwi-pear (K-P) chips were produced in order to develop an alternative product. Dry matter, ash, TPC, ascorbic acid and HMF contents, pH, total acidity and antioxidant activity were determined in fresh, dried and chips samples. Sensory analysis was also carried out in the prepared fruit chips samples using the hedonic scale test.
Results:
The results revealed that dry matter and ash content increased in dried fruit and fruit chip samples. Drying caused a slight increase in pH and total acidity of all fruit samples. The ascorbic acid contents of kiwi and apple significantly decreased during the drying process. The drying process significantly impacted the total phenol content and antioxidant activity in dried slices. The dramatic increase of HMF was observed during oven-drying and chip production.
Conclusions:
Based on results, it can be concluded that drying and baking processes had variable effects on the chemical, sensory and bioactive properties of fruit samples. Sensory analysis revealed that A-O chips were more acceptable in terms of sensorial properties compared to K-P chips.
Bahar Kocabıyık, Derya AlkanPublished: March 10, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101077
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2025.101077Aim:
Dried fruits are consumed by many people around the world as a convenient alternative to fresh fruits with a long shelf life. As well as dried fruits, the manufacturing of baked chips based on fruits having good nutrition and sensory properties represents an alternative to healthier food. The aim of this study is to determine the different chemical properties of dried fruits and fruit chips when they are being fried in ovens. Another aim was to evaluate the changes in total phenolic content (TPC), antioxidant activity, ascorbic acid and hydroxy methyl furfural (HMF) content of chips and dried forms.
Methods:
In this study, apple, pear, orange, and kiwi were dried in a convection oven at 100°–120°C. Moreover, apple-orange (A-O) and kiwi-pear (K-P) chips were produced in order to develop an alternative product. Dry matter, ash, TPC, ascorbic acid and HMF contents, pH, total acidity and antioxidant activity were determined in fresh, dried and chips samples. Sensory analysis was also carried out in the prepared fruit chips samples using the hedonic scale test.
Results:
The results revealed that dry matter and ash content increased in dried fruit and fruit chip samples. Drying caused a slight increase in pH and total acidity of all fruit samples. The ascorbic acid contents of kiwi and apple significantly decreased during the drying process. The drying process significantly impacted the total phenol content and antioxidant activity in dried slices. The dramatic increase of HMF was observed during oven-drying and chip production.
Conclusions:
Based on results, it can be concluded that drying and baking processes had variable effects on the chemical, sensory and bioactive properties of fruit samples. Sensory analysis revealed that A-O chips were more acceptable in terms of sensorial properties compared to K-P chips.
 Effects of bran-enriched flour blends on the antioxidant properties, nutritional quality, and glycemic control of high-fiber biscuitsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes has heightened the demand for low glycemic index food products, leading to the exploration of alternative baking ingredients. This study assesses [...] Read more.
Effects of bran-enriched flour blends on the antioxidant properties, nutritional quality, and glycemic control of high-fiber biscuitsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes has heightened the demand for low glycemic index food products, leading to the exploration of alternative baking ingredients. This study assesses [...] Read more.Aim:
The increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes has heightened the demand for low glycemic index food products, leading to the exploration of alternative baking ingredients. This study assesses the effects of bran-enriched flour blends on the sensory, physical, nutritional, and antioxidant properties and glycemic control of high-fiber biscuits.
Methods:
Wheat, corn, sorghum, and sweet potato were obtained from the market. Linear programming (LP) optimized fiber content to create four high-fiber flour blends assessed for functional properties [water absorption capacity (WAC), oil absorption capacity (OAC), foaming capacity (FC), and stability]. Four high-fiber biscuits were developed and evaluated for nutritional composition (ash, crude fibers, water, carbohydrates, proteins, fats, Zn, Fe, Mg, Na, Ca, and P), sensory attributes (color, aroma, texture, and taste), physical properties (thickness, diameter, weight, spread ratio, browning index; L, a, and b), antioxidant properties (DPPH and FRAP activities), glycemic response, and in vitro glucose-binding capacity.
Results:
The formulated flours exhibited water and oil absorption capacities ranging from 1.95% to 2.70%, with the highest oil absorption in formulated flour 3. FC and stability varied significantly, with the control showing the highest values. Swelling power ranged from 1.27 cm3/g to 2.03 cm3/g. High-fiber biscuits had higher fiber (6.06–12.44%), protein (9.48–11.31%), Fe (3.01–4.55 ppm), and Mg (34.37–78.05 ppm) content, and lower carbohydrate (50.88–59.57%) contents compared to the control. They also demonstrated enhanced antioxidant properties with higher phenolic content (201.91–503.18 mg GAE/100 g) and DPPH-scavenging activity (0.07–0.27 µg/mL). Sensory evaluation indicated general acceptance. Biscuits 2 and 3 maintained steady blood glucose levels over 90 min, with biscuit 3 showing the highest in vitro glucose binding capacity (43.4 ± 4.3%).
Conclusions:
Incorporating diverse bran and flour types improves biscuit quality, particularly in blends like F2 (wheat flour, corn bran, and sorghum bran) and F3 (wheat flour, corn bran, sweet potato flour, and sorghum bran), offering beneficial options for diabetics.
Brice Ulrich Foudjo Saha ... Lifoter Kenneth NavtiPublished: March 06, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101076
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2025.101076
This article belongs to the special issue The food (r)evolution towards food quality/security and human nutritionAim:
The increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes has heightened the demand for low glycemic index food products, leading to the exploration of alternative baking ingredients. This study assesses the effects of bran-enriched flour blends on the sensory, physical, nutritional, and antioxidant properties and glycemic control of high-fiber biscuits.
Methods:
Wheat, corn, sorghum, and sweet potato were obtained from the market. Linear programming (LP) optimized fiber content to create four high-fiber flour blends assessed for functional properties [water absorption capacity (WAC), oil absorption capacity (OAC), foaming capacity (FC), and stability]. Four high-fiber biscuits were developed and evaluated for nutritional composition (ash, crude fibers, water, carbohydrates, proteins, fats, Zn, Fe, Mg, Na, Ca, and P), sensory attributes (color, aroma, texture, and taste), physical properties (thickness, diameter, weight, spread ratio, browning index; L, a, and b), antioxidant properties (DPPH and FRAP activities), glycemic response, and in vitro glucose-binding capacity.
Results:
The formulated flours exhibited water and oil absorption capacities ranging from 1.95% to 2.70%, with the highest oil absorption in formulated flour 3. FC and stability varied significantly, with the control showing the highest values. Swelling power ranged from 1.27 cm3/g to 2.03 cm3/g. High-fiber biscuits had higher fiber (6.06–12.44%), protein (9.48–11.31%), Fe (3.01–4.55 ppm), and Mg (34.37–78.05 ppm) content, and lower carbohydrate (50.88–59.57%) contents compared to the control. They also demonstrated enhanced antioxidant properties with higher phenolic content (201.91–503.18 mg GAE/100 g) and DPPH-scavenging activity (0.07–0.27 µg/mL). Sensory evaluation indicated general acceptance. Biscuits 2 and 3 maintained steady blood glucose levels over 90 min, with biscuit 3 showing the highest in vitro glucose binding capacity (43.4 ± 4.3%).
Conclusions:
Incorporating diverse bran and flour types improves biscuit quality, particularly in blends like F2 (wheat flour, corn bran, and sorghum bran) and F3 (wheat flour, corn bran, sweet potato flour, and sorghum bran), offering beneficial options for diabetics.
 Probiotic potential and antimicrobial efficacy of exopolysaccharide-producing lactic acid bacteria isolated from yoghurtOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The study investigates the probiotic potential of exopolysaccharide (EPS)-producing lactic acid bacteria (LAB) isolated from yoghurt samples. It assesses their antimicrobial efficacy against [...] Read more.
Probiotic potential and antimicrobial efficacy of exopolysaccharide-producing lactic acid bacteria isolated from yoghurtOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The study investigates the probiotic potential of exopolysaccharide (EPS)-producing lactic acid bacteria (LAB) isolated from yoghurt samples. It assesses their antimicrobial efficacy against [...] Read more.Aim:
The study investigates the probiotic potential of exopolysaccharide (EPS)-producing lactic acid bacteria (LAB) isolated from yoghurt samples. It assesses their antimicrobial efficacy against foodborne pathogens, particularly Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. The objective is to identify LAB strains that can be used as natural preservatives and health-promoting probiotics in functional foods.
Methods:
Yoghurt samples were collected from household local markets in Rawalpindi, Pakistan. LAB was isolated and identified using selective media, Gram staining, and biochemical tests. EPS production was quantified using the phenol-sulfuric acid method. Probiotic properties, including antimicrobial activity against E. coli and S. aureus, were evaluated using the disc diffusion method. Strains producing the highest EPS were biochemically characterised using the API Strep system.
Results:
Of 29 LAB isolates, 12 were identified as significant EPS producers, with Streptococcus thermophilus, Lactococcus lactis, and Limosilactobacillus fermentum demonstrating the highest EPS production (up to 62 µg/mL). These strains exhibited strong antimicrobial activity against E. coli and S. aureus, with inhibition zones ranging from 2 mm to 32.1 mm. The results confirmed the dual functionality of these strains as both texture enhancers and natural preservatives in food products.
Conclusions:
The EPS-producing LAB strains, particularly S. thermophilus, L. lactis, and L. fermentum, showed significant potential as probiotics and natural preservatives. Their antimicrobial activity and ability to enhance food texture suggest their applicability in the food industry to promote health and improve food safety. Further research should explore their stability in different food matrices for commercial use.
Nida Ishtiaq, Saad AhmedPublished: March 05, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101075
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2025.101075Aim:
The study investigates the probiotic potential of exopolysaccharide (EPS)-producing lactic acid bacteria (LAB) isolated from yoghurt samples. It assesses their antimicrobial efficacy against foodborne pathogens, particularly Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. The objective is to identify LAB strains that can be used as natural preservatives and health-promoting probiotics in functional foods.
Methods:
Yoghurt samples were collected from household local markets in Rawalpindi, Pakistan. LAB was isolated and identified using selective media, Gram staining, and biochemical tests. EPS production was quantified using the phenol-sulfuric acid method. Probiotic properties, including antimicrobial activity against E. coli and S. aureus, were evaluated using the disc diffusion method. Strains producing the highest EPS were biochemically characterised using the API Strep system.
Results:
Of 29 LAB isolates, 12 were identified as significant EPS producers, with Streptococcus thermophilus, Lactococcus lactis, and Limosilactobacillus fermentum demonstrating the highest EPS production (up to 62 µg/mL). These strains exhibited strong antimicrobial activity against E. coli and S. aureus, with inhibition zones ranging from 2 mm to 32.1 mm. The results confirmed the dual functionality of these strains as both texture enhancers and natural preservatives in food products.
Conclusions:
The EPS-producing LAB strains, particularly S. thermophilus, L. lactis, and L. fermentum, showed significant potential as probiotics and natural preservatives. Their antimicrobial activity and ability to enhance food texture suggest their applicability in the food industry to promote health and improve food safety. Further research should explore their stability in different food matrices for commercial use.
 Elevating sugar beet by-products into healthier, natural, and functional ingredientsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This research was conducted on the hypothesis that refined sugars negatively affect health, require high energy for production, generate significant carbon emissions, and produce environment [...] Read more.
Elevating sugar beet by-products into healthier, natural, and functional ingredientsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This research was conducted on the hypothesis that refined sugars negatively affect health, require high energy for production, generate significant carbon emissions, and produce environment [...] Read more.Aim:
This research was conducted on the hypothesis that refined sugars negatively affect health, require high energy for production, generate significant carbon emissions, and produce environmental waste. Additionally, by-products such as molasses and pulp, which are often underutilized, can be repurposed as value-added products for human consumption. This research focuses on a new, long-shelf-life product derived from sugar beet. The developed product retains nutrients such as protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals that are naturally present in sugar beet.
Methods:
The new method proposes using the entire beet as an unrefined alternative to refined sugar. The processing steps include cleaning, cooking, peeling, shredding, drying, and grinding. Various cooking methods were tested, and the optimum conditions were found to be 4.5 hours at 165°C. To prevent oxidation of peeled beets, a 0.5% citric acid solution was applied for 15 min at 25°C prior to cooking. Drying was performed in a convection oven with pans at 95°C for 7.5 hours.
Results:
The final product had a moisture content of 2.9% and a water activity level of 0.302. The product contained 78.6% total sugars, 12.9% fiber, and 3.45% protein, and was classified as an unrefined sweetener rich in both protein and fiber. Compared to the typical yield of 120 g of refined sugar from 1 kg of beets, this new method produces 219 g of product by utilizing fibers, proteins, and other nutrients, along with by-products such as molasses and pulp.
Conclusions:
Due to its high fiber and protein content, the new product has a low glycemic index. Compared to conventional beet sugar production, the proposed method reduces energy consumption and carbon emissions by 40% per unit of product. The new input obtained has a high potential to be used as a source of sugar and fiber in bakery and confectionery products. It is a more sustainable process than refined sugar.
Ahmet GörgülüPublished: February 25, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101074
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2025.101074Aim:
This research was conducted on the hypothesis that refined sugars negatively affect health, require high energy for production, generate significant carbon emissions, and produce environmental waste. Additionally, by-products such as molasses and pulp, which are often underutilized, can be repurposed as value-added products for human consumption. This research focuses on a new, long-shelf-life product derived from sugar beet. The developed product retains nutrients such as protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals that are naturally present in sugar beet.
Methods:
The new method proposes using the entire beet as an unrefined alternative to refined sugar. The processing steps include cleaning, cooking, peeling, shredding, drying, and grinding. Various cooking methods were tested, and the optimum conditions were found to be 4.5 hours at 165°C. To prevent oxidation of peeled beets, a 0.5% citric acid solution was applied for 15 min at 25°C prior to cooking. Drying was performed in a convection oven with pans at 95°C for 7.5 hours.
Results:
The final product had a moisture content of 2.9% and a water activity level of 0.302. The product contained 78.6% total sugars, 12.9% fiber, and 3.45% protein, and was classified as an unrefined sweetener rich in both protein and fiber. Compared to the typical yield of 120 g of refined sugar from 1 kg of beets, this new method produces 219 g of product by utilizing fibers, proteins, and other nutrients, along with by-products such as molasses and pulp.
Conclusions:
Due to its high fiber and protein content, the new product has a low glycemic index. Compared to conventional beet sugar production, the proposed method reduces energy consumption and carbon emissions by 40% per unit of product. The new input obtained has a high potential to be used as a source of sugar and fiber in bakery and confectionery products. It is a more sustainable process than refined sugar.
 Could the ketogenic diet offer hope in management of neurological diseases?Open AccessReviewThe ketogenic diet (KD) is a nutritional model that includes high fat, moderate protein, and low carbohydrate (less than 50 g). The “KD ratio” is used to determine the amount of macronutrients i [...] Read more.
Could the ketogenic diet offer hope in management of neurological diseases?Open AccessReviewThe ketogenic diet (KD) is a nutritional model that includes high fat, moderate protein, and low carbohydrate (less than 50 g). The “KD ratio” is used to determine the amount of macronutrients i [...] Read more.The ketogenic diet (KD) is a nutritional model that includes high fat, moderate protein, and low carbohydrate (less than 50 g). The “KD ratio” is used to determine the amount of macronutrients in the diet. In classical KD with the ratio of 3:1 or 4:1, 85–90% of the energy is provided from dietary fat. In addition to classical KD, the modified Atkins diet, low glycemic index therapy, and medium-chain triglyceride diet have also been used, and in some studies, ketosis has been achieved with exogenous ketone supplements. KD has long been recognized as a successful dietary approach in the treatment of refractory epilepsy. It is known that KD may also be effective in other neurological diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and migraine through various mechanisms such as providing an alternative energy source for neurons, reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, stimulating neurotransmitter synthesis and regulation of microbiota, etc. However, existing evidence is insufficient to make definitive conclusions about the effect of the KD on neurological diseases other than epilepsy due to the short intervention time, the small sample size, and the heterogeneity in the study methods. Considering factors such as genetics, endocrine differences, timing, and diet composition, it is important to apply and follow precision nutrition programs to increase the benefits of KD and reduce its side effects. In this review, the mechanisms of the KD on neurological diseases, recent evidence on the use of the KD in neurological diseases other than epilepsy, the limitations and difficulties in the literature on the KD, and the contraindications of the KD were discussed in detail.
Büşra Atabilen, Yasemin AkdevelioğluPublished: February 13, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101073
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2025.101073
This article belongs to the special issue Ketogenic Diet as Medical Nutrition TherapyThe ketogenic diet (KD) is a nutritional model that includes high fat, moderate protein, and low carbohydrate (less than 50 g). The “KD ratio” is used to determine the amount of macronutrients in the diet. In classical KD with the ratio of 3:1 or 4:1, 85–90% of the energy is provided from dietary fat. In addition to classical KD, the modified Atkins diet, low glycemic index therapy, and medium-chain triglyceride diet have also been used, and in some studies, ketosis has been achieved with exogenous ketone supplements. KD has long been recognized as a successful dietary approach in the treatment of refractory epilepsy. It is known that KD may also be effective in other neurological diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and migraine through various mechanisms such as providing an alternative energy source for neurons, reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, stimulating neurotransmitter synthesis and regulation of microbiota, etc. However, existing evidence is insufficient to make definitive conclusions about the effect of the KD on neurological diseases other than epilepsy due to the short intervention time, the small sample size, and the heterogeneity in the study methods. Considering factors such as genetics, endocrine differences, timing, and diet composition, it is important to apply and follow precision nutrition programs to increase the benefits of KD and reduce its side effects. In this review, the mechanisms of the KD on neurological diseases, recent evidence on the use of the KD in neurological diseases other than epilepsy, the limitations and difficulties in the literature on the KD, and the contraindications of the KD were discussed in detail.
 AI-powered revolution in plant sciences: advancements, applications, and challenges for sustainable agriculture and food securityOpen AccessReviewArtificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing plant sciences by enabling precise plant species identification, early disease diagnosis, crop yield prediction, and precision agriculture optimizatio [...] Read more.
AI-powered revolution in plant sciences: advancements, applications, and challenges for sustainable agriculture and food securityOpen AccessReviewArtificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing plant sciences by enabling precise plant species identification, early disease diagnosis, crop yield prediction, and precision agriculture optimizatio [...] Read more.Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing plant sciences by enabling precise plant species identification, early disease diagnosis, crop yield prediction, and precision agriculture optimization. AI uses machine learning and image recognition to aid ecological research and biodiversity conservation. It plays a crucial role in plant breeding by accelerating the development of resilient, high-yielding crops with desirable traits. AI models using climate and soil data contribute to sustainable agriculture and food security. In plant phenotyping, AI automates the measurement and analysis of plant characteristics, enhancing our understanding of plant growth. Ongoing research aims to improve AI models’ robustness and interpretability while addressing data privacy and algorithmic biases. Interdisciplinary collaboration is essential to fully harness AI’s potential in plant sciences for a sustainable, food-secure future.
Deependra Kumar Gupta ... Ajay Kumar SinghPublished: August 06, 2024 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2024;2:443–459
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2024.00045Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing plant sciences by enabling precise plant species identification, early disease diagnosis, crop yield prediction, and precision agriculture optimization. AI uses machine learning and image recognition to aid ecological research and biodiversity conservation. It plays a crucial role in plant breeding by accelerating the development of resilient, high-yielding crops with desirable traits. AI models using climate and soil data contribute to sustainable agriculture and food security. In plant phenotyping, AI automates the measurement and analysis of plant characteristics, enhancing our understanding of plant growth. Ongoing research aims to improve AI models’ robustness and interpretability while addressing data privacy and algorithmic biases. Interdisciplinary collaboration is essential to fully harness AI’s potential in plant sciences for a sustainable, food-secure future.
 Olive oil, fruit and leaves in diabetes mellitus type 2 treatmentOpen AccessReviewThe Mediterranean dietary pattern, where extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) takes the central spot, is related to longer life expectancy and lower risk of a number of non-communicable diseases, including [...] Read more.
Olive oil, fruit and leaves in diabetes mellitus type 2 treatmentOpen AccessReviewThe Mediterranean dietary pattern, where extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) takes the central spot, is related to longer life expectancy and lower risk of a number of non-communicable diseases, including [...] Read more.The Mediterranean dietary pattern, where extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) takes the central spot, is related to longer life expectancy and lower risk of a number of non-communicable diseases, including cardiovascular, diabetes, dementias, and cancer. Positive effect of olive oil on a broad spectrum of diseases, including diabetes mellitus type 2 (DMT2), is usually attributed to its fatty acid content (e.g., oleic acid). Yet, in the last two decades researchers confirmed that, the phenolic compounds (e.g., oleuropein) also significantly alter on glycaemic regulation. Other unprocessed parts of olive plant (fruit and leaves) showed positive impact on glycaemic variability among individuals living with DMT2. The present review focuses on the available research findings on the effect of olive oil, fruits, and leaves on DMT2 treatment. Specifically, the focus is on polyphenols and fats of olive oil, fruits, and leaves with regard to their antidiabetic biological activities.
Mario Nosić ... Ines BanjariPublished: October 29, 2023 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2023;1:192–205
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00015
This article belongs to the special issue Natural Products in Health and DiseaseThe Mediterranean dietary pattern, where extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) takes the central spot, is related to longer life expectancy and lower risk of a number of non-communicable diseases, including cardiovascular, diabetes, dementias, and cancer. Positive effect of olive oil on a broad spectrum of diseases, including diabetes mellitus type 2 (DMT2), is usually attributed to its fatty acid content (e.g., oleic acid). Yet, in the last two decades researchers confirmed that, the phenolic compounds (e.g., oleuropein) also significantly alter on glycaemic regulation. Other unprocessed parts of olive plant (fruit and leaves) showed positive impact on glycaemic variability among individuals living with DMT2. The present review focuses on the available research findings on the effect of olive oil, fruits, and leaves on DMT2 treatment. Specifically, the focus is on polyphenols and fats of olive oil, fruits, and leaves with regard to their antidiabetic biological activities.
 Future trends in Food Science and Foodomics: a perspective view by the Editorial Team of Exploration of Foods and FoodomicsOpen AccessPerspectiveIn this perspective article, several internationally recognized experts, members of the editorial team of this journal, discuss a selection of current hot topics identified in Food Science and Foodo [...] Read more.
Future trends in Food Science and Foodomics: a perspective view by the Editorial Team of Exploration of Foods and FoodomicsOpen AccessPerspectiveIn this perspective article, several internationally recognized experts, members of the editorial team of this journal, discuss a selection of current hot topics identified in Food Science and Foodo [...] Read more.In this perspective article, several internationally recognized experts, members of the editorial team of this journal, discuss a selection of current hot topics identified in Food Science and Foodomics. The topics are comprised of the main areas of Food Science and Foodomics, namely, food safety, food authenticity, food processing, and food bioactivity. Logically, several of the discussed topics involve more than one of the mentioned main areas. Regarding food safety, the topics discussed are the use of analytical nanotechnology, nanometrology, nano-chromatography; the determination of organic contaminants based on MS and NMR; the impact of microplastics and nanoplastics on food or the contamination of foods with plant toxins. Regarding food authenticity, the paper discusses the role of MS, NMR, biosensors and the new trends in foodomics for food authentication. In terms of food processing, the work shows interesting perspectives on novel processing technologies, the effect of food processing on the gut microbiota or in the interaction among secondary metabolites and macromolecules; the development of active packaging, and the potential effects of introducing recycled plastics in food packaging; the new green extraction and encapsulation strategies of bioactive compounds from food by-products; and the anti-biofilm capacity of natural compounds/extracts/vegetal oils and essential oils. Food bioactivity and the relation between food and health includes the bioavailability and bioaccessibility of bioactive compounds; new trends and challenges in the interaction of nutraceuticals with biological systems; how food matrix impacts the bioaccessibility of nutrients and bioactive compounds; or the study of biodiversity, food and human health through one-health concept. We anticipate elaborations on these hot topics will promote further studies in Food Science and Foodomics.
Elena Ibáñez ... Alejandro CifuentesPublished: November 28, 2024 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2024;2:707–766
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2024.00060In this perspective article, several internationally recognized experts, members of the editorial team of this journal, discuss a selection of current hot topics identified in Food Science and Foodomics. The topics are comprised of the main areas of Food Science and Foodomics, namely, food safety, food authenticity, food processing, and food bioactivity. Logically, several of the discussed topics involve more than one of the mentioned main areas. Regarding food safety, the topics discussed are the use of analytical nanotechnology, nanometrology, nano-chromatography; the determination of organic contaminants based on MS and NMR; the impact of microplastics and nanoplastics on food or the contamination of foods with plant toxins. Regarding food authenticity, the paper discusses the role of MS, NMR, biosensors and the new trends in foodomics for food authentication. In terms of food processing, the work shows interesting perspectives on novel processing technologies, the effect of food processing on the gut microbiota or in the interaction among secondary metabolites and macromolecules; the development of active packaging, and the potential effects of introducing recycled plastics in food packaging; the new green extraction and encapsulation strategies of bioactive compounds from food by-products; and the anti-biofilm capacity of natural compounds/extracts/vegetal oils and essential oils. Food bioactivity and the relation between food and health includes the bioavailability and bioaccessibility of bioactive compounds; new trends and challenges in the interaction of nutraceuticals with biological systems; how food matrix impacts the bioaccessibility of nutrients and bioactive compounds; or the study of biodiversity, food and human health through one-health concept. We anticipate elaborations on these hot topics will promote further studies in Food Science and Foodomics.
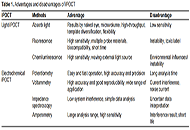
 Intelligent point of care test for food safety via a smartphoneOpen AccessReviewThe on-site, rapid, and intelligence detection methods are the wave in food safety. Recently, intelligent point-of-care test (iPOCT) methods serve as a promising alternative for advanced monitoring [...] Read more.
Intelligent point of care test for food safety via a smartphoneOpen AccessReviewThe on-site, rapid, and intelligence detection methods are the wave in food safety. Recently, intelligent point-of-care test (iPOCT) methods serve as a promising alternative for advanced monitoring [...] Read more.The on-site, rapid, and intelligence detection methods are the wave in food safety. Recently, intelligent point-of-care test (iPOCT) methods serve as a promising alternative for advanced monitoring in food safety. By integrating smartphones with various detection methods, iPOCT methods demonstrate unique merits. Compared with lab-dependent instruments, iPOCT strategies have a short turnaround time (several minutes), high accuracy (μm level or less), and portability (smartphones). This work discussed principles of optical and electrical iPOCT methods, including absorbing light, fluorescence, chemiluminescence, potentiometry, voltammetry, impedance spectroscopy, and amperometry. The review emphasizes the practical applications for testing chemical and biological hazards in complex food matrices. The commercialization, challenges, and future trends of iPOCT are discussed as well.
Le Zhang ... Zhaowei ZhangPublished: August 30, 2023 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2023;1:143–161
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00012The on-site, rapid, and intelligence detection methods are the wave in food safety. Recently, intelligent point-of-care test (iPOCT) methods serve as a promising alternative for advanced monitoring in food safety. By integrating smartphones with various detection methods, iPOCT methods demonstrate unique merits. Compared with lab-dependent instruments, iPOCT strategies have a short turnaround time (several minutes), high accuracy (μm level or less), and portability (smartphones). This work discussed principles of optical and electrical iPOCT methods, including absorbing light, fluorescence, chemiluminescence, potentiometry, voltammetry, impedance spectroscopy, and amperometry. The review emphasizes the practical applications for testing chemical and biological hazards in complex food matrices. The commercialization, challenges, and future trends of iPOCT are discussed as well.
 Atlantic algae as food and their extractsOpen AccessReviewAmong the species of the rich algological flora of the North Atlantic, some can be used for direct consumption in human food, although few are currently cultivated on a large scale and/or marketed f [...] Read more.
Atlantic algae as food and their extractsOpen AccessReviewAmong the species of the rich algological flora of the North Atlantic, some can be used for direct consumption in human food, although few are currently cultivated on a large scale and/or marketed f [...] Read more.Among the species of the rich algological flora of the North Atlantic, some can be used for direct consumption in human food, although few are currently cultivated on a large scale and/or marketed for this purpose. The European tradition regarding this custom is practically nil and the expression of current eating habits is little different from the past. In Europe, only in times of hunger (for example, during the Great World Wars) was seaweed consumed by the populations closest to the coastline. In addition to the multiple applications described, which expanded enormously in the 1970s, based on phycocolloids (agar, carrageenans, and alginates)—used as thickeners in the food industry, in soups, meat preserves, dairy products, and pastries—there is currently a trend of increasing consumption, both in North America and Europe.
Leonel PereiraPublished: April 27, 2023 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2023;1:15–31
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00003
This article belongs to the special issue The food (r)evolution towards food quality/security and human nutritionAmong the species of the rich algological flora of the North Atlantic, some can be used for direct consumption in human food, although few are currently cultivated on a large scale and/or marketed for this purpose. The European tradition regarding this custom is practically nil and the expression of current eating habits is little different from the past. In Europe, only in times of hunger (for example, during the Great World Wars) was seaweed consumed by the populations closest to the coastline. In addition to the multiple applications described, which expanded enormously in the 1970s, based on phycocolloids (agar, carrageenans, and alginates)—used as thickeners in the food industry, in soups, meat preserves, dairy products, and pastries—there is currently a trend of increasing consumption, both in North America and Europe.
 Recent advances in nano-related natural antioxidants, their extraction methods and applications in the food industryOpen AccessReviewNatural antioxidants, such as phenolic compounds, carotenoids, vitamins, and microelements, are predominant in fruits, vegetables, herbs, and spices. The accretion interest of consumers in utilizing [...] Read more.
Recent advances in nano-related natural antioxidants, their extraction methods and applications in the food industryOpen AccessReviewNatural antioxidants, such as phenolic compounds, carotenoids, vitamins, and microelements, are predominant in fruits, vegetables, herbs, and spices. The accretion interest of consumers in utilizing [...] Read more.Natural antioxidants, such as phenolic compounds, carotenoids, vitamins, and microelements, are predominant in fruits, vegetables, herbs, and spices. The accretion interest of consumers in utilizing natural ingredients in food products, have accelerated the appeal for functional “natural” operations. Therefore, understanding how natural antioxidants especially nano-antioxidants, and their delivery systems when used in antioxidant polymers for food packaging are extracted from natural sources, would help prevent oxidation reactions. Given the increasing role of natural antioxidants in the daily lives of today’s communities, a continuous synthesis of relevant literature is pertinent. To supplement existing information, recent advances in nano-related natural antioxidants, their extraction methods and applications in the food industry are discussed in this current work. Insightfully positioning antioxidants within the nano-delivery systems, this current work reveals the potential nanotechnology provides in enhancing the absorption of antioxidants in human metabolic systems.
Ayla Elmi Kashtiban ... Sayna ZahediniaPublished: April 19, 2024 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2024;2:125–154
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2024.00030
This article belongs to the special issue The food (r)evolution towards food quality/security and human nutritionNatural antioxidants, such as phenolic compounds, carotenoids, vitamins, and microelements, are predominant in fruits, vegetables, herbs, and spices. The accretion interest of consumers in utilizing natural ingredients in food products, have accelerated the appeal for functional “natural” operations. Therefore, understanding how natural antioxidants especially nano-antioxidants, and their delivery systems when used in antioxidant polymers for food packaging are extracted from natural sources, would help prevent oxidation reactions. Given the increasing role of natural antioxidants in the daily lives of today’s communities, a continuous synthesis of relevant literature is pertinent. To supplement existing information, recent advances in nano-related natural antioxidants, their extraction methods and applications in the food industry are discussed in this current work. Insightfully positioning antioxidants within the nano-delivery systems, this current work reveals the potential nanotechnology provides in enhancing the absorption of antioxidants in human metabolic systems.
 Future trends in Food Science and Foodomics: a perspective view by the Editorial Team of Exploration of Foods and FoodomicsOpen AccessPerspectiveIn this perspective article, several internationally recognized experts, members of the editorial team of this journal, discuss a selection of current hot topics identified in Food Science and Foodo [...] Read more.
Future trends in Food Science and Foodomics: a perspective view by the Editorial Team of Exploration of Foods and FoodomicsOpen AccessPerspectiveIn this perspective article, several internationally recognized experts, members of the editorial team of this journal, discuss a selection of current hot topics identified in Food Science and Foodo [...] Read more.In this perspective article, several internationally recognized experts, members of the editorial team of this journal, discuss a selection of current hot topics identified in Food Science and Foodomics. The topics are comprised of the main areas of Food Science and Foodomics, namely, food safety, food authenticity, food processing, and food bioactivity. Logically, several of the discussed topics involve more than one of the mentioned main areas. Regarding food safety, the topics discussed are the use of analytical nanotechnology, nanometrology, nano-chromatography; the determination of organic contaminants based on MS and NMR; the impact of microplastics and nanoplastics on food or the contamination of foods with plant toxins. Regarding food authenticity, the paper discusses the role of MS, NMR, biosensors and the new trends in foodomics for food authentication. In terms of food processing, the work shows interesting perspectives on novel processing technologies, the effect of food processing on the gut microbiota or in the interaction among secondary metabolites and macromolecules; the development of active packaging, and the potential effects of introducing recycled plastics in food packaging; the new green extraction and encapsulation strategies of bioactive compounds from food by-products; and the anti-biofilm capacity of natural compounds/extracts/vegetal oils and essential oils. Food bioactivity and the relation between food and health includes the bioavailability and bioaccessibility of bioactive compounds; new trends and challenges in the interaction of nutraceuticals with biological systems; how food matrix impacts the bioaccessibility of nutrients and bioactive compounds; or the study of biodiversity, food and human health through one-health concept. We anticipate elaborations on these hot topics will promote further studies in Food Science and Foodomics.
Elena Ibáñez ... Alejandro CifuentesPublished: November 28, 2024 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2024;2:707–766
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2024.00060In this perspective article, several internationally recognized experts, members of the editorial team of this journal, discuss a selection of current hot topics identified in Food Science and Foodomics. The topics are comprised of the main areas of Food Science and Foodomics, namely, food safety, food authenticity, food processing, and food bioactivity. Logically, several of the discussed topics involve more than one of the mentioned main areas. Regarding food safety, the topics discussed are the use of analytical nanotechnology, nanometrology, nano-chromatography; the determination of organic contaminants based on MS and NMR; the impact of microplastics and nanoplastics on food or the contamination of foods with plant toxins. Regarding food authenticity, the paper discusses the role of MS, NMR, biosensors and the new trends in foodomics for food authentication. In terms of food processing, the work shows interesting perspectives on novel processing technologies, the effect of food processing on the gut microbiota or in the interaction among secondary metabolites and macromolecules; the development of active packaging, and the potential effects of introducing recycled plastics in food packaging; the new green extraction and encapsulation strategies of bioactive compounds from food by-products; and the anti-biofilm capacity of natural compounds/extracts/vegetal oils and essential oils. Food bioactivity and the relation between food and health includes the bioavailability and bioaccessibility of bioactive compounds; new trends and challenges in the interaction of nutraceuticals with biological systems; how food matrix impacts the bioaccessibility of nutrients and bioactive compounds; or the study of biodiversity, food and human health through one-health concept. We anticipate elaborations on these hot topics will promote further studies in Food Science and Foodomics.
 AI-powered revolution in plant sciences: advancements, applications, and challenges for sustainable agriculture and food securityOpen AccessReviewArtificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing plant sciences by enabling precise plant species identification, early disease diagnosis, crop yield prediction, and precision agriculture optimizatio [...] Read more.
AI-powered revolution in plant sciences: advancements, applications, and challenges for sustainable agriculture and food securityOpen AccessReviewArtificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing plant sciences by enabling precise plant species identification, early disease diagnosis, crop yield prediction, and precision agriculture optimizatio [...] Read more.Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing plant sciences by enabling precise plant species identification, early disease diagnosis, crop yield prediction, and precision agriculture optimization. AI uses machine learning and image recognition to aid ecological research and biodiversity conservation. It plays a crucial role in plant breeding by accelerating the development of resilient, high-yielding crops with desirable traits. AI models using climate and soil data contribute to sustainable agriculture and food security. In plant phenotyping, AI automates the measurement and analysis of plant characteristics, enhancing our understanding of plant growth. Ongoing research aims to improve AI models’ robustness and interpretability while addressing data privacy and algorithmic biases. Interdisciplinary collaboration is essential to fully harness AI’s potential in plant sciences for a sustainable, food-secure future.
Deependra Kumar Gupta ... Ajay Kumar SinghPublished: August 06, 2024 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2024;2:443–459
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2024.00045Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing plant sciences by enabling precise plant species identification, early disease diagnosis, crop yield prediction, and precision agriculture optimization. AI uses machine learning and image recognition to aid ecological research and biodiversity conservation. It plays a crucial role in plant breeding by accelerating the development of resilient, high-yielding crops with desirable traits. AI models using climate and soil data contribute to sustainable agriculture and food security. In plant phenotyping, AI automates the measurement and analysis of plant characteristics, enhancing our understanding of plant growth. Ongoing research aims to improve AI models’ robustness and interpretability while addressing data privacy and algorithmic biases. Interdisciplinary collaboration is essential to fully harness AI’s potential in plant sciences for a sustainable, food-secure future.
 Bioaccumulation of environmental pollutants and marine toxins in bivalve molluscs: a reviewOpen AccessReviewSeafood is both nutritionally and economically significant, with bivalve molluscs being particularly valuable for monitoring environmental pollutants due to their filter-feeding nature and ability t [...] Read more.
Bioaccumulation of environmental pollutants and marine toxins in bivalve molluscs: a reviewOpen AccessReviewSeafood is both nutritionally and economically significant, with bivalve molluscs being particularly valuable for monitoring environmental pollutants due to their filter-feeding nature and ability t [...] Read more.Seafood is both nutritionally and economically significant, with bivalve molluscs being particularly valuable for monitoring environmental pollutants due to their filter-feeding nature and ability to bioaccumulate pollutants. While not often linked to food poisoning, these molluscs can occasionally introduce health risks, highlighting the need for vigilant monitoring. This review provides a thorough analysis of pollutants—including persistent and emerging pollutants, as well as marine toxins—found in bivalve molluscs between 2019 and 2024. Among the studied pollutants, plasticizers and alkaloids are the most frequently analyzed, with liquid and gas chromatography (GC) tandem mass spectrometry (MS) the predominant methods, although novel approaches to determine these compounds, such as sensors, have also emerged in recent years. However, many studies are focused on establishing pollutant content without addressing bioaccumulation (BA) factors, and a lack of standardization in species and sampling locations complicates comparisons between the different published works. Despite some studies linking human activity and algal blooms to BA dynamics, more comprehensive research is needed. Additionally, limited data on the depuration capacity of molluscs underscores the need for further investigation. Although pollutant levels generally remain within legal limits, many substances remain unregulated. Environmental factors also play a critical role in influencing BA, emphasizing the need for future studies to focus on BA factors to better understand these complex dynamics.
Clara Ochoa-Esteso ... María Jesús Lerma-GarcíaPublished: December 03, 2024 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2024;2:788–809
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2024.00062
This article belongs to the special issue Food Contaminants: Analysis, Occurrence and Risk AssessmentSeafood is both nutritionally and economically significant, with bivalve molluscs being particularly valuable for monitoring environmental pollutants due to their filter-feeding nature and ability to bioaccumulate pollutants. While not often linked to food poisoning, these molluscs can occasionally introduce health risks, highlighting the need for vigilant monitoring. This review provides a thorough analysis of pollutants—including persistent and emerging pollutants, as well as marine toxins—found in bivalve molluscs between 2019 and 2024. Among the studied pollutants, plasticizers and alkaloids are the most frequently analyzed, with liquid and gas chromatography (GC) tandem mass spectrometry (MS) the predominant methods, although novel approaches to determine these compounds, such as sensors, have also emerged in recent years. However, many studies are focused on establishing pollutant content without addressing bioaccumulation (BA) factors, and a lack of standardization in species and sampling locations complicates comparisons between the different published works. Despite some studies linking human activity and algal blooms to BA dynamics, more comprehensive research is needed. Additionally, limited data on the depuration capacity of molluscs underscores the need for further investigation. Although pollutant levels generally remain within legal limits, many substances remain unregulated. Environmental factors also play a critical role in influencing BA, emphasizing the need for future studies to focus on BA factors to better understand these complex dynamics.
 Exploring the potential of laser photoacoustic spectroscopy (LPAS) for predicting amylose content in rice flourOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Rice, one of the most widely consumed staple foods globally, relies on amylose content for its quality, impacting cooking, digestibility, and health properties. Conventional amylose determin [...] Read more.
Exploring the potential of laser photoacoustic spectroscopy (LPAS) for predicting amylose content in rice flourOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Rice, one of the most widely consumed staple foods globally, relies on amylose content for its quality, impacting cooking, digestibility, and health properties. Conventional amylose determin [...] Read more.Aim:
Rice, one of the most widely consumed staple foods globally, relies on amylose content for its quality, impacting cooking, digestibility, and health properties. Conventional amylose determination methods are time-consuming and involve complex chemical treatments. Thus, there is growing interest in rapid, non-destructive techniques for food quality control. This study explores the potential of laser photoacoustic spectroscopy (LPAS) for predicting amylose content in rice flour.
Methods:
Certified rice flour standards of varying amylose levels have been analyzed using a quantum-cascade LPAS system. Preliminary analysis utilized Fourier transform infrared/attenuated total reflectance (FTIR/ATR) to identify rice starch spectral features in the IR region. Multivariate data tools like principal component analysis (PCA) and partial least squares (PLS) regression have been combined with LPAS measurements to extract information from the complex spectral data set and to demonstrate the ability of the system to predict their amylose content.
Results:
LPAS spectra, recorded between 7.0–11.0 μm, displayed two broad bands, showing a linear increase in signal with amylose content, especially notable in the specific fingerprint region within 8.5–10.0 μm. The prominent peak at 9.3 μm exhibited a high linear correlation with amylose levels (R2 > 0.99). PCA effectively differentiated rice flour samples, while PLS accurately predicted amylose content. The difference between predicted and actual amylose is significantly less than the statistical error of the measurement.
Conclusions:
LPAS combined with chemometric analysis emerges as a promising non-destructive method for rapidly assessing rice amylose content, potentially supplementing or replacing current standard methods. Its advantages, limitations, and future prospects in rice quality analysis are discussed, highlighting its role in preliminary screening.
Florinda Artuso ... Fabio PollastronePublished: September 10, 2024 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2024;2:542–554
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2024.00050
This article belongs to the special issue Metrological Aspects in the Analysis of Nutrients, Functional Compounds, Additives and Contaminants in Food and FeedAim:
Rice, one of the most widely consumed staple foods globally, relies on amylose content for its quality, impacting cooking, digestibility, and health properties. Conventional amylose determination methods are time-consuming and involve complex chemical treatments. Thus, there is growing interest in rapid, non-destructive techniques for food quality control. This study explores the potential of laser photoacoustic spectroscopy (LPAS) for predicting amylose content in rice flour.
Methods:
Certified rice flour standards of varying amylose levels have been analyzed using a quantum-cascade LPAS system. Preliminary analysis utilized Fourier transform infrared/attenuated total reflectance (FTIR/ATR) to identify rice starch spectral features in the IR region. Multivariate data tools like principal component analysis (PCA) and partial least squares (PLS) regression have been combined with LPAS measurements to extract information from the complex spectral data set and to demonstrate the ability of the system to predict their amylose content.
Results:
LPAS spectra, recorded between 7.0–11.0 μm, displayed two broad bands, showing a linear increase in signal with amylose content, especially notable in the specific fingerprint region within 8.5–10.0 μm. The prominent peak at 9.3 μm exhibited a high linear correlation with amylose levels (R2 > 0.99). PCA effectively differentiated rice flour samples, while PLS accurately predicted amylose content. The difference between predicted and actual amylose is significantly less than the statistical error of the measurement.
Conclusions:
LPAS combined with chemometric analysis emerges as a promising non-destructive method for rapidly assessing rice amylose content, potentially supplementing or replacing current standard methods. Its advantages, limitations, and future prospects in rice quality analysis are discussed, highlighting its role in preliminary screening.
 From data to nutrition: the impact of computing infrastructure and artificial intelligenceOpen AccessPerspectiveThis article explores the significant impact that artificial intelligence (AI) could have on food safety and nutrition, with a specific focus on the use of machine learning and neural networks for d [...] Read more.
From data to nutrition: the impact of computing infrastructure and artificial intelligenceOpen AccessPerspectiveThis article explores the significant impact that artificial intelligence (AI) could have on food safety and nutrition, with a specific focus on the use of machine learning and neural networks for d [...] Read more.This article explores the significant impact that artificial intelligence (AI) could have on food safety and nutrition, with a specific focus on the use of machine learning and neural networks for disease risk prediction, diet personalization, and food product development. Specific AI techniques and explainable AI (XAI) are highlighted for their potential in personalizing diet recommendations, predicting models for disease prevention, and enhancing data-driven approaches to food production. The article also underlines the importance of high-performance computing infrastructures and data management strategies, including data operations (DataOps) for efficient data pipelines and findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable (FAIR) principles for open and standardized data sharing. Additionally, it explores the concept of open data sharing and the integration of machine learning algorithms in the food industry to enhance food safety and product development. It highlights the METROFOOD-IT project as a best practice example of implementing advancements in the agri-food sector, demonstrating successful interdisciplinary collaboration. The project fosters both data security and transparency within a decentralized data space model, ensuring reliable and efficient data sharing. However, challenges such as data privacy, model interoperability, and ethical considerations remain key obstacles. The article also discusses the need for ongoing interdisciplinary collaboration between data scientists, nutritionists, and food technologists to effectively address these challenges. Future research should focus on refining AI models to improve their reliability and exploring how to integrate these technologies into everyday nutritional practices for better health outcomes.
Pierpaolo Di Bitonto ... Sabina TangaroPublished: December 03, 2024 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2024;2:810–829
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2024.00063
This article belongs to the special issue Metrological Aspects in the Analysis of Nutrients, Functional Compounds, Additives and Contaminants in Food and FeedThis article explores the significant impact that artificial intelligence (AI) could have on food safety and nutrition, with a specific focus on the use of machine learning and neural networks for disease risk prediction, diet personalization, and food product development. Specific AI techniques and explainable AI (XAI) are highlighted for their potential in personalizing diet recommendations, predicting models for disease prevention, and enhancing data-driven approaches to food production. The article also underlines the importance of high-performance computing infrastructures and data management strategies, including data operations (DataOps) for efficient data pipelines and findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable (FAIR) principles for open and standardized data sharing. Additionally, it explores the concept of open data sharing and the integration of machine learning algorithms in the food industry to enhance food safety and product development. It highlights the METROFOOD-IT project as a best practice example of implementing advancements in the agri-food sector, demonstrating successful interdisciplinary collaboration. The project fosters both data security and transparency within a decentralized data space model, ensuring reliable and efficient data sharing. However, challenges such as data privacy, model interoperability, and ethical considerations remain key obstacles. The article also discusses the need for ongoing interdisciplinary collaboration between data scientists, nutritionists, and food technologists to effectively address these challenges. Future research should focus on refining AI models to improve their reliability and exploring how to integrate these technologies into everyday nutritional practices for better health outcomes.
 Atlantic algae as food and their extractsOpen AccessReviewAmong the species of the rich algological flora of the North Atlantic, some can be used for direct consumption in human food, although few are currently cultivated on a large scale and/or marketed f [...] Read more.
Atlantic algae as food and their extractsOpen AccessReviewAmong the species of the rich algological flora of the North Atlantic, some can be used for direct consumption in human food, although few are currently cultivated on a large scale and/or marketed f [...] Read more.Among the species of the rich algological flora of the North Atlantic, some can be used for direct consumption in human food, although few are currently cultivated on a large scale and/or marketed for this purpose. The European tradition regarding this custom is practically nil and the expression of current eating habits is little different from the past. In Europe, only in times of hunger (for example, during the Great World Wars) was seaweed consumed by the populations closest to the coastline. In addition to the multiple applications described, which expanded enormously in the 1970s, based on phycocolloids (agar, carrageenans, and alginates)—used as thickeners in the food industry, in soups, meat preserves, dairy products, and pastries—there is currently a trend of increasing consumption, both in North America and Europe.
Leonel PereiraPublished: April 27, 2023 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2023;1:15–31
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00003
This article belongs to the special issue The food (r)evolution towards food quality/security and human nutritionAmong the species of the rich algological flora of the North Atlantic, some can be used for direct consumption in human food, although few are currently cultivated on a large scale and/or marketed for this purpose. The European tradition regarding this custom is practically nil and the expression of current eating habits is little different from the past. In Europe, only in times of hunger (for example, during the Great World Wars) was seaweed consumed by the populations closest to the coastline. In addition to the multiple applications described, which expanded enormously in the 1970s, based on phycocolloids (agar, carrageenans, and alginates)—used as thickeners in the food industry, in soups, meat preserves, dairy products, and pastries—there is currently a trend of increasing consumption, both in North America and Europe.
 Development of soy whey fortified orange juice beverages: their physicochemical, rheological, antioxidant, and sensory propertiesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Soy whey is a byproduct of tofu production and is being discarded after tofu preparation. However, soy whey is a rich source of phytochemicals, minerals, and protein. The present study was c [...] Read more.
Development of soy whey fortified orange juice beverages: their physicochemical, rheological, antioxidant, and sensory propertiesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Soy whey is a byproduct of tofu production and is being discarded after tofu preparation. However, soy whey is a rich source of phytochemicals, minerals, and protein. The present study was c [...] Read more.Aim:
Soy whey is a byproduct of tofu production and is being discarded after tofu preparation. However, soy whey is a rich source of phytochemicals, minerals, and protein. The present study was conducted to utilize soy whey for the development of nutraceutical-rich orange juice beverages.
Methods:
The soy whey and orange juice were produced and beverage samples were developed from them. The samples were evaluated for physicochemical, rheological, antioxidant, and sensory properties to evaluate the optimum percentage of soy whey that can be utilized for beverage development.
Results:
The protein content increased from 0.45% to 1.65% with an increase in soy whey from 0% to 50%. The pH of the beverage samples was in the range of 4.27–4.77 with the total soluble solids (TSSs) of 5.75–6.0 for various beverage samples. The lightness (L*), redness (+a*), and yellowness (+b*) of beverage samples range between 31.57–49.04, 1.21–0.54, and 25.37–39.63 respectively. The vitamin C content of the beverage samples was 56.30 mg/L, 52.75 mg/L, 36.97 mg/L, 26.35 mg/L, and 22.87 mg/L for A, B, C, D, and E beverages respectively. The 1, 1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP), reducing power ranges of beverage samples range between 91.2–96.23%, 0.521–0.994%, and 0.204–0.859% respectively, and total phenolic content (TPC) ranges between 112 mg gallic acid equivalents (GAE)/100 mL and 181 mg GAE/100 mL of beverage samples. The beverage samples presented a shear thinning property with a flow index (n) ranging between 0.2371–0.8214. The consistency coefficient of the beverage samples ranges between 0.0405 Pa∙Sn and 0.0041 Pa∙Sn. The control, 20%, and 30% soy whey-containing beverage samples showed higher sensory properties.
Conclusions:
The beverage samples with 0%, 20%, and 30% showed improved DPPH and FRAP percent activity and higher overall acceptability compared to 40% and 50% soy whey-containing beverage samples.
Hilal Ahmad Punoo ... Andleeb MuzaffarPublished: October 29, 2023 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2023;1:206–220
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00016Aim:
Soy whey is a byproduct of tofu production and is being discarded after tofu preparation. However, soy whey is a rich source of phytochemicals, minerals, and protein. The present study was conducted to utilize soy whey for the development of nutraceutical-rich orange juice beverages.
Methods:
The soy whey and orange juice were produced and beverage samples were developed from them. The samples were evaluated for physicochemical, rheological, antioxidant, and sensory properties to evaluate the optimum percentage of soy whey that can be utilized for beverage development.
Results:
The protein content increased from 0.45% to 1.65% with an increase in soy whey from 0% to 50%. The pH of the beverage samples was in the range of 4.27–4.77 with the total soluble solids (TSSs) of 5.75–6.0 for various beverage samples. The lightness (L*), redness (+a*), and yellowness (+b*) of beverage samples range between 31.57–49.04, 1.21–0.54, and 25.37–39.63 respectively. The vitamin C content of the beverage samples was 56.30 mg/L, 52.75 mg/L, 36.97 mg/L, 26.35 mg/L, and 22.87 mg/L for A, B, C, D, and E beverages respectively. The 1, 1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP), reducing power ranges of beverage samples range between 91.2–96.23%, 0.521–0.994%, and 0.204–0.859% respectively, and total phenolic content (TPC) ranges between 112 mg gallic acid equivalents (GAE)/100 mL and 181 mg GAE/100 mL of beverage samples. The beverage samples presented a shear thinning property with a flow index (n) ranging between 0.2371–0.8214. The consistency coefficient of the beverage samples ranges between 0.0405 Pa∙Sn and 0.0041 Pa∙Sn. The control, 20%, and 30% soy whey-containing beverage samples showed higher sensory properties.
Conclusions:
The beverage samples with 0%, 20%, and 30% showed improved DPPH and FRAP percent activity and higher overall acceptability compared to 40% and 50% soy whey-containing beverage samples.
 Atlantic algae as food and their extractsOpen AccessReviewAmong the species of the rich algological flora of the North Atlantic, some can be used for direct consumption in human food, although few are currently cultivated on a large scale and/or marketed f [...] Read more.
Atlantic algae as food and their extractsOpen AccessReviewAmong the species of the rich algological flora of the North Atlantic, some can be used for direct consumption in human food, although few are currently cultivated on a large scale and/or marketed f [...] Read more.Among the species of the rich algological flora of the North Atlantic, some can be used for direct consumption in human food, although few are currently cultivated on a large scale and/or marketed for this purpose. The European tradition regarding this custom is practically nil and the expression of current eating habits is little different from the past. In Europe, only in times of hunger (for example, during the Great World Wars) was seaweed consumed by the populations closest to the coastline. In addition to the multiple applications described, which expanded enormously in the 1970s, based on phycocolloids (agar, carrageenans, and alginates)—used as thickeners in the food industry, in soups, meat preserves, dairy products, and pastries—there is currently a trend of increasing consumption, both in North America and Europe.
Leonel PereiraPublished: April 27, 2023 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2023;1:15–31
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00003
This article belongs to the special issue The food (r)evolution towards food quality/security and human nutritionAmong the species of the rich algological flora of the North Atlantic, some can be used for direct consumption in human food, although few are currently cultivated on a large scale and/or marketed for this purpose. The European tradition regarding this custom is practically nil and the expression of current eating habits is little different from the past. In Europe, only in times of hunger (for example, during the Great World Wars) was seaweed consumed by the populations closest to the coastline. In addition to the multiple applications described, which expanded enormously in the 1970s, based on phycocolloids (agar, carrageenans, and alginates)—used as thickeners in the food industry, in soups, meat preserves, dairy products, and pastries—there is currently a trend of increasing consumption, both in North America and Europe.
 AI-powered revolution in plant sciences: advancements, applications, and challenges for sustainable agriculture and food securityOpen AccessReviewArtificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing plant sciences by enabling precise plant species identification, early disease diagnosis, crop yield prediction, and precision agriculture optimizatio [...] Read more.
AI-powered revolution in plant sciences: advancements, applications, and challenges for sustainable agriculture and food securityOpen AccessReviewArtificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing plant sciences by enabling precise plant species identification, early disease diagnosis, crop yield prediction, and precision agriculture optimizatio [...] Read more.Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing plant sciences by enabling precise plant species identification, early disease diagnosis, crop yield prediction, and precision agriculture optimization. AI uses machine learning and image recognition to aid ecological research and biodiversity conservation. It plays a crucial role in plant breeding by accelerating the development of resilient, high-yielding crops with desirable traits. AI models using climate and soil data contribute to sustainable agriculture and food security. In plant phenotyping, AI automates the measurement and analysis of plant characteristics, enhancing our understanding of plant growth. Ongoing research aims to improve AI models’ robustness and interpretability while addressing data privacy and algorithmic biases. Interdisciplinary collaboration is essential to fully harness AI’s potential in plant sciences for a sustainable, food-secure future.
Deependra Kumar Gupta ... Ajay Kumar SinghPublished: August 06, 2024 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2024;2:443–459
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2024.00045Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing plant sciences by enabling precise plant species identification, early disease diagnosis, crop yield prediction, and precision agriculture optimization. AI uses machine learning and image recognition to aid ecological research and biodiversity conservation. It plays a crucial role in plant breeding by accelerating the development of resilient, high-yielding crops with desirable traits. AI models using climate and soil data contribute to sustainable agriculture and food security. In plant phenotyping, AI automates the measurement and analysis of plant characteristics, enhancing our understanding of plant growth. Ongoing research aims to improve AI models’ robustness and interpretability while addressing data privacy and algorithmic biases. Interdisciplinary collaboration is essential to fully harness AI’s potential in plant sciences for a sustainable, food-secure future.
 Phytochemical screening of Psidium guajava and Carica papaya leaves aqueous extracts cultivated in Greece and their potential as health boostersOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The scope of the present study was to investigate the phytochemical profile of Psidium guajava and Carica papaya leaves aqueous extracts, from plants cultivated on Crete island in Greece. [...] Read more.
Phytochemical screening of Psidium guajava and Carica papaya leaves aqueous extracts cultivated in Greece and their potential as health boostersOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The scope of the present study was to investigate the phytochemical profile of Psidium guajava and Carica papaya leaves aqueous extracts, from plants cultivated on Crete island in Greece. [...] Read more.Aim:
The scope of the present study was to investigate the phytochemical profile of Psidium guajava and Carica papaya leaves aqueous extracts, from plants cultivated on Crete island in Greece.
Methods:
Total phenolic content (TPC) in the aqueous extracts was determined spectrometrically using the Folin-Ciocalteu (F-C) assay. The identification and quantification of different phenolic compounds in the aqueous extracts were conducted using reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) analysis. Different metals were also determined (K, Fe, Zn, Ca, Mg, Pb, and Cd) to investigate the potential health claims or hazards in the water extractable infusion using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) method.
Results:
TPC in the aqueous extracts was found to be 28.0 g gallic acid equivalent (GAE)/kg dry leaves for Psidium guajava leaves aqueous extract and 15.0 g GAE/kg dry leaves for Carica papaya leaves aqueous extract. The dominant phenolic compounds in Psidium guajava leaves aqueous extract were myricetin (3,852 mg/kg dry sample) and rutin (670 mg/kg dry sample) while the dominant phenolic compounds in Carica papaya leaves aqueous extract were salicylic acid (338 mg/kg dry sample) and rutin (264 mg/kg dry sample). Different metals were also determined (K, Fe, Zn, Ca, Mg, Pb, and Cd) to investigate the potential health claims or hazards in the water extractable infusion, and it was found that no toxic metals were extracted whereas some nutritional benefits were achieved.
Conclusions:
Results proved that Psidium guajava and Carica papaya can be provided a strong antioxidant activity and can be used as medicinal plants.
Dimitrios D. Ntakoulas ... Charalampos ProestosPublished: April 26, 2023 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2023;1:5–14
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00002Aim:
The scope of the present study was to investigate the phytochemical profile of Psidium guajava and Carica papaya leaves aqueous extracts, from plants cultivated on Crete island in Greece.
Methods:
Total phenolic content (TPC) in the aqueous extracts was determined spectrometrically using the Folin-Ciocalteu (F-C) assay. The identification and quantification of different phenolic compounds in the aqueous extracts were conducted using reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) analysis. Different metals were also determined (K, Fe, Zn, Ca, Mg, Pb, and Cd) to investigate the potential health claims or hazards in the water extractable infusion using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) method.
Results:
TPC in the aqueous extracts was found to be 28.0 g gallic acid equivalent (GAE)/kg dry leaves for Psidium guajava leaves aqueous extract and 15.0 g GAE/kg dry leaves for Carica papaya leaves aqueous extract. The dominant phenolic compounds in Psidium guajava leaves aqueous extract were myricetin (3,852 mg/kg dry sample) and rutin (670 mg/kg dry sample) while the dominant phenolic compounds in Carica papaya leaves aqueous extract were salicylic acid (338 mg/kg dry sample) and rutin (264 mg/kg dry sample). Different metals were also determined (K, Fe, Zn, Ca, Mg, Pb, and Cd) to investigate the potential health claims or hazards in the water extractable infusion, and it was found that no toxic metals were extracted whereas some nutritional benefits were achieved.
Conclusions:
Results proved that Psidium guajava and Carica papaya can be provided a strong antioxidant activity and can be used as medicinal plants.
 Azadirachta indica A. Juss (neem) phenolic extract inhibits human B-lymphoblastoid cells growth via cell cycle arrest, apoptosis induction, and DNA damageOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: As far as is known, the pharmaceutical effects of neem on human B-lymphoblastoid (TK6) cells have not been studied until now. Hence, the present study aimed to obtain neem phenolic extracts [...] Read more.
Azadirachta indica A. Juss (neem) phenolic extract inhibits human B-lymphoblastoid cells growth via cell cycle arrest, apoptosis induction, and DNA damageOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: As far as is known, the pharmaceutical effects of neem on human B-lymphoblastoid (TK6) cells have not been studied until now. Hence, the present study aimed to obtain neem phenolic extracts [...] Read more.Aim:
As far as is known, the pharmaceutical effects of neem on human B-lymphoblastoid (TK6) cells have not been studied until now. Hence, the present study aimed to obtain neem phenolic extracts for inhibits the proliferation of TK6 cells and explore some possible underlying mechanisms involved in these effects.
Methods:
Hexane extract (HE) was obtained in the first step. After that, the residual hexane was removed from the neem. The dried neem sample was used in a new extraction for obtaining the ethyl acetate extract (EAE). Total phenolic compounds (TPC) and total flavonoid contents (TFC) were determined by spectrophotometric methods. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) tests were used to evaluate the cytotoxicity in TK6 cells. The stop at G0/G1 cell cycle and inducing apoptosis in the TK6 cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. For deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) damage evaluation, the alkaline comet test was used.
Results:
The higher TFC (65.50 mg/g of extract ± 1.17 mg/g of extract) and TPC (52.08 mg of extract ± 0.88 mg of extract) were obtained in EAE compared to HE that was obtained TFC of 14.61 mg/g of extract ± 0.60 mg/g of extract and TPC of 3.20 mg/g of extract ± 1.20 mg/g of extract. EAE was more significantly cytotoxic to TK6 cells than HE. The apoptosis induction was higher after exposure to 15.0 µg/mL of EAE (11.29%) in comparison to 15.0 µg/mL of HE (2.52%). The G0/G1 phase increased from 72% negative control (NC) to 83% after treatment with neem extracts (15 µg/mL). Neem extracts were also able to cause DNA strand breaks in TK6 cells.
Conclusions:
The extraction residue from neem leaf after hexane extraction is a source important of cytotoxic and genotoxic molecules against TK6 cells, the results also can suggest that the toxic effects in TK6 cells can be provided most likely due to the presence of high content of TPC from neem extracts.
Klebson Silva Santos ... Maria Beatriz Pinto Prior OliveiraPublished: August 29, 2023 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2023;1:130–142
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00011Aim:
As far as is known, the pharmaceutical effects of neem on human B-lymphoblastoid (TK6) cells have not been studied until now. Hence, the present study aimed to obtain neem phenolic extracts for inhibits the proliferation of TK6 cells and explore some possible underlying mechanisms involved in these effects.
Methods:
Hexane extract (HE) was obtained in the first step. After that, the residual hexane was removed from the neem. The dried neem sample was used in a new extraction for obtaining the ethyl acetate extract (EAE). Total phenolic compounds (TPC) and total flavonoid contents (TFC) were determined by spectrophotometric methods. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) tests were used to evaluate the cytotoxicity in TK6 cells. The stop at G0/G1 cell cycle and inducing apoptosis in the TK6 cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. For deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) damage evaluation, the alkaline comet test was used.
Results:
The higher TFC (65.50 mg/g of extract ± 1.17 mg/g of extract) and TPC (52.08 mg of extract ± 0.88 mg of extract) were obtained in EAE compared to HE that was obtained TFC of 14.61 mg/g of extract ± 0.60 mg/g of extract and TPC of 3.20 mg/g of extract ± 1.20 mg/g of extract. EAE was more significantly cytotoxic to TK6 cells than HE. The apoptosis induction was higher after exposure to 15.0 µg/mL of EAE (11.29%) in comparison to 15.0 µg/mL of HE (2.52%). The G0/G1 phase increased from 72% negative control (NC) to 83% after treatment with neem extracts (15 µg/mL). Neem extracts were also able to cause DNA strand breaks in TK6 cells.
Conclusions:
The extraction residue from neem leaf after hexane extraction is a source important of cytotoxic and genotoxic molecules against TK6 cells, the results also can suggest that the toxic effects in TK6 cells can be provided most likely due to the presence of high content of TPC from neem extracts.
 Recent advances in nano-related natural antioxidants, their extraction methods and applications in the food industryOpen AccessReviewNatural antioxidants, such as phenolic compounds, carotenoids, vitamins, and microelements, are predominant in fruits, vegetables, herbs, and spices. The accretion interest of consumers in utilizing [...] Read more.
Recent advances in nano-related natural antioxidants, their extraction methods and applications in the food industryOpen AccessReviewNatural antioxidants, such as phenolic compounds, carotenoids, vitamins, and microelements, are predominant in fruits, vegetables, herbs, and spices. The accretion interest of consumers in utilizing [...] Read more.Natural antioxidants, such as phenolic compounds, carotenoids, vitamins, and microelements, are predominant in fruits, vegetables, herbs, and spices. The accretion interest of consumers in utilizing natural ingredients in food products, have accelerated the appeal for functional “natural” operations. Therefore, understanding how natural antioxidants especially nano-antioxidants, and their delivery systems when used in antioxidant polymers for food packaging are extracted from natural sources, would help prevent oxidation reactions. Given the increasing role of natural antioxidants in the daily lives of today’s communities, a continuous synthesis of relevant literature is pertinent. To supplement existing information, recent advances in nano-related natural antioxidants, their extraction methods and applications in the food industry are discussed in this current work. Insightfully positioning antioxidants within the nano-delivery systems, this current work reveals the potential nanotechnology provides in enhancing the absorption of antioxidants in human metabolic systems.
Ayla Elmi Kashtiban ... Sayna ZahediniaPublished: April 19, 2024 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2024;2:125–154
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2024.00030
This article belongs to the special issue The food (r)evolution towards food quality/security and human nutritionNatural antioxidants, such as phenolic compounds, carotenoids, vitamins, and microelements, are predominant in fruits, vegetables, herbs, and spices. The accretion interest of consumers in utilizing natural ingredients in food products, have accelerated the appeal for functional “natural” operations. Therefore, understanding how natural antioxidants especially nano-antioxidants, and their delivery systems when used in antioxidant polymers for food packaging are extracted from natural sources, would help prevent oxidation reactions. Given the increasing role of natural antioxidants in the daily lives of today’s communities, a continuous synthesis of relevant literature is pertinent. To supplement existing information, recent advances in nano-related natural antioxidants, their extraction methods and applications in the food industry are discussed in this current work. Insightfully positioning antioxidants within the nano-delivery systems, this current work reveals the potential nanotechnology provides in enhancing the absorption of antioxidants in human metabolic systems.
Special Issues Enhancing Food Production with Artificial Intelligence: Harnessing Industrial By-Products
Enhancing Food Production with Artificial Intelligence: Harnessing Industrial By-ProductsRaquel Madureira Ana Lúcia da Silva Oliveira
Submission Deadline: September 02, 2025
Published Articles: 0
 Organic and Inorganic Compounds in Foods and Plants from Latin America
Organic and Inorganic Compounds in Foods and Plants from Latin AmericaBruno Lemos Batista Bruno Alves Rocha Camila Neves Lange
Submission Deadline: September 02, 2025
Published Articles: 1
 Metrological Aspects in the Analysis of Nutrients, Functional Compounds, Additives and Contaminants in Food and Feed
Metrological Aspects in the Analysis of Nutrients, Functional Compounds, Additives and Contaminants in Food and FeedMaria Z. Tsimidou Nives Ogrinc Claudia Zoani
Submission Deadline: November 01, 2025
Published Articles: 13
 Food Contaminants: Analysis, Occurrence and Risk Assessment
Food Contaminants: Analysis, Occurrence and Risk AssessmentOlga Pardo Francesc A. Esteve-Turrillas
Submission Deadline: September 02, 2025
Published Articles: 3
 Molecular Targets of Diet in Cancer Therapy and Prevention
Molecular Targets of Diet in Cancer Therapy and PreventionSabrina Battista
Submission Deadline: September 02, 2025
Published Articles: 0
 Food Authenticity and Emerging Challenges of Novel Food
Food Authenticity and Emerging Challenges of Novel FoodDi Wu Guoliang Li
Submission Deadline: September 02, 2025
Published Articles: 4
 Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents in Food Chemistry and Advanced Food Materials
Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents in Food Chemistry and Advanced Food MaterialsMaria Fernanda Silva Federico Gomez Maria de los Angeles Fernandez
Submission Deadline: September 02, 2025
Published Articles: 1
 New Generation Analytical Technologies in Food Analysis
New Generation Analytical Technologies in Food AnalysisBengi Uslu Cem Erkmen
Submission Deadline: September 02, 2025
Published Articles: 3
 Ketogenic Diet as Medical Nutrition Therapy
Ketogenic Diet as Medical Nutrition TherapyLuca Rastrelli Giuseppe Castaldo
Submission Deadline: August 02, 2025
Published Articles: 5
 The food (r)evolution towards food quality/security and human nutrition
The food (r)evolution towards food quality/security and human nutritionJosé Pinela José Ignacio Alonso-Esteban
Submission Deadline: August 02, 2025
Published Articles: 8
 Natural Products in Health and Disease
Natural Products in Health and DiseaseMarcello Iriti
Submission Deadline: May 01, 2025
Published Articles: 6
 Delivery of Hydrophobic Compounds in Food Systems
Delivery of Hydrophobic Compounds in Food SystemsAndrea Gomez-Zavaglia
Submission Deadline: August 01, 2024
Published Articles: 6
-
-
Newsletter
 Sep. 25, 2024EFF in The XVIII National Meeting of the Portuguese Society of Chemistry.
Sep. 25, 2024EFF in The XVIII National Meeting of the Portuguese Society of Chemistry. Sep. 8, 2023MoreEFF in EACR Congress.
Sep. 8, 2023MoreEFF in EACR Congress. Jun. 19, 2023
Jun. 19, 2023 -
Selected Special IssuesTopic: Enhancing Food Production with Artificial Intelligence: Harnessing Industrial By-Products Topic: Organic and Inorganic Compounds in Foods and Plants from Latin America Topic: Metrological Aspects in the Analysis of Nutrients, Functional Compounds, Additives and Contaminants in Food and Feed Topic: Food Contaminants: Analysis, Occurrence and Risk Assessment Topic: Molecular Targets of Diet in Cancer Therapy and Prevention More