-
Guest Editor
Marcello Iriti E-Mail
Plant Biology and Pathology at the Department of Biomedical, Surgical and Dental Sciences, Milan State University, Milan, Italy
Research Keywords: functional foods; nutraceuticals; mediterranean diet; nutritional therapy; pharmaconutrients; phytotherapeutics; bioactive phytochemicals; medicinal and food plants; food security
About the Special Issue
Plant organisms represent an unlimited source of bioactive secondary metabolites. In recent decades, an enormous amount of preclinical (i.e. in vitro and in vivo) studies have indicated that phytochemicals exert a plethora of biological and pharmacological activities in cell cultures and animal models, although the evidence in humans is less substantiated and still fragmentary. Nowadays, we know that bioactive phytochemicals possess antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant/prooxidant, cytotoxic and immunomodulating activities, among others, which make them promising antibiotic, cardioprotective, neuroprotective, anticancer, antidiabetic, anti-obesity and antiaging agents. In general, phytochemicals exert a multi-target mechanism of action which makes them suitable drugs for the prevention and treatment of both communicable and non-communicable diseases, although phytochemicals appear to be more effective in the prevention than in the treatment of chronic-degenerative diseases, as demonstrated by healthy diets rich in plant foods. Furthermore, phytochemicals can be developed as adjuvant and sensitizing agents in association with conventional antibiotic and anticancer therapies to improve their efficacy, decrease their adverse effects, reduce the risk of selecting resistant microbial strains or cancer cells, or even reverse resistance. However, the preclinical pharmacological activities of phytochemicals need to be further substantiated by clinical studies in healthy and unhealthy subjects on their effective dose, route of administration, possible adverse effects and drug interactions.
In this very wide context, we invite investigators to submit both original research and review articles that explore all these aspects.
Keywords: medicinal plants; botanicals; plant extracts; essential oils; marine drugs; nutraceuticals; herbal remedies; antimicrobials; antimicrobial resistance; anticancer drugs; antineoplastic resistance; cardioprotection; neuroprotection; antidiabetic agents; anti-obesity agents; antioxidant activity; ethnopharmacology; one health
Call for Papers
Published Articles
 From botany to bedside: a review of the health benefits of Lycium barbarum as a functional foodOpen AccessReviewNative to East Asia and predominantly cultivated in regions such as the Ningxia Hui and Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Regions of China, Lycium barbarum (L. barbarum), commonly known as goji berry, has [...] Read more.Alois Berisha ... Tao ZhangPublished: January 25, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101070
From botany to bedside: a review of the health benefits of Lycium barbarum as a functional foodOpen AccessReviewNative to East Asia and predominantly cultivated in regions such as the Ningxia Hui and Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Regions of China, Lycium barbarum (L. barbarum), commonly known as goji berry, has [...] Read more.Alois Berisha ... Tao ZhangPublished: January 25, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101070
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2025.101070 In vitro cytotoxicity assessment of phenolic extracts from grapevine bunch stem and cane by-products for their potential use as phytotherapeutic agentsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: In the present study, bunch stem and cane extracts (Vitis vinifera L. cv. Malbec) rich in phenolic compounds (PCs) like flavonoids, phenolic acids, and stilbenes are studied as potential ant [...] Read more.Susana Ferreyra ... Ariel FontanaPublished: September 02, 2024 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2024;2:525–541
In vitro cytotoxicity assessment of phenolic extracts from grapevine bunch stem and cane by-products for their potential use as phytotherapeutic agentsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: In the present study, bunch stem and cane extracts (Vitis vinifera L. cv. Malbec) rich in phenolic compounds (PCs) like flavonoids, phenolic acids, and stilbenes are studied as potential ant [...] Read more.Susana Ferreyra ... Ariel FontanaPublished: September 02, 2024 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2024;2:525–541
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2024.00049 Assessment of the health benefits of phytochemicals in Cynometra cauliflora based on an in silico study against Alzheimer’s diseaseOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Cynometra cauliflora (namnam) belongs to the family Fabaceae and is native to eastern Peninsular Malaysia. It grows well with an annual rainfall of 1,500–2,000 mm. Even though a consider [...] Read more.Jagath Illangasinghe ... Viduranga Yashasvi WaisundaraPublished: January 23, 2024 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2024;2:1–29
Assessment of the health benefits of phytochemicals in Cynometra cauliflora based on an in silico study against Alzheimer’s diseaseOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Cynometra cauliflora (namnam) belongs to the family Fabaceae and is native to eastern Peninsular Malaysia. It grows well with an annual rainfall of 1,500–2,000 mm. Even though a consider [...] Read more.Jagath Illangasinghe ... Viduranga Yashasvi WaisundaraPublished: January 23, 2024 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2024;2:1–29
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2024.00023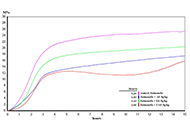 Broccoli by-product extract as a functional ingredient: food applicationOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Food production demand has been promoting an increase in the generation of agro-industrial waste. Food industry waste can contain compounds with added value that, if properly extracted and u [...] Read more.David Q. Martínez ... Presentación GarcíaPublished: October 31, 2023 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2023;1:235–243
Broccoli by-product extract as a functional ingredient: food applicationOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Food production demand has been promoting an increase in the generation of agro-industrial waste. Food industry waste can contain compounds with added value that, if properly extracted and u [...] Read more.David Q. Martínez ... Presentación GarcíaPublished: October 31, 2023 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2023;1:235–243
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00018 Olive oil, fruit and leaves in diabetes mellitus type 2 treatmentOpen AccessReviewThe Mediterranean dietary pattern, where extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) takes the central spot, is related to longer life expectancy and lower risk of a number of non-communicable diseases, including [...] Read more.Mario Nosić ... Ines BanjariPublished: October 29, 2023 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2023;1:192–205
Olive oil, fruit and leaves in diabetes mellitus type 2 treatmentOpen AccessReviewThe Mediterranean dietary pattern, where extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) takes the central spot, is related to longer life expectancy and lower risk of a number of non-communicable diseases, including [...] Read more.Mario Nosić ... Ines BanjariPublished: October 29, 2023 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2023;1:192–205
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00015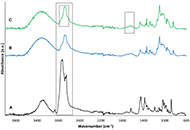 Isolation, characterization, and encapsulation of a lupeol-rich fraction obtained from the hexanic extract of Coccoloba uvifera L. leavesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study aimed to isolate, characterize, and encapsulate a lupeol-rich fraction obtained from the hexanic extract of Coccoloba uvifera L. leaves to evaluate its potential use in nutraceuti [...] Read more.Carla N. Cruz-Salas ... Juan A. Ragazzo-SánchezPublished: August 28, 2023 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2023;1:115–129
Isolation, characterization, and encapsulation of a lupeol-rich fraction obtained from the hexanic extract of Coccoloba uvifera L. leavesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study aimed to isolate, characterize, and encapsulate a lupeol-rich fraction obtained from the hexanic extract of Coccoloba uvifera L. leaves to evaluate its potential use in nutraceuti [...] Read more.Carla N. Cruz-Salas ... Juan A. Ragazzo-SánchezPublished: August 28, 2023 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2023;1:115–129
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00010 -
-
Ongoing Special Issues
-
Completed Special Issues
