Editor's Picks
Open Access
Review
Neuroprotection beyond neurons: integrated biomarker-based and astroglia- or microglia-targeted approaches to combat neurodegenerative diseases
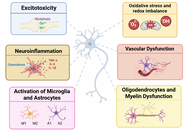
Neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, are characterized by multifactorial pathologies that extend beyond neuronal loss to include neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and glial dysregulation. Despite extensive research, disease-modifying therapies remain elusive, hindered by late diagnosis, limited availability of specific biomarkers, and the persistent dominance of reductionist, single-target strategies. This comprehensive and informative review provides a critical synthesis of integrated neuroprotective strategies, with particular focus on glial mechanisms and biomarker-guided interventions. Therapeutic emphasis is placed on coordinated mechanisms targeting both neurons and non-neuronal cells, such as astrocytes, microglia, and oligodendrocytes. Emerging strategies are reported to include modulation of synaptic plasticity and neurotransmission, delivery of neurotrophic factors, activation of intrinsic cytoprotective pathways (e.g., Nrf2 signaling), restoration of proteostasis, and induction of regeneration via cellular reprogramming. Glial cells are discussed as therapeutic targets involved in inflammation, metabolism, myelination, and neuronal survival. Advances in predictive, preventive, personalized, and participatory (P4) medicine, supported by genomics, multi-omics, imaging, and real-world data, are presented as accelerating biomarker discovery and enabling earlier and more precise stage-specific interventions. Future success in combating neurodegeneration will depend on integrated approaches that combine protective, supportive, and regenerative strategies, appropriate for disease stage and patient profile. By reframing neuroprotection as a systemic, multicellular endeavor, this review highlights the potential to not only extend life expectancy, but also preserve meaningful quality of life in individuals affected by neurodegenerative diseases.
Open Access
Original Article
A brief, comprehensive measure of post-exertional malaise
Aim:
Post-exertional malaise (PEM) has been a challenging construct to measure, particularly with self-report instruments, which have the benefits of being less expensive and less invasive than cardiopulmonary exercise tests. Existing PEM questionnaires have often been used for diagnostic purposes and less frequently as outcome measures. Few self-report PEM measures address comprehensive PEM domains, including types of triggers, duration of symptoms, delayed symptom onset, number of symptoms, frequency and severity of symptoms, as well as whether pacing or other strategies reduce or eliminate PEM. Without characterizing these features, salient aspects of PEM would be overlooked. However, efforts to assess all these domains can be time-consuming and potentially burdensome.
Methods:
The current study offers investigators a brief but comprehensive instrument of critical PEM domains, called the DePaul Symptom Questionnaire (DSQ)-PEM-2, to assess PEM. Validation data were derived from a large sample of individuals with myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS).
Results:
The DSQ-PEM-2 was developed using an existing dataset of individuals with ME, CFS, or both ME and CFS, allowing comprehensive coverage of key PEM domains.
Conclusions:
The DSQ-PEM-2 can be used either for diagnostic purposes or as an outcome measure. The instrument’s time frames for symptom manifestation can be adapted to suit a variety of research or clinical contexts. Future validation studies need to include a healthy control group.

Open Access
Review
Pathophysiology of non-motor signs in Parkinson’s disease: some recent updating with brief presentation
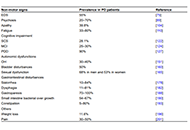
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder affecting 1% of the population above sixty years. It is caused by an interaction between genetic and environmental risk factors. Loss of dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) is pathologically characterizing the disease and responsible for the cardinal motor symptoms, most notably, bradykinesia, rest tremors, rigidity, and loss of postural reflexes. Non-motor signs such as olfactory deficits, cognitive impairment, sleep behavior disorders, and gastrointestinal disturbances are reflecting disturbances in the non-dopaminergic system. They precede dopaminergic neuronal degenerations by 5–10 years and are considered the main contributors to patients’ disability, particularly after the successful implementation of levodopa (L-dopa) treatment of motor symptoms. The present general review aimed to briefly update non-motor signs and their underlying pathophysiology in PD.
Articles
Latest
Most Viewed
Most Downloaded
Most Cited
Open Access
Original Article
Visuospatial attention and intelligence in children with ADHD-hyperactive type
Daniela Smirni ... Michele Roccella
Published: March 11, 2026 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2026;6:1004139
This article belongs to the special issue Advances in the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
Open Access
Systematic Review
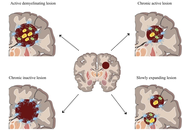
Therapeutic strategies in multiple sclerosis: a systematic review of current and emerging approaches
Carolina Machado, Ana Valado
Published: February 09, 2026 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2026;6:1004138
Open Access
Review
Stem cell-derived exosomes as neurotherapeutic agents: mechanisms of immunomodulation and neural regeneration in neurodegenerative disorders
Afra Wasama Islam ... Saumya Rajesh Kadam
Published: January 27, 2026 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2026;6:1004137
This article belongs to the special issue Breakthroughs in Mechanisms and Treatments for Neurodegenerative Diseases
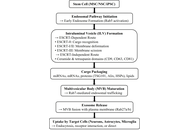
Open Access
Review
Neuroprotection beyond neurons: integrated biomarker-based and astroglia- or microglia-targeted approaches to combat neurodegenerative diseases
Cinzia Volonté ... Rafael Franco
Published: January 04, 2026 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2026;6:1004136

Open Access
Original Article
Geothermal pteridophyte endophyte as a potential producer of anti-aggregation metabolites with relevance to neuroprotection
Agustina Lulustyaningati Nurul Aminin ... Muhammad Ajmal Shah
Published: December 30, 2025 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2025;5:1004135
This article belongs to the special issue Natural Products in Neurotherapeutic Applications
Open Access
Original Article
Cognitive control in children with ADHD and subthreshold ADHD: an eye-tracking study
Rosa Angela Fabio ... Pina Filippello
Published: December 30, 2025 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2025;5:1004134
This article belongs to the special issue Advances in the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
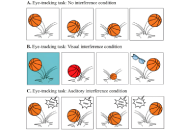
Open Access
Review
Pathophysiology of non-motor signs in Parkinson’s disease: some recent updating with brief presentation
Khaled Radad ... Wolf-Dieter Rausch
Published: February 27, 2023 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2023;3:24–46

Open Access
Review
Balancing cholesterol in the brain: from synthesis to disposal
Lydia Qian ... Andrew J. Brown
Published: January 05, 2022 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2022;2:1–27
This article belongs to the special issue Cholesterol Dyshomeostasis in Neurological Diseases
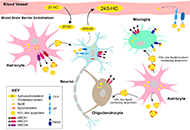
Open Access
Review
Resolving a paradox: antidepressants, neuroinflammation, and neurodegeneration
Ravi Philip Rajkumar
Published: February 23, 2024 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2024;4:11–37
This article belongs to the special issue Neuro-Inflammation as a Target in the Design of Multifunctional Drug Candidates for Neurodegenerative Diseases

Open Access
Review
Biomarkers in small fiber neuropathy
Amanda C. Y. Chan ... Joy Vijayan
Published: December 30, 2022 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2022;2:264–283
This article belongs to the special issue The Future of Biomarkers in CNS Diseases
Open Access
Case Report
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy—a new hope for Alzheimer’s patients: a case report and literature review
Elizabeta B. Mukaetova-Ladinska ... Qadeer Arshad
Published: December 22, 2023 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2023;3:457–469
This article belongs to the special issue Defending the Brain and the Mind: Exploring Neuroprotective Therapies for Mental Health Disorders
Open Access
Review
Omega-3 fatty acids and fetal brain development: implications for maternal nutrition, mechanisms of cognitive function, and pediatric depression
Raghd M Ghazal, Moawiah M Naffaa
Published: May 28, 2025 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2025;5:1004107

Open Access
Perspective
Gut microbiota could modulate the effects of neuro-immune responses and memory traces via the gut-brain-immune axis in schizophrenia
Haruka Sawamura ... Satoru Matsuda
Published: April 24, 2022 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2022;2:74–86
This article belongs to the special issue Intervention of Neuroimmune Responses
Open Access
Review
Balancing cholesterol in the brain: from synthesis to disposal
Lydia Qian ... Andrew J. Brown
Published: January 05, 2022 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2022;2:1–27
This article belongs to the special issue Cholesterol Dyshomeostasis in Neurological Diseases

Open Access
Review
Pathophysiology of non-motor signs in Parkinson’s disease: some recent updating with brief presentation
Khaled Radad ... Wolf-Dieter Rausch
Published: February 27, 2023 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2023;3:24–46

Open Access
Review
Biomarkers in neurodegenerative diseases: a broad overview
Sathish Selvam, Velpandi Ayyavoo
Published: April 16, 2024 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2024;4:119–147
This article belongs to the special issue The Future of Biomarkers in CNS Diseases
Open Access
Review
Striking a balance: PIP2 and PIP3 signaling in neuronal health and disease
Kamran Tariq, Bryan W. Luikart
Published: October 29, 2021 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2021;1:86–110
This article belongs to the special issue Cholesterol Dyshomeostasis in Neurological Diseases
Open Access
Review
Neuroprotective agents in acute ischemic stroke
Grace YY Chia ... Benjamin YQ Tan
Published: February 28, 2023 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2023;3:47–70
This article belongs to the special issue The Future of Biomarkers in CNS Diseases
Open Access
Review
Striking a balance: PIP2 and PIP3 signaling in neuronal health and disease
Kamran Tariq, Bryan W. Luikart
Published: October 29, 2021 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2021;1:86–110
This article belongs to the special issue Cholesterol Dyshomeostasis in Neurological Diseases

Open Access
Review
Pathophysiology of non-motor signs in Parkinson’s disease: some recent updating with brief presentation
Khaled Radad ... Wolf-Dieter Rausch
Published: February 27, 2023 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2023;3:24–46

Open Access
Review
Blocking cholesterol storage to treat Alzheimer’s disease
Ta Yuan Chang ... James G. Gow
Published: December 30, 2021 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2021;1:173–184
This article belongs to the special issue Cholesterol Dyshomeostasis in Neurological Diseases
Open Access
Review
Balancing cholesterol in the brain: from synthesis to disposal
Lydia Qian ... Andrew J. Brown
Published: January 05, 2022 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2022;2:1–27
This article belongs to the special issue Cholesterol Dyshomeostasis in Neurological Diseases

Open Access
Review
Biomarkers in neurodegenerative diseases: a broad overview
Sathish Selvam, Velpandi Ayyavoo
Published: April 16, 2024 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2024;4:119–147
This article belongs to the special issue The Future of Biomarkers in CNS Diseases

Open Access
Review
Advancing diagnosis and treatment of Niemann-Pick C disease through biomarker discovery
Xuntian Jiang, Daniel S. Ory
Published: December 30, 2021 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2021;1:146–158
This article belongs to the special issue Cholesterol Dyshomeostasis in Neurological Diseases
Special Issues
Ongoing Special lssues
Completed Special lssues
Mitochondrial Transfer and Transplantation: Emerging Frontiers in Neuroprotection
Guest Editors: Prof. Keshav K. Singh; Dr. Shalini Mani
Submission Deadline: August 31, 2026
Published Articles: 0
The New Neurobiology of Neurodevelopmental Disorders: From Neuroinflammation to Neurochemical Modulation
Guest Editors: Prof. Marco Carotenuto; Dr. Giuditta Bargiacchi
Submission Deadline: July 31, 2026
Published Articles: 0

Novel Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets for Human Neurodegenerative Diseases
Guest Editor: Dr. Zhi Dong Zhou
Submission Deadline: August 30, 2026
Published Articles: 0

Neuroprotection in Pediatric Neurological Disorders: from Rare Diseases to Perinatal Brain Injury
Guest Editor: Dr. Jinwei Zhang
Submission Deadline: September 30, 2026
Published Articles: 0

Neuropsychology of Handwriting
Guest Editor: Prof. Maurizio Balestrino
Submission Deadline: April 30, 2026
Published Articles: 0

Innovations in Neurotechnology: Integrating AI, Neuroimaging, and VR for the Assessment and Treatment of Neurological Conditions
Guest Editor: Prof. Marco Cavallo
Submission Deadline: March 31, 2026
Published Articles: 0
Role of Microbiota in Neurological Diseases
Guest Editors: Dr. Antonio Ibarra; Dr. Andrea Paola Ibarra-García
Submission Deadline: June 30, 2026
Published Articles: 3

Breakthroughs in Mechanisms and Treatments for Neurodegenerative Diseases
Guest Editors: Dr. Rong Ma; Dr. Guoku Hu
Submission Deadline: March 31, 2026
Published Articles: 2

Advances in the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
Guest Editors: Dr. Michele Roccella; Dr. Luigi Vetri
Submission Deadline: June 30, 2026
Published Articles: 5

Interdisciplinary Approach to Therapeutic Strategies of Neuroprotection in Present and Future
Guest Editor: Prof. Athanasios K. Petridis
Submission Deadline: June 30, 2026
Published Articles: 1

Defending the Brain and the Mind: Exploring Neuroprotective Therapies for Mental Health Disorders
Guest Editor: Dr. Masaru Tanaka
Submission Deadline: June 30, 2026
Published Articles: 2

Neuro-Inflammation as a Target in the Design of Multifunctional Drug Candidates for Neurodegenerative Diseases
Guest Editors: Prof. Claudio Viegas Jr.; Prof. Arthur Eugen Kümmerle; Prof. Vanessa Silva Gontijo
Submission Deadline: June 30, 2026
Published Articles: 3

Therapeutic Targets for Neuroprotection in Ischemic Stroke
Guest Editor: Dr. Silvia Fischer
Submission Deadline: March 31, 2026
Published Articles: 6

Natural Products in Neurotherapeutic Applications
Guest Editor: Prof. Marcello Iriti
Submission Deadline: March 31, 2026
Published Articles: 8

Focus
Neuroprotective and Neurorestorative Strategies: from Bench-to-Bedside
Prof. Antonio Ibarra
Jul. 13, 2023
2729


Journal Information
Journal Indexing
Journal Metrics






















 Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys
Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys


