-
 Special Issue Topic
Special Issue TopicBioactive Peptides discovery and development
Submission Deadline: November 30, 2024Guest Editor
Prof. Xuechen Li E-Mail
Professor of Department of Chemistry, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Research Keywords: synthetic protein; antibiotics; glycoconjugates; drug conjugates
About the Special Issue
Peptides have emerged as an exciting therapeutic modality with middle-sized molecular weights and pharmacological properties in between traditional small molecule drugs and therapeutic proteins. Many peptide drugs have been clinically used for various diseases, including antimicrobial peptides, supplementary peptide hormones, peptide-drug conjugates and so on. In addition, peptides hold great promise for disrupting protein-protein interactions (PPIs) and drug delivery.
The past decades have witnesses great advances in bioactive peptides discovery and development. For instance, genome mining has led to many new ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides (RiPPs), various chemical methods have been developed to effectively cyclize peptides, peptide ligation allows for efficient synthesis of long peptides, super diverse peptide libraries provide powerful tools for high throughput screening and new knowledges have been gained for peptide intracellular delivery.
This special issue calls for the submission in all aspect in peptides, including, but not limited to, new bioactive peptide discovery, biosynthesis, peptide synthesis, peptide delivery, cyclic peptides, peptide-drug conjugates, medicinal chemistry, etc
Keywords: bioactive peptide, peptide synthesis, ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides, peptide conjugates, peptide delivery, peptide high throughput screening
Call for Papers
Published Articles
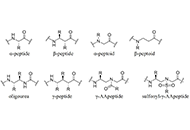 Recent exploration of γ-AApeptide based antimicrobial peptide mimics as potential therapeutics towards drug-resistant bacteriaOpen AccessCommentaryOver the last 60 years, only four new classes of antibiotics have been introduced, while the prevalence of antibiotic-resistant Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria has risen. This underscores the urgent need for new antibacte [...] Read more.Jarais Fontaine, Jianfeng CaiPublished: February 19, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. 2025;3:100888
Recent exploration of γ-AApeptide based antimicrobial peptide mimics as potential therapeutics towards drug-resistant bacteriaOpen AccessCommentaryOver the last 60 years, only four new classes of antibiotics have been introduced, while the prevalence of antibiotic-resistant Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria has risen. This underscores the urgent need for new antibacte [...] Read more.Jarais Fontaine, Jianfeng CaiPublished: February 19, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. 2025;3:100888
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eds.2025.100888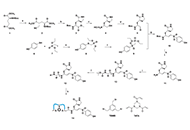 Bicyclic peptide-enhanced covalent inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 3CL proteaseOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Develop technology to apply bicyclic peptides for discovering covalent inhibitors of proteases and use this technology to create bicyclic peptide—warhead conjugates for targeting the sever [...] Read more.Qian Wang ... Shiyu ChenPublished: October 17, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. 2024;2:719–733
Bicyclic peptide-enhanced covalent inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 3CL proteaseOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Develop technology to apply bicyclic peptides for discovering covalent inhibitors of proteases and use this technology to create bicyclic peptide—warhead conjugates for targeting the sever [...] Read more.Qian Wang ... Shiyu ChenPublished: October 17, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. 2024;2:719–733
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eds.2024.00071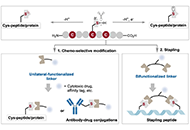 Chemo-selective modification of cysteine residue: synthesis and application in the discovery of potential drug candidatesOpen AccessReviewChemo-select modification of peptides, targeting a handful of the most reactive proteinogenic amino acids (AAs), is gradually utilized to address the medical needs of peptide drugs and biopharmaceut [...] Read more.Yanyan Liao, Xuefeng JiangPublished: September 06, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. 2024;2:540–554
Chemo-selective modification of cysteine residue: synthesis and application in the discovery of potential drug candidatesOpen AccessReviewChemo-select modification of peptides, targeting a handful of the most reactive proteinogenic amino acids (AAs), is gradually utilized to address the medical needs of peptide drugs and biopharmaceut [...] Read more.Yanyan Liao, Xuefeng JiangPublished: September 06, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. 2024;2:540–554
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eds.2024.00060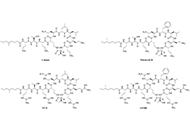 Lipopeptide adjuvants for antibiotics and vaccines: the future step in the fight against multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant pathogensOpen AccessReviewWith the surge of antibiotic resistance in bacteria, the need for a larger arsenal of effective antibiotics and vaccines has drastically increased in the past decades. Antibiotics like vaccines can [...] Read more.Chloé O. Sebilleau, Steven J. SucheckPublished: April 29, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. 2024;2:203–233
Lipopeptide adjuvants for antibiotics and vaccines: the future step in the fight against multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant pathogensOpen AccessReviewWith the surge of antibiotic resistance in bacteria, the need for a larger arsenal of effective antibiotics and vaccines has drastically increased in the past decades. Antibiotics like vaccines can [...] Read more.Chloé O. Sebilleau, Steven J. SucheckPublished: April 29, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. 2024;2:203–233
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eds.2024.00043 Daropeptide natural productsOpen AccessPerspectiveCyclophane-containing peptides comprise an important group of macrocyclic peptides with unique structural properties and pharmaceutical relevance. Darobactin A is a ribosomally synthesized and post- [...] Read more.Suze Ma ... Qi ZhangPublished: April 19, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. 2024;2:190–202
Daropeptide natural productsOpen AccessPerspectiveCyclophane-containing peptides comprise an important group of macrocyclic peptides with unique structural properties and pharmaceutical relevance. Darobactin A is a ribosomally synthesized and post- [...] Read more.Suze Ma ... Qi ZhangPublished: April 19, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. 2024;2:190–202
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eds.2024.00042 Stapled peptides: targeting protein-protein interactions in drug developmentOpen AccessReviewProtein-protein interactions (PPIs) impersonate a significant role in many biological processes and are potential therapeutic targets in numerous human diseases. Stapled peptides, as the most promis [...] Read more.Qian Zhang ... Chunqiu ZhangPublished: April 18, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. 2024;2:154–189
Stapled peptides: targeting protein-protein interactions in drug developmentOpen AccessReviewProtein-protein interactions (PPIs) impersonate a significant role in many biological processes and are potential therapeutic targets in numerous human diseases. Stapled peptides, as the most promis [...] Read more.Qian Zhang ... Chunqiu ZhangPublished: April 18, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. 2024;2:154–189
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eds.2024.00041 Therapeutic proteins immunogenicity: a peptide point of viewOpen AccessReviewProtein therapeutics are extensively used in the treatment of autoimmune diseases, but a subset of patients appears to be refractory to these treatments, mainly due to the development of an immune r [...] Read more.Feliciana Real-Fernandez ... Paolo RoveroPublished: October 26, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:377–387
Therapeutic proteins immunogenicity: a peptide point of viewOpen AccessReviewProtein therapeutics are extensively used in the treatment of autoimmune diseases, but a subset of patients appears to be refractory to these treatments, mainly due to the development of an immune r [...] Read more.Feliciana Real-Fernandez ... Paolo RoveroPublished: October 26, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:377–387
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eds.2023.00025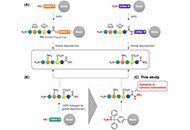 Late-stage diversification strategy for the synthesis of peptide acids and amides using hydrazidesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Modification of the C-terminus of a peptide to improve its properties, particularly after constructing the peptide chain, has great promise in the development of peptide therapeutics. This s [...] Read more.Shoko Tanaka ... Kohei SatoPublished: October 09, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:322–335
Late-stage diversification strategy for the synthesis of peptide acids and amides using hydrazidesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Modification of the C-terminus of a peptide to improve its properties, particularly after constructing the peptide chain, has great promise in the development of peptide therapeutics. This s [...] Read more.Shoko Tanaka ... Kohei SatoPublished: October 09, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:322–335
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eds.2023.00023 A dextrorotatory residues-incorporated bioactive dodecapeptide against enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coliOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study aims to report an engineered peptide zp39 with favorable bioactivity against enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (E. coli, EHEC). Its antibacterial mechanisms and application in a [...] Read more.Ping Zeng ... Lanhua YiPublished: June 30, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:210–220
A dextrorotatory residues-incorporated bioactive dodecapeptide against enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coliOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study aims to report an engineered peptide zp39 with favorable bioactivity against enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (E. coli, EHEC). Its antibacterial mechanisms and application in a [...] Read more.Ping Zeng ... Lanhua YiPublished: June 30, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:210–220
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eds.2023.00014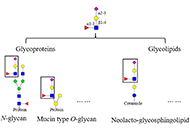 Essential functions, syntheses and detection of sialyl Lewis X on glycoproteinsOpen AccessReviewIt is widely acknowledged that sialyl Lewis X (sLeX), the composition and linkage of which are N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac) α2-3 galactose (Gal) β1-4 [fucose (Fuc) α1-3] N-acetylglucosamine, is usually attached to the cell [...] Read more.Qiushi Chen ... Xuechen LiPublished: February 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:31–54
Essential functions, syntheses and detection of sialyl Lewis X on glycoproteinsOpen AccessReviewIt is widely acknowledged that sialyl Lewis X (sLeX), the composition and linkage of which are N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac) α2-3 galactose (Gal) β1-4 [fucose (Fuc) α1-3] N-acetylglucosamine, is usually attached to the cell [...] Read more.Qiushi Chen ... Xuechen LiPublished: February 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:31–54
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eds.2023.00004 -
-
Ongoing Special Issues
-
Completed Special Issues