Autoantibodies Associated to Thrombosis and Hemostasis
Guest Editor
Dr. Jean Amiral E-Mail
Scientific Director (SH-Consulting, Franconville, France) and consultant (HYPHEN BioMed, France and Sysmex Corp., Japan), Franconville, France
Research Keywords: Hemostasis, coagulation, thrombosis, fibrinolysis, autoantibodies, pathogenicity, laboratory methods, molecular mechanisms
About the Special lssue
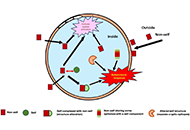
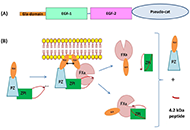
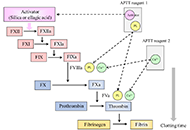
These past decades, occurrence of some life-threatening complications, often unresponsive to the drugs indicated for treating the clinical symptoms, have been reported. The presence of pathogenic autoantibodies, targeted to hemostasis proteins or to their complexes with non-self-components like drugs or infectious products, has been evidenced in many cases. If now these allo-immune or auto-immune complications are progressively better diagnosed, their development conditions still remain unclear. Possible factors can concern individual biological sensitivity or predisposition, but the accidental presentation of a self-component in an unusual way or complexed with an external product can be a leading risk. An open question remains on why in apparently identical situations only rare patients develop the pathogenic antibodies, and why, when present, these antibodies remain asymptomatic in many cases or conversely cause severe and deleterious pathologies. The experience from some extensively studied induced autoimmune diseases helps to better document this domain. In this issue, we focus on autoantibodies targeted to hemostasis proteins, which can lead to critical bleeding episodes or thrombo-embolic manifestations. Diseases are strongly dependent on how the autoantibody interferes with the targeted protein function. They can be targeted to the body’s cells or tissues, deviating then the immune response, which then becomes harmful. The most known, investigated and documented diseases concern anti-phospholipid antibodies and lupus anticoagulant, with autoantibodies mainly targeted to β2-Glyco-Protein 1, Prothrombin, Annexin V or to their complexes with phospholipids, or heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, with a high incidence of associated thrombosis, and which is induced by a heparin-dependent antibody targeted to Platelet Factor 4 complexed with heparin, or to the chemokine itself. However, many other very rare autoantibody-induced thrombotic complications have been reported for antibodies to Protein S, Thrombomodulin, Protein Z, antithrombin, or to other hemostasis proteins, whilst other autoantibodies are associated with severe bleeding like those to Factor VIII, vWF, Factor V, Factor XIII, a list which is not exhaustive. This is what we would like to describe and synthesize in this special issue, by presenting the latest updates and understanding. The major objectives are to review: i) the various autoimmune complications generating thrombotic or bleeding episodes; ii) the laboratory diagnostic tools available; iii) the mechanisms which can lead to the generation of autoantibodies, and when present, how they become pathogenic; iv) the available therapeutic approaches; v) case reports and experience. We are pleased to call for contributions in this field, and we invite you to submit your contributions, which will follow a peer-review process, and when approved, will be published in this special issue of Exploration of Immunology.
Keywords: Autoantibodies, hemostasis proteins, autoimmune complications, thrombotic, bleeding
Published Articles