-
 Special Issue Topic
Special Issue TopicEmerging Nanomedicine Technologies for Enhanced Cancer Theranostics
Submission Deadline: May 31, 2025Guest Editor
Prof. Xiangyang Shi E-Mail
Professor of Biomedical Engineering, College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology, Donghua University, Shanghai, China
Research Keywords: dendrimers; polymer nanogels; cancer nanomedicine; drug/gene delivery; theranostics
About the Special Issue
Cancer theranostics have been demonstrated as the advanced platforms that can diagnose cancer at early stages and initiate subsequent therapy to impove the survival rate of patients. With the development of nanotechnologies, multifunctional nanoplatforms have shown a good application prospect in enhanced cancer theranostics. Through the ingenious design of nanoplatforms, various imaging and therapeutic agents can be physically loaded or chemically conjugated onto the platforms to optimally exert their functionalities of theranostics. Nanomedicines are contimuously seeking contribution from the therapeutic and diagnostic agents at the nanoscale through creative leveraging of their mechanical, electrical, optical, magnetic, and biological properties. This special issue entitled “Emerging nanomedicine technologies for enhanced cancer theranostics” brings together some of the world's foremost experts to discuss the current key developments in the area of emerging nanomedicine technologies in cancer nanotheranotics, including but not limited to strategic design of nanomedicines to tackcle multi-drug resistance, tumor targeting delivery, modulation of tumor microenvironment, combination therapy, precision imaging, inhibition of cancer metastasis and recurrence, and modulation of immune cells.
Keywords: drug delivery systems; gene delivery; molecular imaging; cancer theranostics; tumor microenvironment
Call for Papers
Published Articles
 Effect of the size of nucleic acid delivery systems on their fate in cancer treatmentOpen AccessReviewNucleic acid therapeutics are emerging as a promising class of medicines, offering unique therapeutic options for cancer at the gene level. However, the druggability of nucleic acid therapeutics is [...] Read more.Mengyun Ye ... Dandan ZhuPublished: February 01, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. 2024;2:38–49
Effect of the size of nucleic acid delivery systems on their fate in cancer treatmentOpen AccessReviewNucleic acid therapeutics are emerging as a promising class of medicines, offering unique therapeutic options for cancer at the gene level. However, the druggability of nucleic acid therapeutics is [...] Read more.Mengyun Ye ... Dandan ZhuPublished: February 01, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. 2024;2:38–49
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eds.2024.00035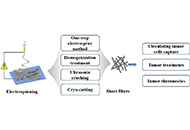 Electrospun short fibers: a new platform for cancer nanomedicine applicationsOpen AccessReviewWith the continuous development of nanomaterials, nanofibers prepared by electrospinning have gradually occupied people’s vision because of their unique advantages, such as crisscross network and [...] Read more.Yifan Huang ... Xiangyang ShiPublished: December 27, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:454–467
Electrospun short fibers: a new platform for cancer nanomedicine applicationsOpen AccessReviewWith the continuous development of nanomaterials, nanofibers prepared by electrospinning have gradually occupied people’s vision because of their unique advantages, such as crisscross network and [...] Read more.Yifan Huang ... Xiangyang ShiPublished: December 27, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:454–467
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eds.2023.00030 Nano theranostics involved in bladder cancer treatmentOpen AccessReviewBladder cancer (BC) is a complex disease with multiple clinical manifestations and treatment challenges, and current standard-of-care therapies remain limited and unfavorable. Theranostics, the inte [...] Read more.Kunpeng Liu ... Qingsong YuPublished: April 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:81–106
Nano theranostics involved in bladder cancer treatmentOpen AccessReviewBladder cancer (BC) is a complex disease with multiple clinical manifestations and treatment challenges, and current standard-of-care therapies remain limited and unfavorable. Theranostics, the inte [...] Read more.Kunpeng Liu ... Qingsong YuPublished: April 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:81–106
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eds.2023.00008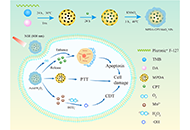 Surface functionalized mesoporous polydopamine nanocomposites for killing tumor cells through collaborative chemo/photothermal/chemodynamic treatmentOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The development of a collaborative strategy with improved efficacy holds great promise in tumor treatment. This study aims to develop an effective collaborative strategy based on functionalized mesoporous polydopamine (MPDA) [...] Read more.Yi Ouyang ... Hui LiuPublished: February 27, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:18–30
Surface functionalized mesoporous polydopamine nanocomposites for killing tumor cells through collaborative chemo/photothermal/chemodynamic treatmentOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The development of a collaborative strategy with improved efficacy holds great promise in tumor treatment. This study aims to develop an effective collaborative strategy based on functionalized mesoporous polydopamine (MPDA) [...] Read more.Yi Ouyang ... Hui LiuPublished: February 27, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:18–30
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eds.2023.00003 -
-
Ongoing Special Issues
-
Completed Special Issues