Affiliation:
1Institute of Cardiovascular Sciences, St. Boniface Hospital Albrechtsen Research Centre, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Manitoba R2H 2A6, Canada
Affiliation:
2School of Kinesiology, Nutrition and Food Science, California State University, Los Angeles, CA 90032, USA
Affiliation:
1Institute of Cardiovascular Sciences, St. Boniface Hospital Albrechtsen Research Centre, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Manitoba R2H 2A6, Canada
3Department of Physiology and Pathophysiology, Max Rady College of Medicine, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Manitoba R3E 3P5, Canada
Email: nsdhalla@sbrc.ca
Explor Med. 2021;2:352–371 DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2021.00054
Received: April 28, 2021 Accepted: June 27, 2021 Published: August 31, 2021
Academic Editor: Carlos Ferrario, Wake Forest School of Medicine, USA
The article belongs to the special issue Angiotensins—A Century of Progress
The development of heart failure under various pathological conditions such as myocardial infarction (MI), hypertension and diabetes are accompanied by adverse cardiac remodeling and cardiac dysfunction. Since heart function is mainly determined by coordinated activities of different subcellular organelles including sarcolemma, sarcoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria and myofibrils for regulating the intracellular concentration of Ca2+, it has been suggested that the occurrence of heart failure is a consequence of subcellular remodeling, metabolic alterations and Ca2+-handling abnormalities in cardiomyocytes. Because of the elevated plasma levels of angiotensin II (ANG II) due to activation of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) in heart failure, we have evaluated the effectiveness of treatments with angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and ANG II type 1 receptor (AT1R) antagonists in different experimental models of heart failure. Attenuation of marked alterations in subcellular activities, protein content and gene expression were associated with improvement in cardiac function in MI-induced heart failure by treatment with enalapril (an ACE inhibitor) or losartan (an AT1R antagonist). Similar beneficial effects of ANG II blockade on subcellular remodeling and cardiac performance were also observed in failing hearts due to pressure overload, volume overload or chronic diabetes. Treatments with enalapril and losartan were seen to reduce the degree of RAS activation as well as the level of oxidative stress in failing hearts. These observations provide evidence which further substantiate to support the view that activation of RAS and high level of plasma ANG II play a critical role in inducing subcellular defects and cardiac dysfunction during the progression of heart failure.
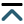
Heart failure affects an estimated 40 million people worldwide and the prevalence of this global pandemic in the United States is expected to increase to about 8 million by 2030 from the current level of 6.4 million [1–3]. It should be noted that heart failure is associated with inability of the heart to pump sufficient blood to meet metabolic requirements of the body. Resulting as a consequence of cardiovascular abnormalities, this progressive and complex clinical disorder includes several organs and reveals various symptoms like fluid retention, breathlessness and exercise intolerance. Several pathological conditions such as hypertension, ischemicheartdisease, valvular heartdisease, myocarditis and diabetes are known toresultin the development of cardiac dysfunction and heart failure. Although heart failure is invariably associated with cardiac hypertrophy (an increase in muscle mass and enlargement of the heart), changes in size, shape, and structure of the myocardium (cardiac remodeling) as well as neurohormonal activation are considered to account for its progression [4–12]. Since heart function is either augmented or unaltered during the development of cardiac hypertrophy, it should be indicated as adaptive cardiac remodeling. On the other hand, heart failure is associated with cardiac dysfunction in hypertrophied myocardium and thus should be indicated as adverse cardiac remodeling. A wide variety of experimental evidence has suggested that degradation of glycocalyx proteins in the extracellular matrix results in the transition of cardiac hypertrophy to heart failure whereas subcellular defects with respect to Ca2+-handling and metabolic abnormalities reflect the progression of heart failure [7–13]. It is pointed out that heart function is mainly determined by the coordinated activities of subcellular organelles such as sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR), sarcolemma (SL), myofibrils (MF) and mitochondria (MT) with respect to Ca2+-handling and metabolic processes in cardiomyocytes. Thus, any defect in the function of these subcellular organelles can be seen to induce heart dysfunction under diverse pathological conditions. Some of the affected sites and associated functional abnormalities in subcellular organelles in failing hearts are shown in Figure 1. Accordingly, it has been suggested that the progression of cardiac dysfunction during the development of heart failure is associated with subcellular remodeling in terms of molecular, biochemical and structural alterations in cardiomyocytes as a consequence of various pathological stimuli [14–24]. Such subcellular remodeling leading to the induction of Ca2+-handling abnormalities, metabolic defects and cardiac dysfunction are promoted by changes in cardiac gene expression as well as activation of different proteases and phospholipases due to prolonged effects of the elevated levels of several neurohormones in the circulation [6, 9, 17, 18, 23–29].
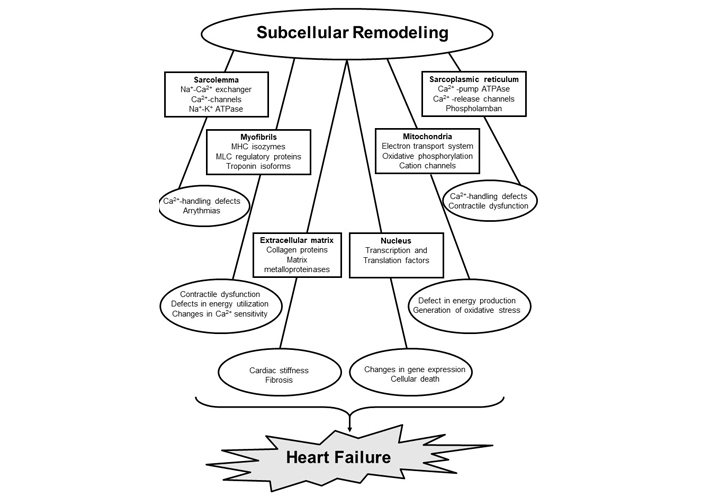
Subcellular targets, sites affected and functional abnormalities in cardiomyocytes during the development of heart failure. MHC, myosin heavy chain; MLC, myosin light chain
It is now well known that the renin-angiotensinsystem (RAS) is one of the most important neuro-endocrine systems, which is activated during the development of diabetes, ischemic heart disease and heart failure [6, 7, 19, 20, 30–36]. The RAS is present in both peripheral system and myocardial interstitium, and its activation results in the formation of angiotensin II (ANG II) due to the involvement of different components including angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE). By virtue of its action on ANG II type 1 receptor (AT1R), ANG II activates signal transduction mechanism, increases the intracellular concentration of Ca2+ and promotes the occurrence of adaptive cardiac remodeling or cardiac hypertrophy. However, the elevated levels of circulating ANG II for a prolonged period result in the development of heart dysfunction and adverse cardiac remodeling or heart failure [30–36]. In view of the increased clinical severity of heart failure and prognostic value of the elevated levels of ANG II, various ACE inhibitors and AT1R antagonists are considered to represent the most effective pharmacological treatments of heart failure [37–41]. Not only these treatments for ANG II blockade improve heart function and delay the development of end-stage heart failure, this drug therapy also reduces the occurrence of apoptosis, fibrosis and endothelial dysfunction in the failing heart [42–47]. In addition, different ACE inhibitors and AT1R have been reported to attenuate subcellular remodeling and changes in various signal transduction mechanisms in heart failure [44–53].
In view of the complexities of mechanisms for the formation and actions of ANG II [19, 30, 31, 54, 55], a great caution should be exercised while implicating its role in the development of cardiac remodeling and subcellular defects in heart failure. In this regard, it is noteworthy that ANG II is synthetized by circulating (peripheral) RAS involving renin and ACE whereas alternative enzymes such as chymase and cathepsins are involved in its formation in the tissue (intracellular) RAS [55]. The role of chymase in cardiac remodeling is evident from the observation that inhibitors of chymase were found to exert cardioprotection in different types of heart failure [54, 55]. Furthermore, while no chymase-mediated ANG II synthesis was observed in fibroblast, the tissue ANG II synthesis in the cardiac cells was depressed by both renin and ACE inhibitors. It has also been observed that the activity of tissue RAS is increased in some pathological conditions and its regulationisdependent upon the type of tissue and pathological conditions[54]. Nonetheless, the major actions of both circulating and tissue RAS are mediated through the activation of AT1R [19, 30, 31]. Elevated levels of ANG II during early stages of pathological stimulus are considered to induce adaptive changes such as cardiac hypertrophy in the heart for maintaining cardiovascular homeostasis but adverse effects such as heart failure become evident upon prolonged exposure. Various signal transduction mechanisms have been suggested to explain both the adaptive and adverse effects of ANG II and are detailed elsewhere [12, 17, 31, 37, 51–53]. It should be mentioned that a new axis of RAS namely ACE2/ANG 1-7/Mas receptor axis, has been demonstrated to counter-act the adverse effects of ACE/ANG II/AT1R during the development of heart failure [56–59]. It is also pointed out that ACE2, a homologue of ACE, has been shown to convert ANG II into ANG 1-7 involving Mas receptors; its loss has been reported to enhance the susceptibility to heart failure and increase was associated with prevention of the heart failure phenotype [56, 57]. Thus ACE2/ANG 1-7/Mas receptor axis of RAS can be seen as a potential target for the development of improved therapy of heart failure.
Over the past two decades, several experimental and clinical observations have uncovered some key molecular and cellular mechanisms in the heart regarding actions of ANG II and its signaling pathways beyond its role in the regulation of blood pressure [51–53, 60–63]. It has now become clear that ANG II released due to the activation of both peripheral and cardiac RAS plays an important role in the development of both adaptive and adverse cardiac remodeling at early and late stages of heart failure. Furthermore, treatments of heart failure subjects with different pharmacological interventions known to not only reduce the increased muscle mass and improve cardiac function but also delay the progression of adverse cardiac remodeling. However, not much attention has been paid with respect to the role of ANG II for the occurrence of subcellular defects, Ca2+-handling abnormalities and metabolic alterations in heart failure. This article is therefore intended to describe the participation of subcellular remodeling in inducing changes in Ca2+-handling and heart dysfunction during the progression of adverse cardiac remodeling. It is also planned to discuss the evidence regarding the beneficial effects of ANG II blockade in attenuating subcellular remodeling for improving cardiac function in some experimental models of heart failure including those due to myocardial infarction (MI), pressure overload, volume overload and chronic diabetes. Although a wide variety of ACE inhibitors and AT1R antagonists are known to exert beneficial effects in heart failure, we have chosen to show observations regarding the effectiveness of enalapril (an ACE inhibitor) and losartan (an AT1R antagonist) in heart failure. It is also pointed out that renin is an essential component of RAS as well as aldosterone is invariably released during the activation of RAS, and their antagonists have been reported to improve cardiovascular function in heart failure [64–67]; however, discussion on these aspects is considered beyond the scope of this review.
Several studies have revealed that heart failure is mainly due to adverse cardiac remodeling [7, 10, 68, 69] and is accompanied by remodeling of subcellular organelles including SL, SR, MT, MF, and extracellular matrix [8, 9, 24, 26, 27, 29, 46]. Depending upon the type and stage of heart failure, varying degrees of defects in the biochemical and molecular composition of these organelles have been identified to account for cardiac dysfunction in the failing heart [17–19, 24, 26, 29, 70–72]. Activation of different proteases and phospholipases, and alterations in gene expression have been demonstrated to explain changes in these organelles [9, 22, 73, 74]. While alterations in cardiomyocyte architecture and gene expression are considered to occur due to remodeling of extracellular matrix and nucleus, respectively [9, 26, 46, 75–77], the transition of cardiac hypertrophy to heart failure has been suggested to be due to the degradation of extracellular matrix proteins [75, 76]. Remodeling of SL can be seen to induce alterations in myocardial cation composition and signal transduction as a consequence of changes in different receptors, cation channels and cation transporters [18, 19, 78, 79]. On the other hand, remodeling of MT would produce defects in the process of energy production as well as redox status in the failing heart due to alterations in electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation systems [50, 80–83]. Impairment of mitochondrial function is generally associated with the generation of oxidative stress [23]. Furthermore, remodeling of SR can be seen to be associated with defects in Ca2+-cycling proteins and changes in Ca2+-uptake and release activities [15–19], whereas changes in MF in the failing heart will induce changes in their sensitivity to Ca2+ [84, 85]. Remodeling of MF is also associated with alterations in both contractile and regulatory proteins to produce changes in cardiac contraction and relaxation [24, 26, 86–89]. In addition, marked changes in different receptor-mediated signal transduction mechanisms, which are known to affect subcellular functions, have been reported in the failing hearts [9, 71, 84, 90]. Thus, subcellular remodeling, metabolic defects, Ca2+-handling abnormalities, and oxidative stress play a significant role in cardiac dysfunction during the development of heart failure.
It needs to be emphasized that various subcellular organelles are intimately involved in the generation of cardiac contractile force as a consequence of increase in the cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) due to Ca2+-entry through the SL Ca2+-channels and opening of the SR Ca2+-release channel (ryanodine receptor type 2, RyR2) [91, 92]. This Ca2+ then binds with Troponin C (TnC), relieves its inhibitory effect on tropomyosin and promotes the interaction of myosin and actin filaments. It is now well established that the catalytic activity of myosin ATPase enzyme is influenced by the myosin heavy chain (MHC) isoforms for the occurrence of the cardiac contraction [93–95]. On the other hand, cardiac relaxation occurs upon the sequestration of [Ca2+]i and dissociation of myosin filaments from actin filaments. It should be mentioned that Ca2+ sequestration is influenced mainly by the sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-pump ATPase (SERCA2a) and SL Na+-Ca2+ exchanger [19, 94, 96, 97]. It is also pointed out that MT are primarily concerned with the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is required for cardiac contraction and relaxation; however, these organelles are also known to serve as Ca2+-buffer under conditions when cardiomyocyte is faced with an excessive level of [Ca2+]i [17, 18, 84]. Thus, it is evident that a defect in any subcellular organelle could produce disturbance in the coordination of the contraction-relaxation cycle and lead to the development of cardiac dysfunction.
In view of the marked activation of RAS, elevated levels of circulating ANG II, cardiac remodeling and cardiac dysfunction in heart failure [98, 99], extensive efforts have been made to understand the mechanisms of cardiovascular actions of ANG II as well as discovering some therapeutic strategies for the management and treatment of heart failure [6, 31, 39, 62, 100–104]. The AT1R-mediated intracellular signal transductions have been shown to contribute to progression of cardiac remodeling, production of reactive oxygen species, elevation of [Ca2+]i as well as activation of protein kinase C and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) [105–109]. Thus, reduction in the formation of ANG II and blockade of its effects have been shown to partially prevent cardiac abnormalities and delay the progression of heart failure. In this regard, various ACE inhibitors such as captopril, benazepril, enalapril, ramipril, perindopril, imidapril and trandolapril [110–115], and different AT1R antagonists including losartan, valsartan, irbesartan, candesartan cilexetil, telmisartan and eprosartan [116–122] have been reported to prevent alterations in the failing heart at subcellular and molecular levels and improve heart function in heart failure. It should also be mentioned that ANG II blockade has been shown to attenuate changes in collagen expression, β-adrenoceptor signal transduction system and ATP-induced increase in [Ca2+]i in the failing heart [123–126]. These observations support the view that the activation of RAS and elevated plasma levels of ANG II play an important role in the pathogenesis of cardiac dysfunction and subcellular abnormalities in heart failure. Furthermore, these studies have provided justification for the use of ACE inhibitors and AT1R antagonists for the treatment of heart failure.
Ischemic heart disease or MI, which becomes evident as a consequence of blockade of the coronary arteries, is most prevalent among several cardiovascular abnormalities leading to the development of heart failure. Elevated level of plasma ANG II in acute MI activates membrane receptors (AT1R) and produces cardiac hypertrophy by stimulating different signal transduction pathways; the activities of subcellular organelles as well as cardiac function are increased during this early period [5, 12, 127]. On the other hand, prolonged elevation of plasma ANG II in chronic MI has been reported to promote the formation of oxyradicals, induce Ca2+-handling abnormalities, depress cardiac gene expression, activate different proteases and result in the development of cardiac dysfunction in the hypertrophied heart [26, 46, 47, 128]. The role of ANG II in inducing subcellular defects and cardiac dysfunction in MI-induced heart failure was examined in a well-established rat model of heart failure due to coronary occlusion [129, 130] with or without ACE inhibitors and AT1R antagonists treatments [113, 116]. It should be mentioned that myocardial infarct in the experimental animals is fully healed in about 3 weeks, cardiac function begins to decline thereafter and the moderate degree of heart failure was seen at about 7 weeks. Accordingly, drug treatments were started at 3 weeks and the animals were examined at 7 weeks after inducing MI. The data on cardiac function, status of RAS activities and levels of oxidative stress in MI groups with or without enalapril and losartan treatments are given in Table 1. It can be seen that different parameters for cardiac function such as left ventricular (LV) end-diastolic pressure was elevated without any changes in LV systolic pressure whereas both ± dP/dt were depressed in the failing heart. Furthermore, RAS activities as measured by plasma ANG II, plasma ACE and LV ACE were increased in heart failure. High level of oxidative stress in the failing heart was evident from increased content of malondialdehyde, conjugated dienes formation, and oxidized glutathione as well as decreased content of reduced glutathione (Table 1). Treatment of infarcted animals with enalapril and losartan was observed to improve cardiac function and decrease the level of oxidative stress. It should also be noted that enalapril, which inhibits ACE activity, depressed plasma ANG II levels, and plasma as well as LV ACE activities whereas losartan, which inhibits the action of ANG II by blocking AT1R did not reduce any of the parameters for the activation of RAS. These observations provide evidence that ANG II is involved in depressing cardiac function and increasing the level of oxidative stress during the development of MI-induced heart failure.
Cardiac performance, status of RAS and oxidative stress in control and MI animals with or without ENP and LOS treatments for 4 weeks starting at 3 weeks after induction of MI
| Parameters | Control | MI | MI + ENP | MI + LOS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. Hemodynamic parameters | ||||
| LVEDP (mmHg) | 4.0 ± 0.2 | 15.9 ± 1.3 | 7.5 ± 0.6 | 6.9 ± 0.5 |
| LVSP (mmHg) | 133 ± 4.9 | 128 ± 3.2 | 131 ± 3.8 | 127 ± 3.9 |
| LV + dP/dt (mmHg/s) | 9,208 ± 1075 | 4,806 ± 745 | 7,690 ± 680 | 7,544 ± 722 |
| LV − dP/dt (mmHg/s) | 8,788 ± 956 | 4,326 ± 590 | 7,248 ± 702 | 7,312 ± 690 |
| B. RAS activity parameters | ||||
| Plasma ANG II (fmol/mL) | 8.3 ± 1.4 | 125 ± 6.9 | 34 ± 3.5 | 192 ± 9.9 |
| Plasma ACE activity (nmol/min per mL) | 51 ± 3.3 | 85 ± 7.1 | 32 ± 2.4 | 145 ± 7.1 |
| LV ACE activity (nmol/min per mg protein) | 0.45 ± 0.03 | 0.69 ± 0.04 | 0.23 ± 0.02 | 0.84 ± 0.05 |
| C. Oxidative stress levels | ||||
| LV MDA (nmol/mg tissue lipids) | 5.9 ± 0.4 | 19.1 ± 0.8 | 12.7 ± 0.3 | 10.1 ± 0.4 |
| LV conjugated dienes formation (nmol/mg tissue lipids) | 33 ± 1.9 | 56 ± 4.9 | 41 ± 3.0 | 37 ± 3.3 |
| LV GSH (μmol/g tissue) | 82 ± 1.6 | 36 ± 4.1 | 74 ± 4.1 | 68 ± 3.7 |
| LV GSSG (μmol/g tissue) | 12.4 ± 0.8 | 25.2 ± 2.6 | 14.2 ± 1.4 | 15.3 ± 1.6 |
Values are mean ± standard error (SE) of 4–6 animals in each group. ENP: enalapril (10 mg/kg per day); LOS: losartan (20 mg/kg per day); MI: myocardial infarction; RAS: renin-angiotensin system; ACE: angiotensin-converting enzyme; LVEDP: LV end diastolic pressure; LVSP: LV systolic pressure; + dP/dt: maximum rate of pressure development; -dP/dt: maximum rate of pressure decay; MDA: malondialdehyde; GSH: reduced glutathione; GSSG: oxidized glutathione. Data are based on the analysis of the information in our papers Shao et al. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005;288:H2637–46 [116]; and Shao et al. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005;288:H1674–82 [113]. *P < 0.05 compared with control; †P < 0.05 compared with MI group
Since Na+-K+ ATPase activity as well as associated gene expression and corresponding protein contents of different isoforms of the enzyme were altered in the failing hearts, it was suggested that there occurs remodeling of SL membrane in MI-induced failure [17, 19]. In this regard, reduction in Na+-K+-ATPase activity in MI-induced heart failure and depression in gene expression and protein contents of Na+-K+-ATPase isoforms were attenuated by a long acting ACE inhibitor, imidapril [116]. The data in Table 2, show that the depressed activities of both SL Na+-Ca2+ exchange and Na+-K+ ATPase activities in the failing hearts were attenuated by treatments with enalapril and losartan. Furthermore, changes in protein content as well as messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) levels for different isoforms of Na+-K+ ATPase were partially or fully prevented by enalapril and losartan treatments [131]. Likewise, the MI-induced alterations in MF Ca2+-stimulated ATPase activities, myosin gene expression and protein content were attenuated by the blockade of RAS by treatments of infarcted rats with agents such as imidapril [24, 93]. The beneficial effects of enalapril and losartan treatments on changes in MF Ca2+-stimulated ATPase and MHC isoforms and mRNA levels are shown in Table 3 [119].
Sarcolemmal activities of Na+-Ca2+ exchange and N+-K+ ATPase as well protein content and mRNA levels of N+-K+ ATPase in control and MI animals with or without ENP and LOS treatments for 4 weeks starting at 3 weeks after induction of MI
| Parameters | Control | MI | MI + ENP | MI + LOS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. SL activities | ||||
| Na+-Ca2+ exchange activity (nmol Ca2+ mg/2s) | 8.2 ± 0.51 | 3.8 ± 0.26 | 7.4 ± 0.45 | 7.0 ± 0.21 |
| Na+-K+-ATPase activity (μmol Pi/mg per h) | 22.1 ± 0.82 | 12.9 ± 0.64 | 18.3 ± 0.59 | 18.6 ± 0.84 |
| B. Na+-K+-ATPase isoform protein content (% of control) | ||||
| α2 | 100 | 79.6 ± 3.4 | 89.9 ± 1.6 | 92.9 ± 2.5 |
| α3 | 100 | 134.0 ± 5.2 | 114.7 ± 4.2 | 113.6 ± 5.5 |
| β2 | 100 | 73.6 ± 3.1 | 98.6 ± 8.5 | 99.2 ± 8.5 |
| β3 | 100 | 66.8 ± 1.6 | 81.1 ± 4.5 | 90.3 ± 6.7 |
| C. Na+-K+-ATPase isoform mRNA level (% of control) | ||||
| α1 | 100 | 107.5 ± 2.5 | 110.2 ± 4.8 | 112.2 ± 4.5 |
| α2 | 100 | 72.9 ± 2.1 | 86.3 ± 3.6 | 85.5 ± 4.5 |
| α3 | 100 | 170.5 ± 9.5 | 116.2 ± 4.8 | 115.3 ± 14.8 |
| β1 | 100 | 110.7 ± 7.2 | 120.5 ± 6.5 | 120.2 ± 7.5 |
Values are mean ± SE of 6 animals in each group. Data are based on the analysis of the information in our papers Shao et al. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005;288:H2637–46 [116] and Guo et al. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2008;86:139–47 [131]. *P < 0.05 compared with control; †P < 0.05 compared with MI group
Myofibrillar ATPase activities, protein content and mRNA levels in control and MI animals with or without ENP and LOS for 5 weeks starting at 3 weeks after induction of MI
| Parameters | Control | MI | MI + ENP | MI + LOS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. MF activities (μmol Pi/mg per h) | ||||
| Ca2+-stimulated ATPase activity | 10.8 ± 0.4 | 7.1 ± 0.4 | 8.3 ± 0.65 | 7.9 ± 0.52 |
| Mg2+-ATPase activity | 3.6 ± 0.4 | 3.8 ± 0.45 | 3.2 ± 0.3 | 3.2 ± 0.3 |
| B. Myosin heavy chain content (% of total) | ||||
| Total MHC | 100 | 96.2 ± 4.9 | 100.0 ± 4.6 | 96.0 ± 9.8 |
| α-MHC | 93.5 ± 2.4 | 71.0 ± 1.8 | 83.6 ± 1.3 | 85.4 ± 1.6 |
| β-MHC | 6.5 ± 0.3 | 29.0 ± 1.5 | 17.6 ± 1.2 | 13.8 ± 0.4 |
| C. Myosin heavy chain mRNA levels (Relative intensity) | ||||
| α-MHC | 92.25 ± 0.25 | 71.25 ± 1.25 | 81.90 ± 1.9 | 82.75 ± 2.5 |
| β-MHC | 7.50 ± 0.25 | 30.00 ± 1.25 | 19.75 ± 1.75 | 15.62 ± 0.12 |
Values are mean ± SE of 7 animals in each group. MLC: myosin light chain. Data are based on the analysis of the information in Figures 1, 2 and 3 in our paper Wang et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1690:177–84 [119]. *P < 0.05 compared with control; †P < 0.05 compared with MI group
Several studies have reported that SR Ca2+ transport and heart function during MI-induced heart failure is attenuated by treatments with agents such as ACE inhibitors, captopril and trandolapril, which are known to reduce the level of ANG II formation or block its action [113, 114, 132]. Both enalapril and cilazapril (ACE inhibitors) as well as AT1R antagonists (telmisartan, losartan), have also been reported to attenuate MI-induced SR remodeling [118, 122, 133]. Imidapril has been demonstrated to prevent the MI-induced changes in cardiac function, protein kinase C (PKC) activities and isoforms, and phospholipase C and D activities as well as SR Ca2+ uptake and Ca2+ release activities [134–137]. The results shown in Table 4 indicate that marked alterations in SR Ca2+ uptake and Ca2+ release activities as well as protein content and gene expressions, unlike calsequestrin, in the failing hearts, were partially or fully prevented by treatments with enalapril or losartan [113, 118] (Table 4). These observations provide evidence that ANG II plays an important role in SR remodeling during the development of MI-induced heart failure. It should also be pointed out SR remodeling, like that for SL and MF remodeling, may involve the activations of proteases and phospholipases as well as changes in cardiac gene expressions [17–19]. Furthermore, the actions of ANG II on subcellular remodeling have been suggested to be mediated due to the development of oxidative stress and increased level of [Ca2+]i in the failing cardiomyocyte [45, 84, 108].
Sarcoplasmic reticular Ca2+ uptake and Ca2+ release activities, protein content and mRNA levels in control and MI animals with or without ENP and LOS treatments for 4 weeks starting at 3 weeks after induction of MI
| Parameters | Control | MI | MI+ENP | MI+LOS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. Ca2+ uptake activity (nmol/mg per 2 min) | 110 ± 8.15 | 63.5 ± 4.8 | 92 ± 6.3 | 82 ± 4.8 |
| B. Ca2+ release activity (nmol/mg per 15 s) | 8.25 ± 0.32 | 4.95 ± 0.43 | 7.60 ± 0.37 | 7.20 ± 0.24 |
| C. Protein content (% of control) | ||||
| Ryanodine receptor | 100 | 58.5 ± 1.5 | 85.9 ± 3.1 | 83.8 ± 2.2 |
| Ca2+-stimulated ATPase | 100 | 50.5 ± 2.5 | 78.2 ± 1.8 | 67 ± 2.5 |
| Calsequestrin | 100 | 105.2 ± 4.8 | 98.3 ± 4.7 | 96.9 ± 13.1 |
| Phospholamban | 100 | 69.1 ± 5.9 | 86.6 ± 4.4 | 80.8 ± 8.2 |
| D. mRNA levels (% of control) | ||||
| Ryanodine receptor | 100 | 64.8 ± 5.3 | 84.75 ± 2.6 | 86.8 ± 4.5 |
| Ca2+-stimulated ATPase | 100 | 73.9 ± 4.1 | 86.7 ± 5.3 | 98.6 ± 6.4 |
| Calsequestrin | 100 | 105.4 ± 1.6 | 97.9 ± 7.1 | 97.4 ± 4.6 |
| Phospholamban | 100 | 78.3 ± 3.7 | 97.3 ± 5.7 | 92.0 ± 6.5 |
Values are mean ± SE of 7 animals in each group. Data are based on the analysis of the information in table 5 and figures 3 and 4 in our papers Shao et al. Am J Physiol Circ Physiol. 2005;288:H1674–82 [113] and Guo et al. Mol Cell Biochem. 2003;254:163–72 [118]. *P < 0.05 compared with control; †P < 0.05 compared with MI group
Various reports have indicated that heart failure due to pressure overload is associated with changes in the activities of different subcellular organelles as well as gene expression [138–148]. Accordingly, it has been suggested that cardiac dysfunction due to pressure overload is a consequence of SL, SR, MF and MT remodeling [149]. It is noteworthy that ANG II has been shown to alter gene expression of Ca2+-transport proteins in cardiomyocytes [150]. Furthermore, some ACE inhibitors were demonstrated to increase heart function, lower pressure overload and reduce cardiac hypertrophy [151, 152]. It can be seen from Table 5, that treatment of pressure overloaded animals with both captopril and losartan [153] improved cardiac function and attenuated depressions in SR Ca2+-transport as well as depressed SR Ca2+-stimulated ATPase protein content and mRNA levels. Furthermore, changes in MF Ca2+-stimulated and myosin ATPase activities as well as MHC mRNA were prevented by treatments with these agents. Inhibition of ACE and antagonism of AT1R were also observed to improve cardiac function and SR Ca2+-stimulated ATPase expression in hypertensive cardiomyopathy [154]. It is thus evident that the improvement of cardiac function by RAS blockade may be elicited by prevention of subcellular remodeling in the pressure-overloaded heart. It should be noted that the activity as well as mRNA levels of ACE are increased in the heart due to pressure overload [155] and both ACE inhibitors and AT1R antagonists are used clinically for the therapy of heart disease [156–158].
Sarcoplasmic reticular and myofibrillar activities in PO-induced cardiac dysfunction in rats with or without CAP and LOS treatments for 8 weeks
| Parameters | Control | PO | PO + CAP | PO + LOS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. Cardiac function | ||||
| LVDP (mmHg) | 122 ± 2.8 | 90 ± 3.1 | 114 ± 2.5 | 112 ± 2.5 |
| LVEDP (mmHg) | 3.6 ± 1.0 | 10.8 ± 2.1 | 4.5 ± 0.6 | 5.7 ± 0.4 |
| B. SR activity and protein and gene expression | ||||
| Ca2+-uptake (nmol Ca2+/mg per min) | 80.0 ± 3.6 | 46.7 ± 1.8 | 70.7 ± 1.8 | 67.0 ± 3.7 |
| Ca2+-release (nmol Ca2+/mg per min) | 20.5 ± 1.9 | 13.0 ± 0.9 | 18.2 ± 0.9 | 17.2 ± 0.9 |
| Ca2+-stimulated ATPase protein content (% of control) | 100 | 80.0 ± 0.4 | 94.0 ± 2.0 | 92.06 ± 3.0 |
| Ca2+-stimulated ATPase mRNA levels (% of control) | 100 | 56.0 ± 2.0 | 88.0 ± 3.0 | 86.0 ± 3.0 |
| C. MF and myosin activities | ||||
| MF Ca2+-stimulated ATPase (μmol Pi/mg per h) | 11.5 ± 0.8 | 5.9 ± 0.02 | 10.1 ± 0.88 | 9. 81 ± 0.22 |
| Myosin Ca2+-ATPase (μmol Pi/mg per h) Myosin mRNA levels (Relative intensity) | 18.8 ± 0.5 | 12.7 ± 0.02 | 17.4 ± 0.5 | 16.9 ± 0.5 |
| α-MHC | 0.28 ± 0.02 | 0.13 ± 0.03 | 0.23 ± 0.02 | 0.22 ± 0.01 |
| β-MHC | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 1.18 ± 0.10 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.02 |
Values are mean ± SE of 6 animals in each group. CAP: captopril (2 g/L); PO: pressure overload; LVDP: left ventricular developed pressure. Data are based on the analysis of the information in Figures 1, 3, 4, 5 and 6 in our paper Liu et al. Clin Exp Hypertens. 1999;21:145–56 [153]. *P < 0.05 compared with control; †P < 0.05 compared with PO group
Although ANG II has been reported to play an important role in pathogenesis of different types of cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure [159], Leenen and associates [160–162] have shown both cardiac and peripheral RAS are activated by MI and volume overload. Different functions of cardiac SR were also altered by the induction of volume overload [163]. ANG II elicits its response by acting on AT1R-mediated MAPK signal transduction pathways as well as upon stimulating nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase, which has further been shown to produce cardiac hypertrophy, oxidative stress, and heart failure [105–108, 164–167]. The effects of both enalapril and losartan on cardiac remodeling and cardiac dysfunction were examined in heart failure due to volume overload. The data in Table 6 show that cardiac remodeling (as reflected by increased heart weight and heart weight to body weight ratio) and cardiac dysfunction (as reflected by depressed LVSP, +dP/dt and -dP/dt as well as increased left ventricular end diastolic pressure (LVEDP)) are evident in failing hearts due to volume overload [168]. Furthermore, phosphorylated extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1 and phosphorylated ERK2 content as well as ERK1/ERK2 activity [as measured by phospho-ERK1/ERK2 activity (phospho-ELK1) content] were also observed to be increased in heart failure due to volume overload. It can also be seen from Table 6 that cardiac remodeling, cardiac dysfunction and changes in phosphorylated MAPK content and activities in hearts failing due to volume overload were attenuated by treatments of animals with enalapril and losartan. It should be mentioned that treatment of heart failure animals with imidrapil has been observed to partially prevent alterations in SL, SR and MF activities due to volume overload (Dhalla-unpublished observations). Thus, activation of RAS is considered to be involved in inducing cardiac remodeling as well as changes in cardiac function and subcellular organelles during the development of heart failure due to volume overload.
Cardiac dysfunction, cardiac remodeling and alterations in protein content of phospho- ERK1, ERK2 and ELK1 in rats following the induction of heart failure by VO with or without ENP and LOS treatment for 16 weeks
| Parameters | Control | VO | VO + ENP | VO + LOS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. Cardiac remodeling | ||||
| Heart wt (mg) | 1364 ± 41 | 2209 ± 117 | 1671 ± 97 | 1526 ± 105 |
| LV wt (mg) | 1067 ± 29 | 1640 ± 142 | 1217 ± 61 | 1119 ± 66 |
| RV wt (mg) | 300 ± 13 | 554 ± 42 | 462 ± 25 | 394 ± 36 |
| HW/BW ratio (mg/g) | 2.23 ± 0.13 | 3.37 ± 0.14 | 2.68 ± 0.14 | 2.47 ± 0.17 |
| B. Phospho-ERK1 and phospho-ERK2 content as well as ERK1/ERK2 activity | ||||
| Phospho-ERK1 (% of control) | 100 | 552 ± 81 | 309 ± 40 | 127 ± 40 |
| Phospho-ERK2 (% of control) | 100 | 572 ± 52 | 312 ± 26 | 131 ± 30 |
| Phospho-ELK1 (% of control) | 100 | 777 ± 28 | 144 ± 21 | 87 ± 28 |
| C. Cardiac function | ||||
| LVSP (mm Hg) | 115 ± 5 | 85 ± 2 | 91 ± 6 | 93 ± 7 |
| LVEDP (mm Hg) | 5.2 ± 1.4 | 28.0 ± 1.9 | 18.6 ± 1.5 | 13.8 ± 0.6 |
| + dP/dt (mm Hg/sec) | 10,000 ± 429 | 4752 ± 240 | 6995 ± 364 | 7989 ± 88 |
| − dP/dt (mm Hg/sec) | 10,208 ± 511 | 4724 ± 259 | 7638 ± 380 | 8068 ± 409 |
Values are mean ± SE of 8 hearts in each group. VO: volume overload; LV wt: left ventricular weight; RV wt: right ventricular wt; BW: body weight; HW: heart weight. Data are based on the analysis of the information in Table 2 and Figures 3, 4 and 5 in our paper Zhang et al. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2010;15:84–92 [168]. *P < 0.05 compared with control; †P < 0.05 compared with VO group
Diabetic cardiomyopathy has been shown to be associated with the activation of RAS and subcellular remodeling [23, 169]. The elevated levels of circulating (level of) ANG II in chronic diabetes have been reported to produce marked alterations in myocardial metabolism and remodeling of SL, SR, MF and MT [170–173]. The data in Table 7 show that the diabetes-induced changes in cardiac function and oxidative stress by treatments with both enalapril and losartan; these changes were not associated with any reduction of hyperglycemia [174, 175]. The decreased SL Na+-K+ ATPase and Na+-dependent Ca2+-uptake activities, reduced SR Ca2+-release and Ca2+-pump activities as well as depressed myosin-ATPase activities in the heart were also attenuated by treatments of diabetic animals with enalapril and losartan (Table 7). These observations support the view that the improvement of cardiac performance by RAS blockade in chronic diabetes may be related to the attenuation of oxidative stress as well as subcellular remodeling.
Cardiac performance, status of RAS, oxidative stress and subcellular activities in 8 weeks diabetic rats with or without ENP and LOS treatments
| Parameters | Control | Diabetic | Diabetic + ENP | Diabetic + LOS |
| A. Cardiac function parameters | ||||
| LVSP (mm Hg) | 140 ± 12.1 | 85 ± 8.4 | 119 ± 7.6 | 116 ± 6.9 |
| + dP/dt (mm Hg/sec) | 8856 ± 815 | 5380 ± 621 | 7176 ± 702 | 7044 ± 516 |
| B. RAS activities | ||||
| Plasma ANG II (fmol/ml) | 7.2 ± 0.8 | 7.4 ± 0.5 | 6.4 ± 0.6 | 10.9 ± 0.4 |
| Plasma ACE activity (nmol/min per ml) | 48 ± 2.5 | 52 ± 3.1 | 49 ± 3.5 | 57 ± 2.6 |
| LV ACE activity (nmol/min per mg) | 0.57 ± 0.03 | 0.89 ± 0.04 | 0.56 ± 0.3 | 0.79 ± 0.03 |
| C. Oxidative stress levels | ||||
| LV GSH/GSSG Ratio | 6.8 ± 0.4 | 2.5 ± 0.2 | 4.3 ± 0.5 | 4.8 ± 0.2 |
| MDA content (nmol/mg tissue lipids) | 3.8 ± 0.13 | 7.1 ± 0.49 | 4.9 ± 0.46 | 5.4 ± 0.48 |
| D. Myosin ATPase activities | ||||
| Mg2+-ATPase (nmol Pi/mg per 5 min) | 1.2 ± 0.03 | 0.78 ± 0.07 | 1.06 ± 0.05 | 1.00 ± 0.06 |
| Ca2+-ATPase (nmol Pi/mg per 5 min) | 6.22 ± 0.18 | 3.14 ± 0.21 | 4.91 ± 0.23 | 4.86±0.28 |
| E. SL activities | ||||
| Na+-K+-ATPase (μmol Pi/mg per h) | 23.2 ± 3.5 | 13.1 ± 1.8 | 18.2 ± 1.6 | 18.3 ± 1.5 |
| Na+-Ca2+-exchanger (nmol Ca2+/mg per 10s) | 21.3 ± 1.2 | 12.1 ± 0.9 | 17.3 ± 1.2 | 16.1 ± 1.5 |
| F. SR activities | ||||
| Ca2+-stimulated ATPase (nmol Pi/mg per 5 min) | 165 ± 7 | 115 ± 10 | 154 ± 5 | 153 ± 6 |
| Ca2+-uptake (nmol Ca2+/mg per 2 min) | 62.7 ± 2.3 | 36.5 ± 3.1 | 50.3 ± 2.1 | 53.4 ± 2.7 |
Values are mean SE of 6 to 8 animals in each group. Data are based on the analysis of the information in Tables 1 and 2 in our paper Liu et al. Ann. N.Y. Acad Sci. 2006;1084:141–54 [174] and Figures 1A, 3B, 5A and 6A in our paper Machackova et al. Mol Cell Biochem. 2004;261:271–8 [175]. *Significantly different (P < 0.05) from control; †Significantly different (P < 0.05) from untreated diabetic
A great deal of progress has been made for the development of therapy for heart failure and various interventions including those for RAS blockade have been observed to improve heart function and delay the occurrence of heart failure but their beneficial effects in reducing mortality and morbidity are not satisfactory. This is primarily due to the fact that heart failure is a complex problem and involves several hormones including ANG II. Thus, any treatment based on the antagonism of a single hormone may not be appropriate and thus a combination therapy may prove to be more beneficial. Furthermore, the current treatments of heart failure are based on the concepts of hemodynamic alterations and cardiac remodeling; however, very little attention has been paid to drug developments targeting at the molecular and subcellular levels. Accordingly, it is suggested that some new targets must be identified for improving the therapy of heart failure. Since it is becoming increasingly evident that remodeling of subcellular organelles such as SR, SL and MF is intimately involved in cardiac dysfunction during the development of heart failure, future therapeutic approaches that may focus on molecular mechanisms for remodeling of subcellular organelles. Particularly, the targeting pathological factors, such as Ca2+-handling abnormalities, metabolic defects, oxidative stress, inflammatory system, protease activation, and cell signaling pathways, which are known to adversely affect subcellular organelles, may improve cardiac performance and prevent the progression of heart failure.
[Ca2+]i: cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration
+ dP/dt: maximum rate of pressure development
ACE: angiotensin converting enzyme
ANG II: angiotensin II
AT1R: angiotensin II type 1 receptor
CAP: captopril
ENP: enalapril
ERK: extracellular-signal-regulated kinase
GSH: reduced glutathione
GSSG: oxidized glutathione
LOS: losartan
LV: left ventricular
LVEDP: left ventricular end diastolic pressure
LVSP: left ventricular systolic pressure
MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase
MF: myofibrils
MI: myocardial infarction
MT: mitochondria
PO: pressure overload
RAS: renin-angiotensin system
SL: sarcolemma
SR: sarcoplasmic reticulum
The infrastructure support for this project was provided by the St. Boniface Hospital Research Foundation, Winnipeg, Canada. Thanks are also due to Ms. Andrea Opsima for typing this manuscript.
SKB searched the literature, analyzed the data and wrote the first draft; AKS analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript; NSD conceived, designed and edited the article. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Copyright: © The Author(s) 2021. This is an Open Access article licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, for any purpose, even commercially, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Rafael Luzes ... Adalberto Vieyra
Natalia L. Rukavina Mikusic ... Mariela M. Gironacci
Gian Paolo Rossi ... Teresa Maria Seccia
Kristin E. Reeve ... Babbette LaMarca
Eran S. Zacks ... Richard B. Devereux
Casper N. Bang ... Peter M. Okin
Casper N. Bang ... Peter M. Okin
Marcello Chinali ... Richard B. Devereux